A random sample is drawn from a population with mean μ = 56 and standard deviation σ = 4.7. [You may find it useful to reference the z table.] a. Is the sampling distribution of the sample mean with n = 14 and n = 34 normally distributed? (Round the standard error to 3 decimal places.) b. Can you conclude that the sampling distribution of the sample mean is normally distributed for both sample sizes? multiple choice 1 Yes, both the sample means will have a normal distribution. No, both the sample means will not have a normal distribution. No, only the sample mean with n = 14 will have a normal distribution. No, only the sample mean with n = 34 will have a normal distribution. c. If the sampling distribution of the sample mean is normally distributed with n = 14, then calculate the probability that the sample mean falls between 56 and 58. (If appropriate, round final answer to 4 decimal places.) Probability We cannot assume that the sampling distribution of the sample mean is normally distributed. We can assume that the sampling distribution of the sample mean is normally distributed and the probability that the sample mean falls between 56 and 58 is
Can you explain question C
A random sample is drawn from a population with
a. Is the sampling distribution of the sample mean with n = 14 and n = 34
b. Can you conclude that the sampling distribution of the sample mean is normally distributed for both sample sizes?
multiple choice 1
-
Yes, both the sample means will have a normal distribution.
-
No, both the sample means will not have a normal distribution.
-
No, only the sample mean with n = 14 will have a normal distribution.
-
No, only the sample mean with n = 34 will have a normal distribution.
c. If the sampling distribution of the sample mean is normally distributed with n = 14, then calculate the probability that the sample mean falls between 56 and 58. (If appropriate, round final answer to 4 decimal places.)
|
-
We cannot assume that the sampling distribution of the sample mean is normally distributed.
-
We can assume that the sampling distribution of the sample mean is normally distributed and the probability that the sample mean falls between 56 and 58 is
![4
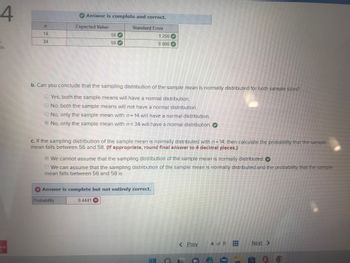
A random sample is drawn from a population with mean = 56 and standard deviation o=4.7. [You may find it useful to reference the
z table.]
a. Is the sampling distribution of the sample mean with n=14 and n = 34 normally distributed? (Round the standard error to 3 decimal
places.)
2/12.5
Expected Value
Standard Error
nts awarded
56
56
1.256
0.806
Scored
34
b. Can you conclude that the sampling distribution of the sample mean is normally distributed for both sample sizes?
Yes, both the sample means will have a normal distribution.
No, both the sample means will not have a normal distribution.
No, only the sample mean with n=14 will have a normal distribution.
No, only the sample mean with n= 34 will have a normal distribution.
c. If the sampling distribution of the sample mean is normally distributed with n=14, then calculate the probability that the sample
mean falls between 56 and 58. (If appropriate, round final answer to 4 decimal places.)
We cannot assume that the sampling distribution of the sample mean is normally distributed.
We can assume that the sampling distribution of the sample mean is normally distributed and the probability that the sample
mean falls between 56 and 58 is
Probability
0.2037 X
d. If the sampling distribution of the sample mean is normally distributed with n= 34, then calculate the probability that the sample
mean falls between 56 and 58. (If appropriate, round final answer to 4 decimal places.)
We cannot assume that the sampling distribution of the sample mean is normally distributed](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F62a36a92-9998-435b-aa26-d1bff96a7483%2F83539aa6-2354-4bfb-bd41-74d87feee65f%2Fweu0oe_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images

a and c are incorrect