6. Consider the phase diagram shown for substance X. (a) What phase(s) is (are) present at point A? E? F? H? B? C? (b) Which point corresponds to the critical point? Which point corresponds to the triple point? (c) What curve corresponds to conditions at which the solid and gas are in equilibrium? (d) Describe what happens when you start at point A and increase the temperature at constant pressure. (e) Describe what happens when you start at point H and decrease the pressure at constant temperature. (f) Is liquid X more or less dense than solid X? E H. •C Temperature - - Pressure
6. Consider the phase diagram shown for substance X. (a) What phase(s) is (are) present at point A? E? F? H? B? C? (b) Which point corresponds to the critical point? Which point corresponds to the triple point? (c) What curve corresponds to conditions at which the solid and gas are in equilibrium? (d) Describe what happens when you start at point A and increase the temperature at constant pressure. (e) Describe what happens when you start at point H and decrease the pressure at constant temperature. (f) Is liquid X more or less dense than solid X? E H. •C Temperature - - Pressure
Chemistry for Engineering Students
4th Edition
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Chapter8: Molecules And Materials
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8.87PAE: 8.87 Use the vapor pressure curves illustrated here to answer the questions that follow. (a) What is...
Related questions
Question
100%
Consider the phase diagram shown for substance X.
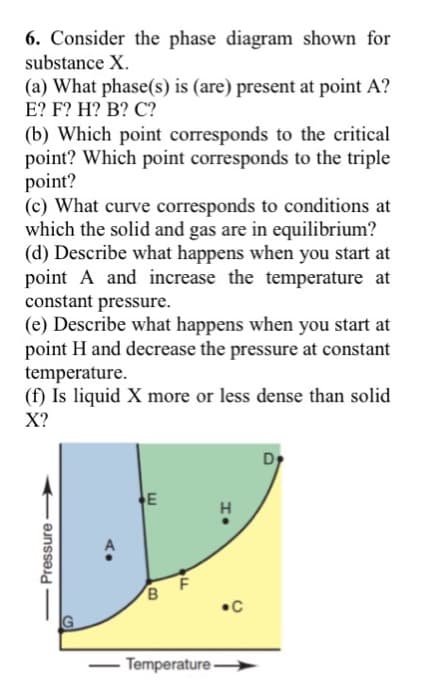
Transcribed Image Text:6. Consider the phase diagram shown for
substance X.
(a) What phase(s) is (are) present at point A?
E? F? H? B? C?
(b) Which point corresponds to the critical
point? Which point corresponds to the triple
point?
(c) What curve corresponds to conditions at
which the solid and gas are in equilibrium?
(d) Describe what happens when you start at
point A and increase the temperature at
constant pressure.
(e) Describe what happens when you start at
point H and decrease the pressure at constant
temperature.
(f) Is liquid X more or less dense than solid
X?
Dy
E
B
•C
IG
Temperature →
- Pressure
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning