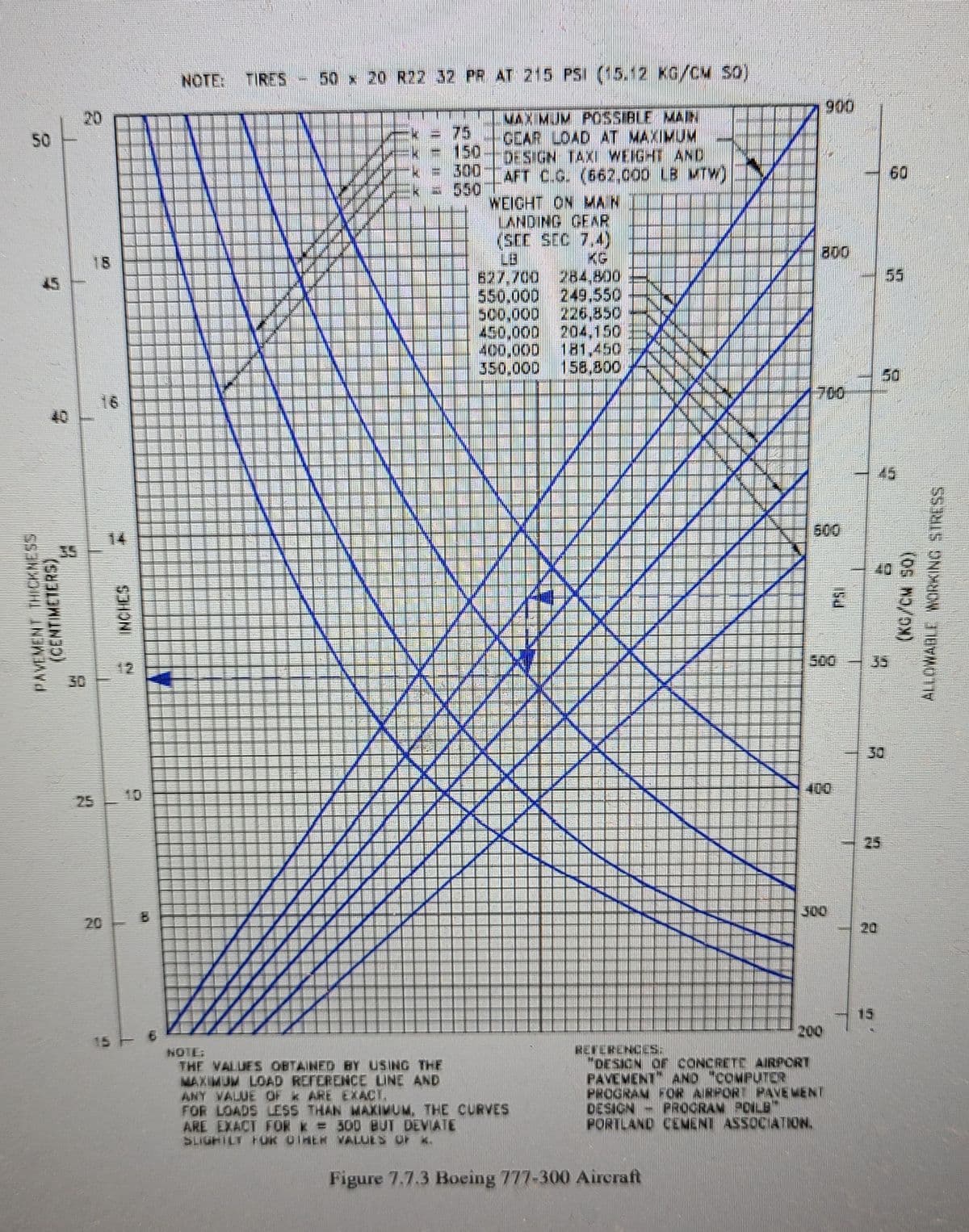
28. The PCA rigid pavement design chart for a B-777-300 aircraft is shown in Figure 7.7.3 attached. What would be the required pavement thickness if the weight on the main landing gear is 627,700 lb, a modulus of subgrade reaction=300 psi/in, and a 28-concrete flexural strength=820 psi? The pavement is to be designed for a critical area and requires a safety factor-2.0. a. 6.0 inches b. 8.0 inches c. 14.0 inches d. 17.0 inches
28. The PCA rigid pavement design chart for a B-777-300 aircraft is shown in Figure 7.7.3 attached. What would be the required pavement thickness if the weight on the main landing gear is 627,700 lb, a modulus of subgrade reaction=300 psi/in, and a 28-concrete flexural strength=820 psi? The pavement is to be designed for a critical area and requires a safety factor-2.0. a. 6.0 inches b. 8.0 inches c. 14.0 inches d. 17.0 inches
Traffic and Highway Engineering
5th Edition
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Garber, Nicholas J.
Chapter20: Design Of Rigid Pavements
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 17P
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:28. The PCA rigid pavement design chart for a B-777-300 aircraft is shown in Figure 7.7.3 attached. What
would be the required pavement thickness if the weight on the main landing gear is 627,700 lb, a
modulus of subgrade reaction-300 psi/in, and a 28-concrete flexural strength=820 psi? The pavement is
to be designed for a critical area and requires a safety factor-2.0.
a. 6.0 inches
b. 8.0 inches
c. 14.0 inches
17.0 inches
d.
Transcribed Image Text:50
PAVEMENT THICKNESS
G
15
(CENTIMETERS)
3
4
50
KM
41
I
SCHONI
KA
2
NOTE: TIRES - 50 x 20 R22 32 PR AT 215 PSI (15.12 KG/CM SO)
- MAX MJV POSSIBLE MAIN
GEAR LOAD AT MAXIMUM
DESIGN TAXI WEIGHT AND
[AFT C.G. (662,000 LB MTW)
****
WEIGHT ON MAIN
LANDING GEAR
(SEE SEC 7,4)
627,700 284,800
550,000 249,550
500,000 226,850
450,000 204,150
400,000
350.000 158,800
NOTE:
THE VALUES OBTAINED BY USING THE
MAXIMUM LOAD REFERENCE LINE AND
ANY VALUE OF ARE EXACT.
FOR LOADS LESS THAN MAXIMUM. THE CURVES
ARE EXACT FOR K = 500 BUT DEVIATE
SLIGHILT FOR OTHER VALUES OF K.
Figure 7.7.3 Boeing 777-300 Aircraft
800
200
REFERENCES:
"DESIGN OF CONCRETE AIRPORT
PAVEMENT" AND "COMPUTER
PROGRAM FOR AIRPORT PAVEMENT
DESIGN - PROGRAM POILE™
PORTLAND CEMENT ASSOCIATION.
900
-60
4
2
in
(OS NO/DX)
ALLOWABLE WORKING STRESS
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305156241
Author:
Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305156241
Author:
Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning