5. Both neopentane and n-pentane have a CsH12 formula. Lag ae for interactiom Small area for interaction CH, CH, n-Pentane molar mass = 72.15 g/mol boiling point = 36.1 °C Neopentane molar mass = 72.15 gimol boiling point = 9.5 °Č CH Cí, CH, e n-Pentane 0) Neopentane Cvee tae a. Which compound has a higher boiling point? b. Which compound has stronger London forces? c. What conclusion can be drawn about straight chain and branched chain hydrocarbons from this example?
5. Both neopentane and n-pentane have a CsH12 formula. Lag ae for interactiom Small area for interaction CH, CH, n-Pentane molar mass = 72.15 g/mol boiling point = 36.1 °C Neopentane molar mass = 72.15 gimol boiling point = 9.5 °Č CH Cí, CH, e n-Pentane 0) Neopentane Cvee tae a. Which compound has a higher boiling point? b. Which compound has stronger London forces? c. What conclusion can be drawn about straight chain and branched chain hydrocarbons from this example?
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
2nd Edition
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Andrei Straumanis
ChapterL2: Mass Spectrometry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 20CTQ
Related questions
Question
Please help answer question 4 and 5
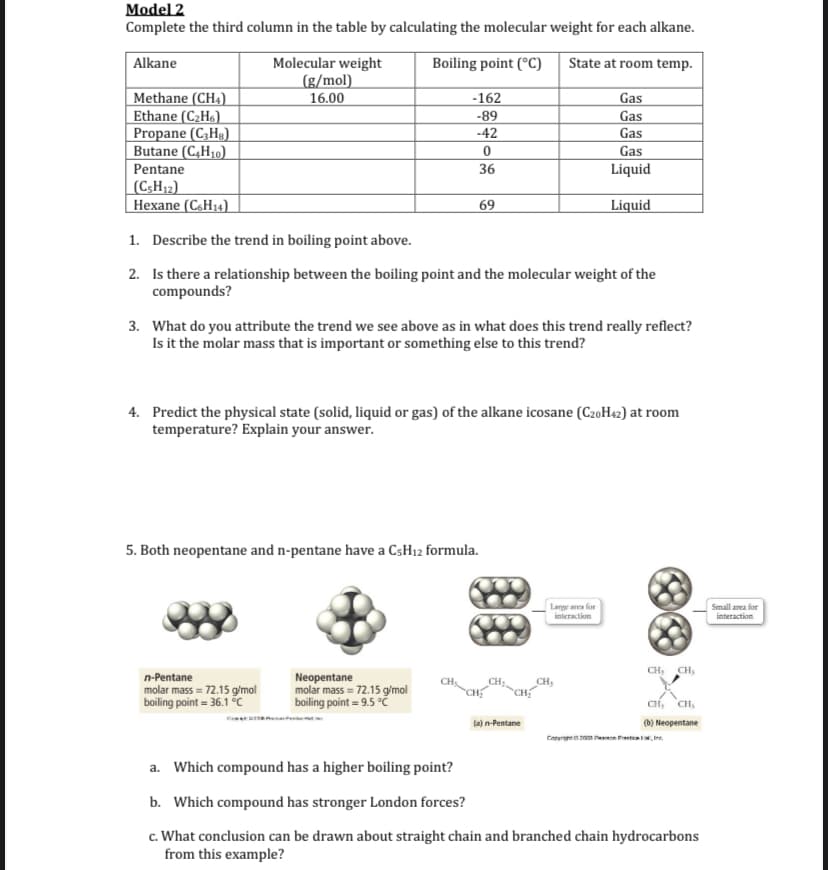
Transcribed Image Text:Model 2
Complete the third column in the table by calculating the molecular weight for each alkane.
Molecular weight
(g/mol).
16.00
Alkane
Boiling point (°C)
State at room temp.
Methane (CH4)
Ethane (C2H«)
Propane (C;Hg)
Butane (C,H10)
-162
Gas
-89
Gas
Gas
-42
Gas
Pentane
36
Liquid
(C;H12)
Нехane (C.H)
69
Liquid
1. Describe the trend in boiling point above.
2. Is there a relationship between the boiling point and the molecular weight of the
compounds?
3. What do you attribute the trend we see above as in what does this trend really reflect?
Is it the molar mass that is important or something else to this trend?
4. Predict the physical state (solid, liquid or gas) of the alkane icosane (CzoH42) at room
temperature? Explain your answer.
5. Both neopentane and n-pentane have a CSH12 formula.
Lange ares for
Small area for
imieraction
interaction
CH:
CH,
Neopentane
molar mass = 72.15 g/mol
boiling point = 9.5 °Č
n-Pentane
CH
CH,
molar mass = 72.15 g/mol
boiling point = 36.1 °C
CH, CH,
la) n-Pentane
(b) Neopentane
Cenyrata zon Pan Pretica , Ire
a. Which compound has a higher boiling point?
b. Which compound has stronger London forces?
c. What conclusion can be drawn about straight chain and branched chain hydrocarbons
from this example?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning