53°F Partly sunny H Q Search the air follows an adiabatic saturation curve (constant compared wet-bulb temperature line) on the psychrometric chart. 1. Air at 30°C, 10% relative humidity Figure 8.4-1 h,= 0.0026 kg H₂O/kg DA TwbT13.2°C 2. The state of the outlet air must lie on the Tb 13.2°C line. From the intersection of this line with the curve for h, = 40%, the absolute humidity of the exit gas is determined to be 0.0063 kg H₂O/kg DA. The inlet (and outlet) flow rate of dry air, mp, is DA(1000 kg air/h)(1 kg DA/1.0026 kg air) 997.4 kg DA/h The amount of water that must be evaporated, mo, may be calculated as the difference between the outlet and inlet water flow rates in the air stream. ^ENG
53°F Partly sunny H Q Search the air follows an adiabatic saturation curve (constant compared wet-bulb temperature line) on the psychrometric chart. 1. Air at 30°C, 10% relative humidity Figure 8.4-1 h,= 0.0026 kg H₂O/kg DA TwbT13.2°C 2. The state of the outlet air must lie on the Tb 13.2°C line. From the intersection of this line with the curve for h, = 40%, the absolute humidity of the exit gas is determined to be 0.0063 kg H₂O/kg DA. The inlet (and outlet) flow rate of dry air, mp, is DA(1000 kg air/h)(1 kg DA/1.0026 kg air) 997.4 kg DA/h The amount of water that must be evaporated, mo, may be calculated as the difference between the outlet and inlet water flow rates in the air stream. ^ENG
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P
Related questions
Question
For 1, locate the absolute humidity and the web-bulb temperature.
Transcribed Image Text:||!
PDF Elementary Principles of Chemica X PDF *Elementary Principles of Chemic X +
53°F
Partly sunny
File | E:/Elementary%20Principles%20of%20Chemical%20Processes,%204th%20Edition%20(%20PDFDrive%20).pdf
Draw
T Read aloud
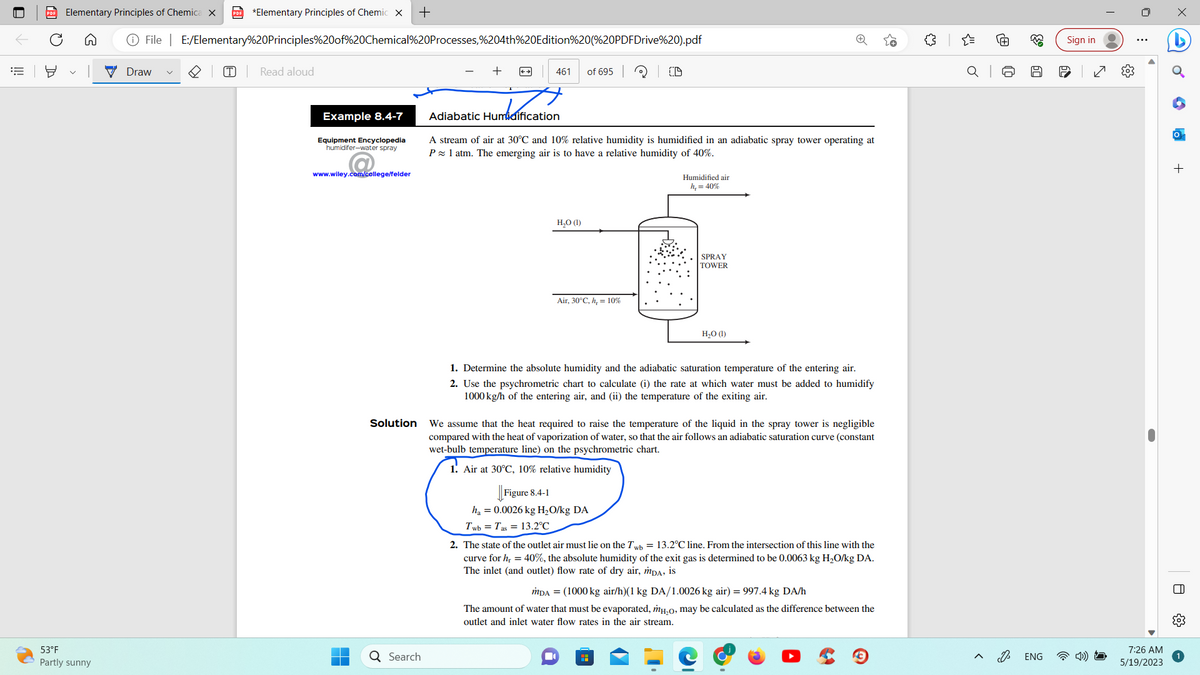
Example 8.4-7
Equipment Encyclopedia
humidifer-water spray
www.wiley.com/college/felder
Solution
Q Search
461 of 695
Adiabatic Humidification
mbarmes
A stream of air at 30°C and 10% relative humidity is humidified in an adiabatic spray tower operating at
P≈ 1 atm. The emerging air is to have a relative humidity of 40%.
H₂O (1)
Air, 30°C, h, = 10%
CD
Figure 8.4-1
ha = 0.0026 kg H₂O/kg DA
Twb Tas 13.2°C
Humidified air
h, = 40%
SPRAY
TOWER
1. Determine the absolute humidity and the adiabatic saturation temperature of the entering air.
2. Use the psychrometric chart to calculate (i) the rate at which water must be added to humidify
1000 kg/h of the entering air, and (ii) the temperature of the exiting air.
H₂O (1)
We assume that the heat required to raise the temperature of the liquid in the spray tower is negligible
compared with the heat of vaporization of water, so that the air follows an adiabatic saturation curve (constant
wet-bulb temperature line) on the psychrometric chart.
1. Air at 30°C, 10% relative humidity
H
2. The state of the outlet air must lie on the Twb = 13.2°C line. From the intersection of this line with the
curve for hr = 40%, the absolute humidity of the exit gas is determined to be 0.0063 kg H₂O/kg DA.
The inlet (and outlet) flow rate of dry air, MDA, is
MDA = (1000 kg air/h)(1 kg DA/1.0026 kg air) = 997.4 kg DA/h
The amount of water that must be evaporated, mH₂o, may be calculated as the difference between the
outlet and inlet water flow rates in the air stream.
{"
J
63
50
ENG
Sign in
(0)
7:26 AM
5/19/2023
+
□
{0}
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781285061238
Author:
Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:
Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780072848236
Author:
Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Companies, The