26. Many of the people living with incomes below the global poverty line (around $500/person) are farmers. Max decides that he wants to help peanut farmers in a competitive market earn larger profit from their crops and invent a new method that helps conserve fertilizer and lower costs. (Some economists actually did some research like that.) This problem is about the short run and long run consequences. Suppose that before Max introduces the new method each farm has these costs. The farms are all assumed to be identical for simplicity. MC(q) = 2q + 12 9. ATC(q) =-+ 12 + q Fixed cost = $9 The units are all in kgs or $/kg. What is an individual farm's supply curve? а. q (P) 3D 0.5Р — 2 b. q(P) = –0.5P + 2 c. q(P) = 0.5P – 6 d. q(P) 3D —0.5Р + 6 %3D =
26. Many of the people living with incomes below the global poverty line (around $500/person) are farmers. Max decides that he wants to help peanut farmers in a competitive market earn larger profit from their crops and invent a new method that helps conserve fertilizer and lower costs. (Some economists actually did some research like that.) This problem is about the short run and long run consequences. Suppose that before Max introduces the new method each farm has these costs. The farms are all assumed to be identical for simplicity. MC(q) = 2q + 12 9. ATC(q) =-+ 12 + q Fixed cost = $9 The units are all in kgs or $/kg. What is an individual farm's supply curve? а. q (P) 3D 0.5Р — 2 b. q(P) = –0.5P + 2 c. q(P) = 0.5P – 6 d. q(P) 3D —0.5Р + 6 %3D =
Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Course List)
16th Edition
ISBN:9781305506893
Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Chapter8: Costs And The Supply Of Goods
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 19CQ
Related questions
Question
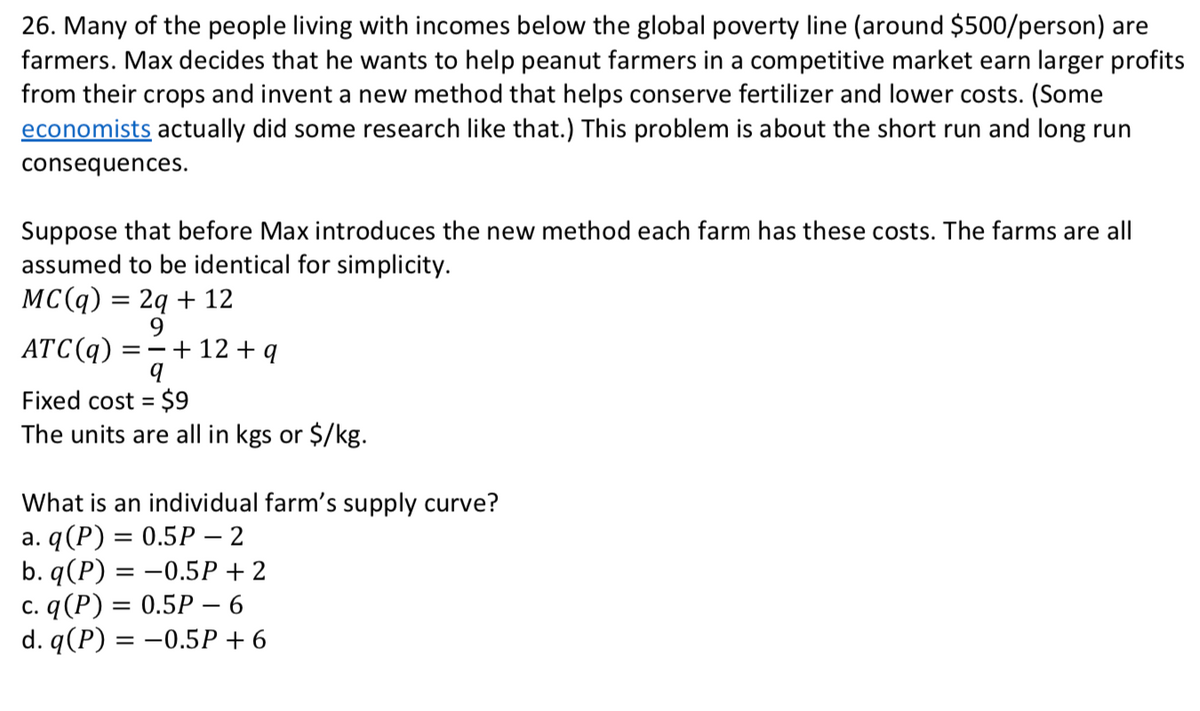
Transcribed Image Text:26. Many of the people living with incomes below the global poverty line (around $500/person) are
farmers. Max decides that he wants to help peanut farmers in a competitive market earn larger profits
from their crops and invent a new method that helps conserve fertilizer and lower costs. (Some
economists actually did some research like that.) This problem is about the short run and long run
consequences.
Suppose that before Max introduces the new method each farm has these costs. The farms are all
assumed to be identical for simplicity.
MC(q) = 2q + 12
ATC(q)
9
+ 12 + q
Fixed cost = $9
The units are all in kgs or $/kg.
%3D
What is an individual farm's supply curve?
a. q(P) = 0.5P – 2
b. q (P) %3D — 0.5Р + 2
с. q (Р) 3D 0.5Р — 6
d. q (P) %3D — 0.5Р +6
![27. (continued) There are four farms so what is the short run market supply curve? Combine that market
supply with this estimated market demand, Q(P) = 60 – P, to find the market price. Determine how
much each firm produces and what each firm makes in profit.
N = $
%3D
28. (continued) Now you introduce the new method which reduces the variable costs. As a result the MC
and ATC are lower:
MCС(q) %3D 2q + 6
9.
=-+6+q
ATC(q)
Repeat the steps above to find the new short run equilibrium.
How much profit does each firm now make? (this should be higher)
29. (continued) What will happen in the long run as farmers are allowed to enter or exit? Check the
boxes below for the variables that will decrease in the long run compared to the short run equilibrium
you found in the previous question.
[] N, the number of firms
[] P, the market price
[] q, the quantity each firm produces
[] T, the profit of an individual firm
[] ATC, the average total cost of each firm](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Ff0aac786-f258-42a6-87e3-0118f536800f%2F22caad20-e42a-4737-a9a1-1d0dc4c7281e%2Fwpunjxp_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:27. (continued) There are four farms so what is the short run market supply curve? Combine that market
supply with this estimated market demand, Q(P) = 60 – P, to find the market price. Determine how
much each firm produces and what each firm makes in profit.
N = $
%3D
28. (continued) Now you introduce the new method which reduces the variable costs. As a result the MC
and ATC are lower:
MCС(q) %3D 2q + 6
9.
=-+6+q
ATC(q)
Repeat the steps above to find the new short run equilibrium.
How much profit does each firm now make? (this should be higher)
29. (continued) What will happen in the long run as farmers are allowed to enter or exit? Check the
boxes below for the variables that will decrease in the long run compared to the short run equilibrium
you found in the previous question.
[] N, the number of firms
[] P, the market price
[] q, the quantity each firm produces
[] T, the profit of an individual firm
[] ATC, the average total cost of each firm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506893
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506725
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506893
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506725
Author:
James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. Macpherson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax