20.1 Current Electric Current Electric current is defined to be the rate at which charge flows. A large current, such as that used to start a truck engine, moves a large amount of charge in a small time, whereas a small current, such as that used to operate a hand-held calculator, moves a small amount of charge over a long period of time. In equation form, electric current I is defined to be ΔΟ I = Δι (20.1) where AQ is the amount of charge passing through a given area in time At . (As in previous chapters, initial time is often taken to be zero, in which case At = 1.) (See Figure 20.2.) The SI unit for current is the ampere (A), named for the French physicist André-Marie Ampère (1775–1836). Since I = AQ/At , we see that an ampere is one coulomb per second: 1A = 1 C/s (20.2) Not only are fuses and circuit breakers rated in amperes (or amps), so are many electrical appliances. Current = flow of charge Figure 20.2 The rate of flow of charge is current. An ampere is the flow of one coulomb through an area in one second.
20.1 Current Electric Current Electric current is defined to be the rate at which charge flows. A large current, such as that used to start a truck engine, moves a large amount of charge in a small time, whereas a small current, such as that used to operate a hand-held calculator, moves a small amount of charge over a long period of time. In equation form, electric current I is defined to be ΔΟ I = Δι (20.1) where AQ is the amount of charge passing through a given area in time At . (As in previous chapters, initial time is often taken to be zero, in which case At = 1.) (See Figure 20.2.) The SI unit for current is the ampere (A), named for the French physicist André-Marie Ampère (1775–1836). Since I = AQ/At , we see that an ampere is one coulomb per second: 1A = 1 C/s (20.2) Not only are fuses and circuit breakers rated in amperes (or amps), so are many electrical appliances. Current = flow of charge Figure 20.2 The rate of flow of charge is current. An ampere is the flow of one coulomb through an area in one second.
College Physics
10th Edition
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Chapter18: Direct-Current Circuits
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 63AP: An electric eel generates electric currents through its highly specialized Hunters organ, in which...
Related questions
Question
Current
• Define
• Describe the direction of charge flow in conventional current.
• Use drift velocity to calculate current and vice versa.
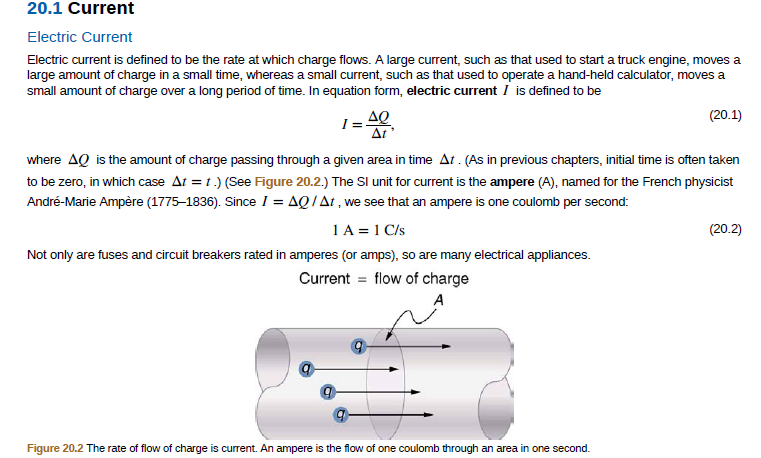
Transcribed Image Text:20.1 Current
Electric Current
Electric current is defined to be the rate at which charge flows. A large current, such as that used to start a truck engine, moves a
large amount of charge in a small time, whereas a small current, such as that used to operate a hand-held calculator, moves a
small amount of charge over a long period of time. In equation form, electric current I is defined to be
ΔΟ
I =
Δι
(20.1)
where AQ is the amount of charge passing through a given area in time At . (As in previous chapters, initial time is often taken
to be zero, in which case At = 1.) (See Figure 20.2.) The SI unit for current is the ampere (A), named for the French physicist
André-Marie Ampère (1775–1836). Since I = AQ/At , we see that an ampere is one coulomb per second:
1A = 1 C/s
(20.2)
Not only are fuses and circuit breakers rated in amperes (or amps), so are many electrical appliances.
Current = flow of charge
Figure 20.2 The rate of flow of charge is current. An ampere is the flow of one coulomb through an area in one second.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College


Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
