22. An unprotonated primary amino group in a blood protein can n- is react with carbon dioxide to form a carbamate as shown here: R-NH2 + CO2→R-NH–COO¯+ H+ de Carbamate al The rate constant k for this reaction is 4950 M.s. a. What is the M. order of this reaction? b. Calculate the velocity of the reaction of an a-amino group in a blood protein at 37°C if its concentration is 0.6 mM and the partial pressure of carbon dioxide is 40 torr. (Hint: Convert the units of partial pressure to molar concentration using the ideal gas law. The value of R is 0.0821 L·atm · K-l · mol-1.) c. How would the rate constant for this reaction vary with pH? Explain. ed of d. What CO, partial pressure is required to yield a velocity of 0.045 M·s for the reaction?
22. An unprotonated primary amino group in a blood protein can n- is react with carbon dioxide to form a carbamate as shown here: R-NH2 + CO2→R-NH–COO¯+ H+ de Carbamate al The rate constant k for this reaction is 4950 M.s. a. What is the M. order of this reaction? b. Calculate the velocity of the reaction of an a-amino group in a blood protein at 37°C if its concentration is 0.6 mM and the partial pressure of carbon dioxide is 40 torr. (Hint: Convert the units of partial pressure to molar concentration using the ideal gas law. The value of R is 0.0821 L·atm · K-l · mol-1.) c. How would the rate constant for this reaction vary with pH? Explain. ed of d. What CO, partial pressure is required to yield a velocity of 0.045 M·s for the reaction?
Chemistry: Principles and Practice
3rd Edition
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Chapter13: Chemical Kinetics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 13.99QE
Related questions
Question
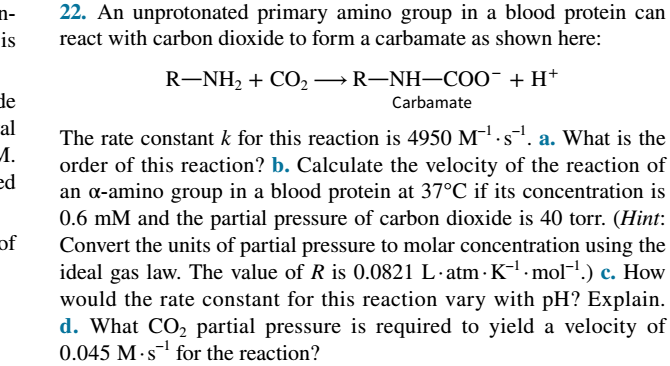
Transcribed Image Text:22. An unprotonated primary amino group in a blood protein can
n-
is
react with carbon dioxide to form a carbamate as shown here:
R-NH2 + CO2→R-NH–COO¯+ H+
de
Carbamate
al
The rate constant k for this reaction is 4950 M.s. a. What is the
M.
order of this reaction? b. Calculate the velocity of the reaction of
an a-amino group in a blood protein at 37°C if its concentration is
0.6 mM and the partial pressure of carbon dioxide is 40 torr. (Hint:
Convert the units of partial pressure to molar concentration using the
ideal gas law. The value of R is 0.0821 L·atm · K-l · mol-1.) c. How
would the rate constant for this reaction vary with pH? Explain.
ed
of
d. What CO, partial pressure is required to yield a velocity of
0.045 M·s for the reaction?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning