3. In genetic investigations, one frequently samples from a binomial distribution. Except that observations of x = 0 are impossible; so in fact, the sampling is from the conditional (truncated) distribution: px (1-p) m-x f(x) = (x) - Ppm 11.2...m) (x) Find the maximum likelihood estimator for p in the case of m = 2 samples of size n. 3
3. In genetic investigations, one frequently samples from a binomial distribution. Except that observations of x = 0 are impossible; so in fact, the sampling is from the conditional (truncated) distribution: px (1-p) m-x f(x) = (x) - Ppm 11.2...m) (x) Find the maximum likelihood estimator for p in the case of m = 2 samples of size n. 3
College Algebra
7th Edition
ISBN:9781305115545
Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Chapter9: Counting And Probability
Section9.4: Expected Value
Problem 1E: If a game gives payoffs of $10 and $100 with probabilities 0.9 and 0.1, respectively, then the...
Related questions
Question
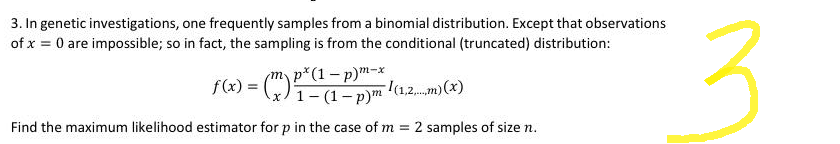
Transcribed Image Text:3. In genetic investigations, one frequently samples from a binomial distribution. Except that observations
of x = 0 are impossible; so in fact, the sampling is from the conditional (truncated) distribution:
px
m-x
f(x) = (²-1² 1 (1.2) (x()
Find the maximum likelihood estimator for p in the case of m = 2 samples of size n.
3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning