7. Consider the following mechanism and reaction coordinate diagram. Step 1: A(g) + B(g) → AB(g) 60 Step 2: AB(g) + A(g) → ABA(g) 50- 40 Step 3: ABA(g) → A2(g) + B(g) 30 Write the overall reaction. (2 pts) 20 а. 10 Reachon Coordinare b. Calculate each valu (5 pts) Activation energy (step 1): Activation energy (step 2): Activation energy (step 3): Activation energy (overall): Enthalpy change (AH): C. Identify any intermediates. (2 pts) d. Identify any catalysts. (2 pts) e. Use the mechanism to identify the rate law for the overall reaction. You may assume that the faster reactions are at equilibrium. (9 pts) PotentiaL Eneray OTma)
7. Consider the following mechanism and reaction coordinate diagram. Step 1: A(g) + B(g) → AB(g) 60 Step 2: AB(g) + A(g) → ABA(g) 50- 40 Step 3: ABA(g) → A2(g) + B(g) 30 Write the overall reaction. (2 pts) 20 а. 10 Reachon Coordinare b. Calculate each valu (5 pts) Activation energy (step 1): Activation energy (step 2): Activation energy (step 3): Activation energy (overall): Enthalpy change (AH): C. Identify any intermediates. (2 pts) d. Identify any catalysts. (2 pts) e. Use the mechanism to identify the rate law for the overall reaction. You may assume that the faster reactions are at equilibrium. (9 pts) PotentiaL Eneray OTma)
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Chapter14: Chemical Kinetics: The Rates Of Chemical Reactions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 52PS: The mechanism for the reaction of CH3OH and HBr is believed to involve two steps. The overall...
Related questions
Question
Question 7
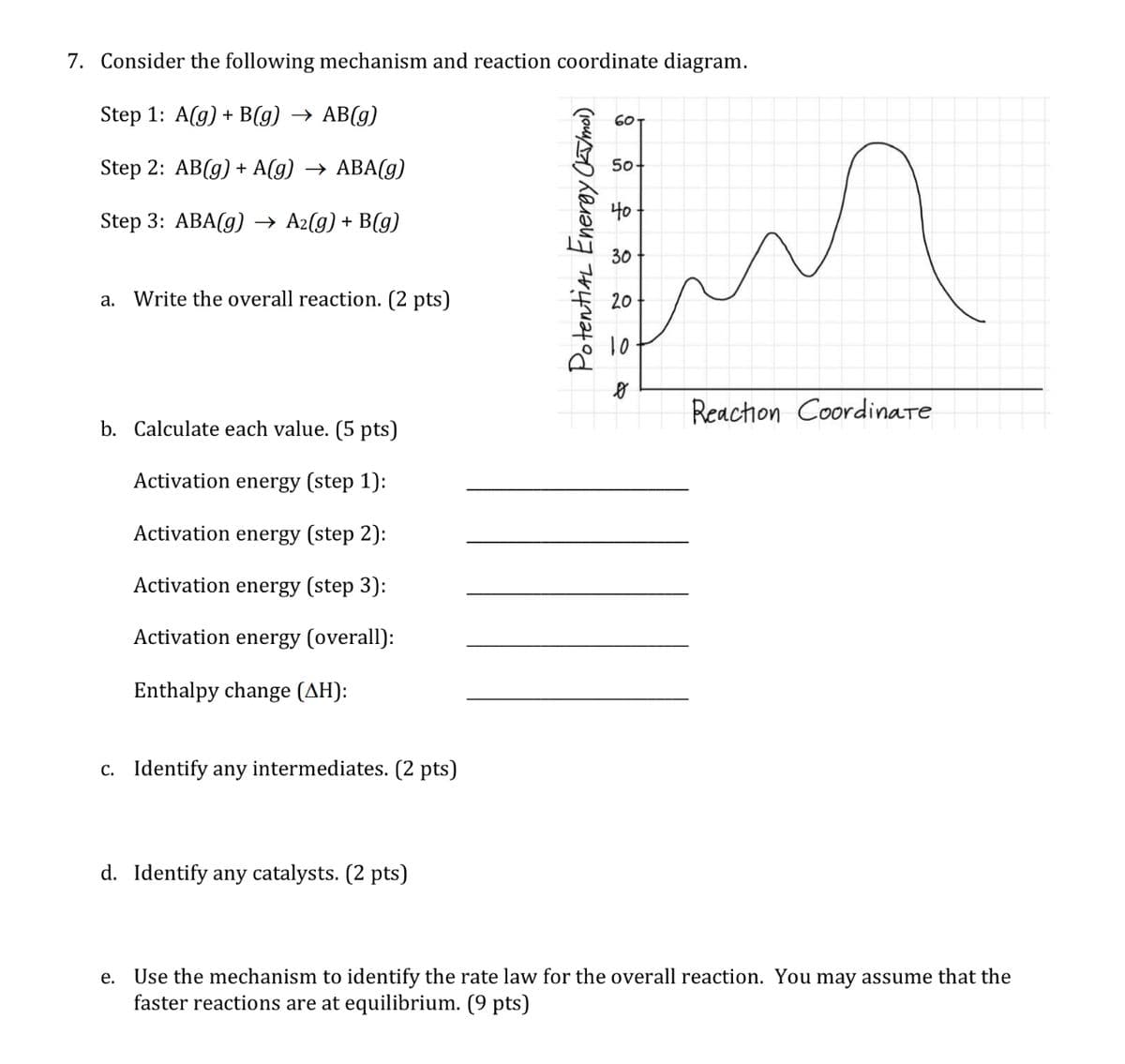
Transcribed Image Text:7. Consider the following mechanism and reaction coordinate diagram.
Step 1: A(g) + B(g) > АВ(g)
60T
Step 2: AB(g) + A(g) > АВА(g)
50-
Step 3: ABA(g) → A2(g) + B(g)
30
a. Write the overall reaction. (2 pts)
20
Reachon Coordinare
b. Calculate each value. (5 pts)
Activation energy (step 1):
Activation energy (step 2):
Activation energy (step 3):
Activation energy (overall):
Enthalpy change (AH):
c. Identify any intermediates. (2 pts)
d. Identify any catalysts. (2 pts)
e. Use the mechanism to identify the rate law for the overall reaction. You may assume that the
faster reactions are at equilibrium. (9 pts)
PotentiaL Eneroy Oa hmai)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning