4 A block with a mass of m = 7.4kg block starts at rest 1.2m above the ground, at the top of a frictionless ramp. At the bottom of the ramp is a flat stretch of rough (uk = 0.15) ground. After sliding a distance d = 3.0m, the ground becomes frictionless, and the block hits a spring (k = 1.6kN/m). a. Calculate the speed of the block at the bottom of the ramp. d b. Calculate the speed of the block just before it hits the spring. c. Calculate how far the spring is compressed.
4 A block with a mass of m = 7.4kg block starts at rest 1.2m above the ground, at the top of a frictionless ramp. At the bottom of the ramp is a flat stretch of rough (uk = 0.15) ground. After sliding a distance d = 3.0m, the ground becomes frictionless, and the block hits a spring (k = 1.6kN/m). a. Calculate the speed of the block at the bottom of the ramp. d b. Calculate the speed of the block just before it hits the spring. c. Calculate how far the spring is compressed.
College Physics
10th Edition
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Chapter5: Energy
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10WUE: A puck of mass 0.170 kg slides across ice in the positive x-direction with a kinetic friction...
Related questions
Question
Thank you in advance!
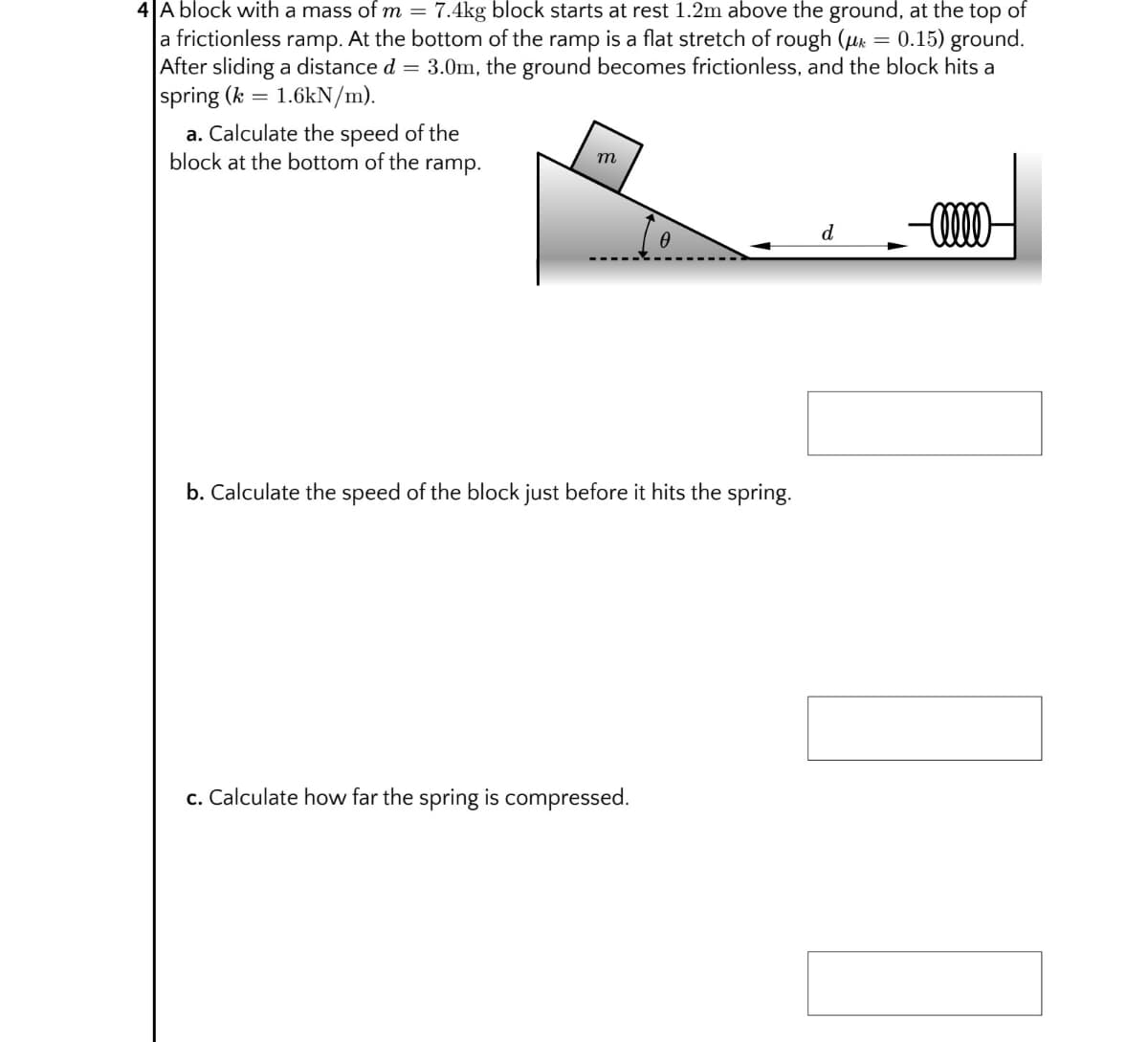
Transcribed Image Text:4 A block with a mass of m = 7.4kg block starts at rest 1.2m above the ground, at the top of
a frictionless ramp. At the bottom of the ramp is a flat stretch of rough (µr = 0.15) ground.
After sliding a distance d = 3.0m, the ground becomes frictionless, and the block hits a
spring (k =
1.6kN/m).
a. Calculate the speed of the
block at the bottom of the ramp.
m
d
b. Calculate the speed of the block just before it hits the spring.
c. Calculate how far the spring is compressed.

Transcribed Image Text:ANSWERS
1 a. they are all the same; b. car, c. they are all the same; d. car, e. car, f. they are all the
same; g. car
2 a. 37.0kJ; b. 74.1kJ; c. 39.4m;
3 a. VB =
11.7m/s, vc = 8.85m/s, vD =
9.90m/s; b. 1.63m/s²-; c. 0.167;
4 a. 4.85m/s; b. 3.83m/s; c. 26.1cm;
5 a. 12.2J; b. 5.75J ; c. 2.46m/s; d. 2.13i + 1.23j m/s; e. 7.74cm;
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning