5.4 What is the thermodynamically stable form of He at 3.5 K and standard pressure? 5.5 materials this would be described as being in a defect free single crystal solid. What is the stable phase (solid, liquid, or gas) of He at absolute zero and standard pressure? Recall that at absolute zero (0 K), all materials have zero entropy. For most 5.6 states? What type(s) of intermolecular forces hold He together in the liquid
5.4 What is the thermodynamically stable form of He at 3.5 K and standard pressure? 5.5 materials this would be described as being in a defect free single crystal solid. What is the stable phase (solid, liquid, or gas) of He at absolute zero and standard pressure? Recall that at absolute zero (0 K), all materials have zero entropy. For most 5.6 states? What type(s) of intermolecular forces hold He together in the liquid
Chapter4: The Second Law Of Thermodynamics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10CQ: An ideal gas goes from state (pi,vi,) to state (pf,vf,) when it is allowed to expand freely. Is it...
Related questions
Question
PLEASE ANSWER ASAP! 5.4, 5.5,5.6,5.7,5.8
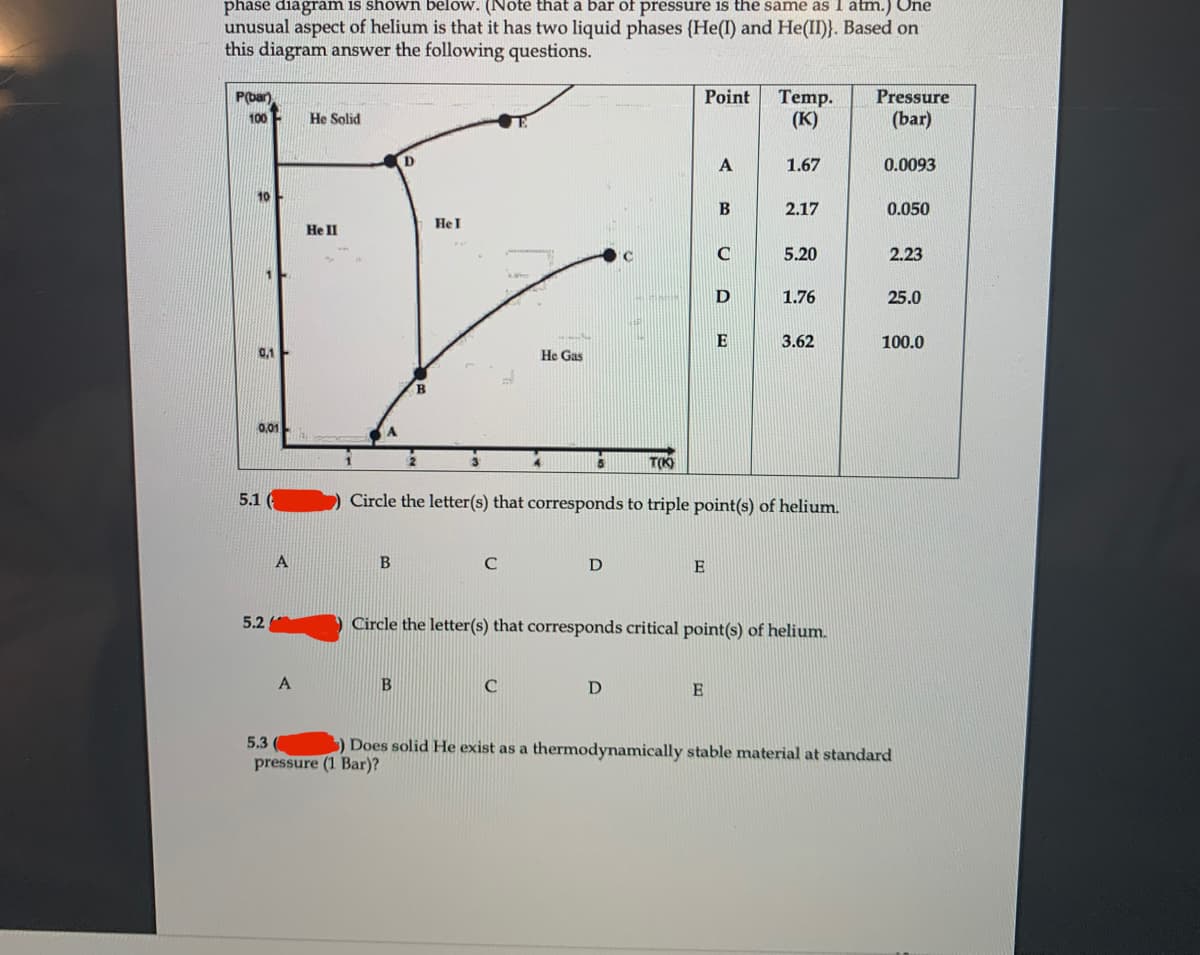
Transcribed Image Text:phase diagram is shown below. (Note that a bar of pressure is the same as 1 atm.) One
unusual aspect of helium is that it has two liquid phases (He(I) and He(II)}. Based on
this diagram answer the following questions.
Point
Temp.
(К)
P(bar)
Pressure
100
He Solid
(bar)
D
1.67
0.0093
2.17
0.050
He I
He Il
5.20
2.23
1.76
25.0
3.62
100.0
0,1
He Gas
B
0,01
T(K
5.1
Circle the letter(s) that corresponds to triple point(s) of helium.
A
D
E
5.2
Circle the letter(s) that corresponds critical point(s) of helium.
A
E
5.3
) Does solid He exist as a thermodynamically stable material at standard
pressure (1 Bar)?

Transcribed Image Text:5.4
pressure?
What is the thermodynamically stable form of He at 3.5 K and standard
5.5
:Recall that at absolute zero (0 K), all materials have zero entropy. For most
materials this would be described as being in a defect free single crystal solid. What is
the stable phase (solid, liquid, or gas) of He at absolute zero and standard pressure?
5.6
states?
What type(s) of intermolecular forces hold He together in the liquid
5.7
Given your answer to question 5.6, why does it require such low
temperatures to form liquid He from gaseous He?
5.8
Calculate the value for the Heat of Vaporization, AHvap, for He (I).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning