6. A solid cylinder of mass M and radius R is connect to a rod of length L= 2R and mass = ½ M which suspended by an axis at its end. The cylinder is released from a horizontal position. What is its angular velocity, w, at the lowest point of its swing? I em= ½ mR? L= Lem + md? stick: Lend = 1/3 m L² axis
6. A solid cylinder of mass M and radius R is connect to a rod of length L= 2R and mass = ½ M which suspended by an axis at its end. The cylinder is released from a horizontal position. What is its angular velocity, w, at the lowest point of its swing? I em= ½ mR? L= Lem + md? stick: Lend = 1/3 m L² axis
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter10: Rotational Motion
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 83P: A solid sphere of mass m and radius r rolls without slipping along the track shown in Figure P10.83....
Related questions
Question
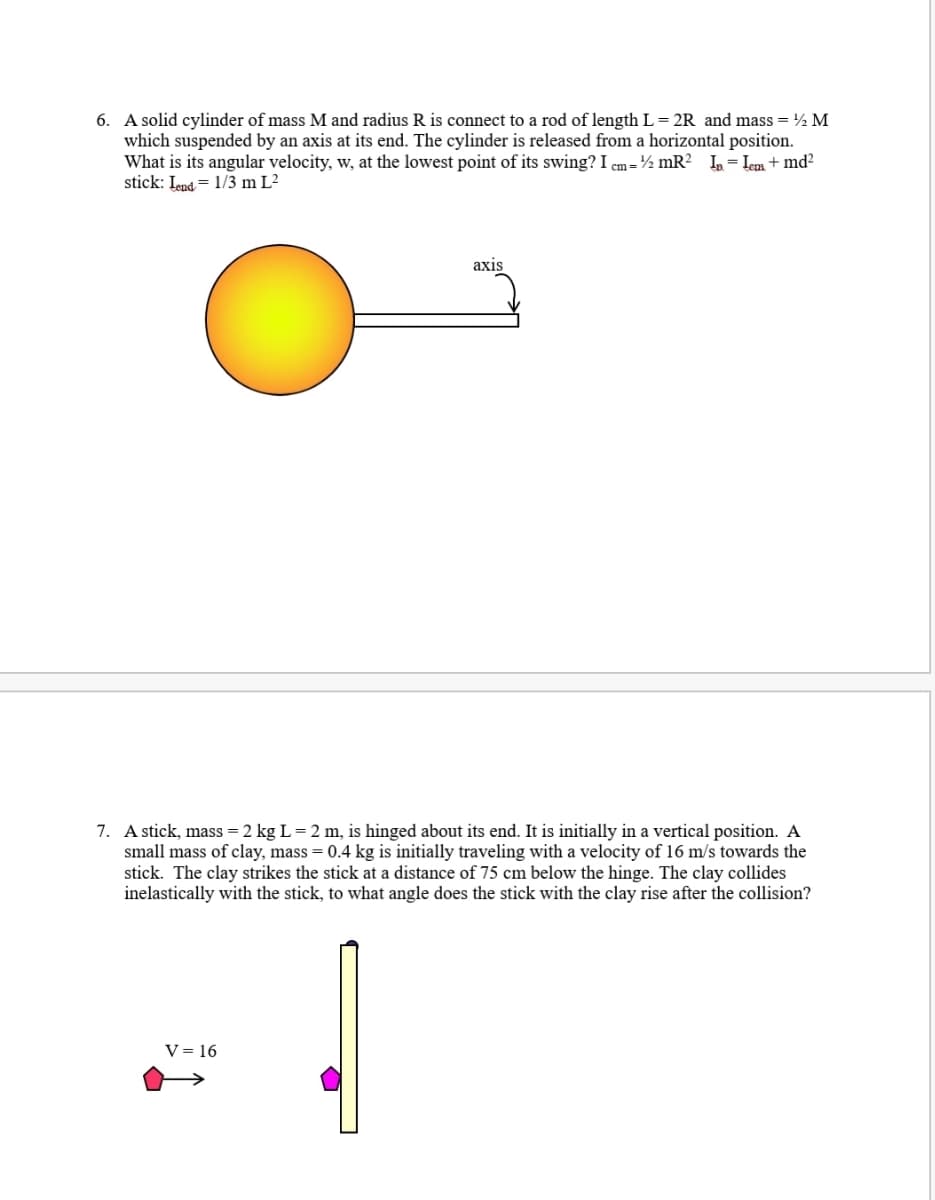
Transcribed Image Text:6. A solid cylinder of mass M and radius R is connect to a rod of length L= 2R and mass = ½ M
which suspended by an axis at its end. The cylinder is released from a horizontal position.
What is its angular velocity, w, at the lowest point of its swing? I cm=½ mR² I,= Lem + md²
stick: Iend = 1/3 m L²
аxis
7. A stick, mass = 2 kg L= 2 m, is hinged about its end. It is initially in a vertical position. A
small mass of clay, mass = 0.4 kg is initially traveling with a velocity of 16 m/s towards the
stick. The clay strikes the stick at a distance of 75 cm below the hinge. The clay collides
inelastically with the stick, to what angle does the stick with the clay rise after the collision?
V = 16
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College