2.1 u Be 1.0 1.5 NDF BC 1.5 25 3.0 3.5 4.0 Na Mg 0.9 1.2 Al Si 1.5 1.8 2.1 S CI 3.5 3.0 P K Ca Sc Tivr Mn Fe Co NI Cu 0.8 1.0 13 15 1.6 1.6 15 1.8 1.9 1.8 1.9 Zn Ga Ge As Se Br 2.4 2.8 1.6 1.6 1.8 2.0 Rb Sr 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 1.9 2.2 2.2 22 1.9 Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd Sn Sb 1.7 1.7 1.8 In Te I 1.9 2.1 2.5 Cs Ba 0.7 0.9 Hf Ta w Re Os Ir Au Hg TI Pb Bi 1.3 1.5 1.7 1.9 2.2 2.2 2.2 2.4 1.9 1.8 1.9 Pt Po At 1.9 2.0 2.2 Fr Ra 0.7 0.9 Using the above table of electronegatives, classify the O-H bond in water as either pure covalent, polar covalent or ionic. (Electronegativity difference, A EN >17 = ionic, AEN 0.4-1.7 = polar covalent, and AEN <0.4 = nonpolar covalent). O nonpolar covalent O polar covanent O ionic
2.1 u Be 1.0 1.5 NDF BC 1.5 25 3.0 3.5 4.0 Na Mg 0.9 1.2 Al Si 1.5 1.8 2.1 S CI 3.5 3.0 P K Ca Sc Tivr Mn Fe Co NI Cu 0.8 1.0 13 15 1.6 1.6 15 1.8 1.9 1.8 1.9 Zn Ga Ge As Se Br 2.4 2.8 1.6 1.6 1.8 2.0 Rb Sr 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 1.9 2.2 2.2 22 1.9 Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd Sn Sb 1.7 1.7 1.8 In Te I 1.9 2.1 2.5 Cs Ba 0.7 0.9 Hf Ta w Re Os Ir Au Hg TI Pb Bi 1.3 1.5 1.7 1.9 2.2 2.2 2.2 2.4 1.9 1.8 1.9 Pt Po At 1.9 2.0 2.2 Fr Ra 0.7 0.9 Using the above table of electronegatives, classify the O-H bond in water as either pure covalent, polar covalent or ionic. (Electronegativity difference, A EN >17 = ionic, AEN 0.4-1.7 = polar covalent, and AEN <0.4 = nonpolar covalent). O nonpolar covalent O polar covanent O ionic
Principles of Instrumental Analysis
7th Edition
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Chapter15: Molecular Luminescence Spectrometry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 15.12QAP: Equations for the chemiluminescence determination of SO2 are given on page 383. Derive an expression...
Related questions
Question
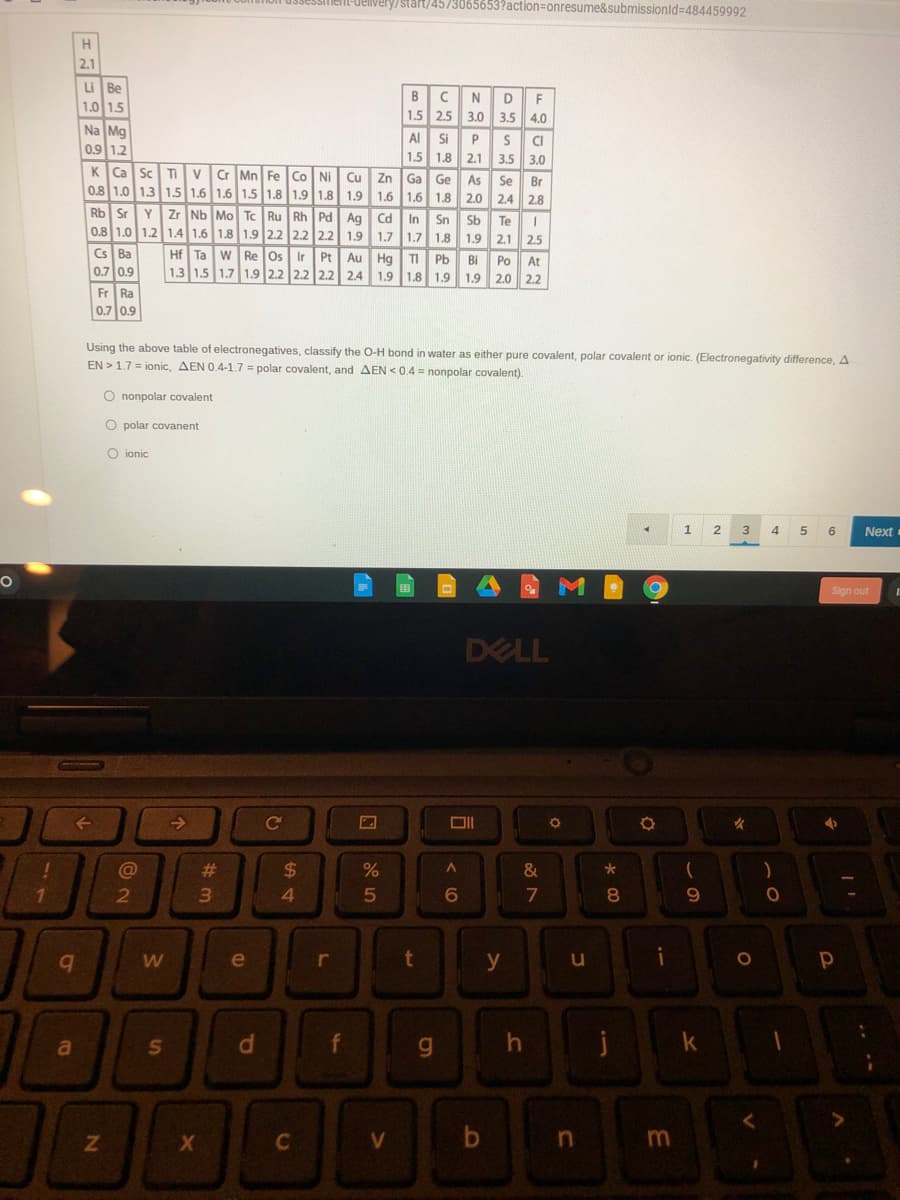
Transcribed Image Text:nent-delivery/start/4573065653?action=onresume&submissionld=484459992
H
2.1
Li Be
1.0 1.5
B
N
D
1.5 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0
Na Mg
0.9 1.2
Al Si
PS
CI
1.5 1.8 2.1 3.5 3.0
K Ca Sc Tiv Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br
0.8 1.0 1.3 1.5 1.6 1.6 1.5 1.8 1.9 1.8 1.9 1.6 1.6 1.8 2.0 2.4 2.8
Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te
0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 1.9 2.2 2.2 2.2 1.9 1.71.7 1.8 1.9 2.1 2.5
Hf Ta w ReOs Ir Pt Au Hg TI Pb Bi Po At
1.3 1.5 1.7 1.9 2.2 2.2 2.2 2.4 1.9 1.8 1.9 1.9 2.0
Cs Ba
0.7 0.9
2.2
Fr Ra
0.7 0.9
Using the above table of electronegatives, classify the O-H bond in water as either pure covalent, polar covalent or ionic. (Electronegativity difference, A
EN > 1.7 = ionic, AEN 0.4-1.7 = polar covalent, and AEN < 0.4 = nonpolar covalent).
O nonpolar covalent
O polar covanent
O ionic
1
4
Next
Sign out
DELL
->
女
@
23
24
%
4.
e
r
t
y
a
d.
C
1,
41
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning