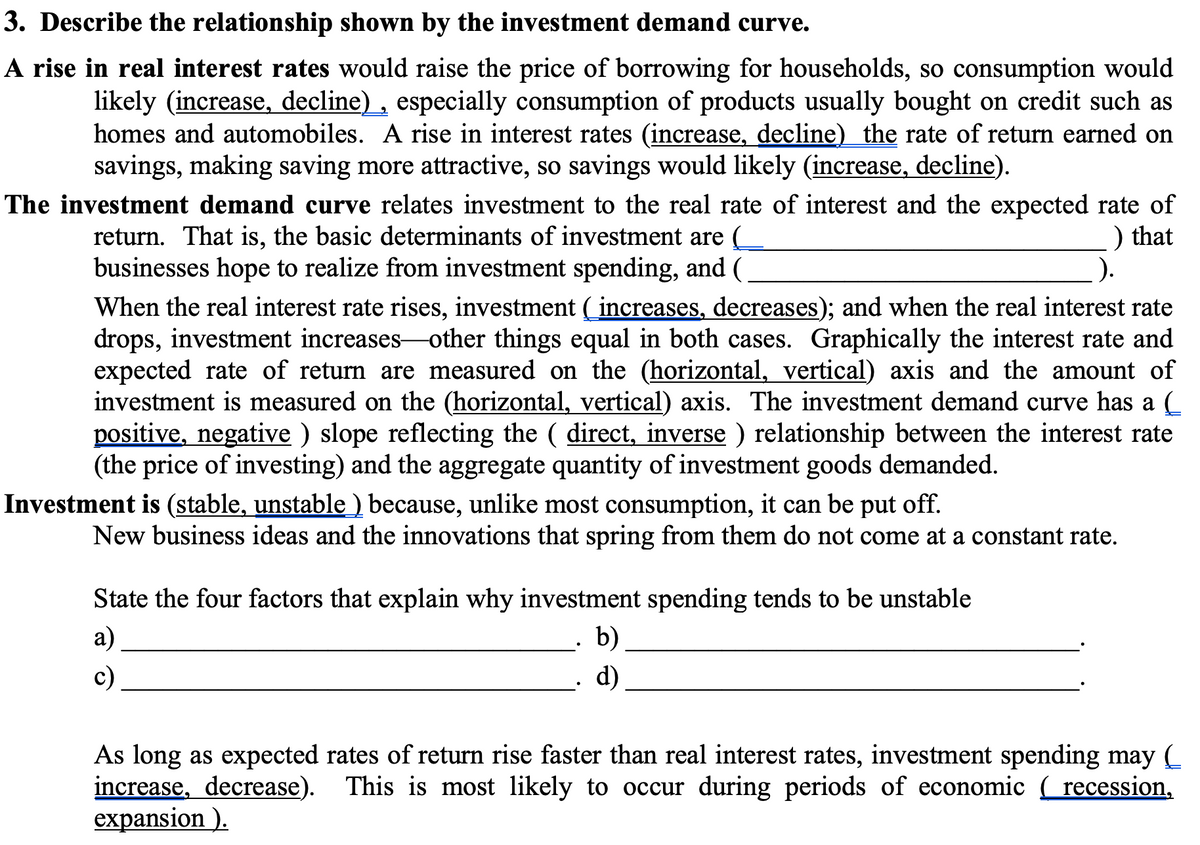
3. Describe the relationship shown by the investment demand curve. A rise in real interest rates would raise the price of borrowing for households, so consumption would likely (increase, decline) , especially consumption of products usually bought on credit such as homes and automobiles. A rise in interest rates (increase, decline) the rate of return earned on savings, making saving more attractive, so savings would likely (increase, decline). The investment demand curve relates investment to the real rate of interest and the expected rate of ) that return. That is, the basic determinants of investment are ( businesses hope to realize from investment spending, and ( . When the real interest rate rises, investment ( increases, decreases); and when the real interest rate drops, investment increases-other things equal in both cases. Graphically the interest rate and expected rate of return are measured on the (horizontal, vertical) axis and the amount of investment is measured on the (horizontal, vertical) axis. The investment demand curve has a (_ positive, negative ) slope reflecting the ( direct, inverse ) relationship between the interest rate (the price of investing) and the aggregate quantity of investment goods demanded. Investment is (stable, unstable ) because, unlike most consumption, it can be put off. New business ideas and the innovations that spring from them do not come at a constant rate. State the four factors that explain why investment spending tends to be unstable a) b) c) d) As long as expected rates of return rise faster than real interest rates, investment spending may ( increase, decrease). This is most likely to occur during periods of economic ( recession, expansion ).
3. Describe the relationship shown by the investment demand curve. A rise in real interest rates would raise the price of borrowing for households, so consumption would likely (increase, decline) , especially consumption of products usually bought on credit such as homes and automobiles. A rise in interest rates (increase, decline) the rate of return earned on savings, making saving more attractive, so savings would likely (increase, decline). The investment demand curve relates investment to the real rate of interest and the expected rate of ) that return. That is, the basic determinants of investment are ( businesses hope to realize from investment spending, and ( . When the real interest rate rises, investment ( increases, decreases); and when the real interest rate drops, investment increases-other things equal in both cases. Graphically the interest rate and expected rate of return are measured on the (horizontal, vertical) axis and the amount of investment is measured on the (horizontal, vertical) axis. The investment demand curve has a (_ positive, negative ) slope reflecting the ( direct, inverse ) relationship between the interest rate (the price of investing) and the aggregate quantity of investment goods demanded. Investment is (stable, unstable ) because, unlike most consumption, it can be put off. New business ideas and the innovations that spring from them do not come at a constant rate. State the four factors that explain why investment spending tends to be unstable a) b) c) d) As long as expected rates of return rise faster than real interest rates, investment spending may ( increase, decrease). This is most likely to occur during periods of economic ( recession, expansion ).
Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781337091985
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:N. Gregory Mankiw
Chapter8: Savings,investment And The Financial System
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8PA
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:3. Describe the relationship shown by the investment demand curve.
A rise in real interest rates would raise the price of borrowing for households, so consumption would
likely (increase, decline) , especially consumption of products usually bought on credit such as
homes and automobiles. A rise in interest rates (increase, decline) the rate of return earned on
savings, making saving more attractive, so savings would likely (increase, decline).
The investment demand curve relates investment to the real rate of interest and the expected rate of
) that
).
return. That is, the basic determinants of investment are (
businesses hope to realize from investment spending, and (
When the real interest rate rises, investment ( increases, decreases); and when the real interest rate
drops, investment increases-other things equal in both cases. Graphically the interest rate and
expected rate of return are measured on the (horizontal, vertical) axis and the amount of
investment is measured on the (horizontal, vertical) axis. The investment demand curve has a (
positive, negative ) slope reflecting the ( direct, inverse ) relationship between the interest rate
(the price of investing) and the aggregate quantity of investment goods demanded.
Investment is (stable, unstable ) because, unlike most consumption, it can be put off.
New business ideas and the innovations that spring from them do not come at a constant rate.
State the four factors that explain why investment spending tends to be unstable
а)
· b)
c)
d)
As long as expected rates of return rise faster than real interest rates, investment spending may (
increase, decrease). This is most likely to occur during periods of economic recession,
expansion ).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours…
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091985
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165912
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours…
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091985
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165912
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971509
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning