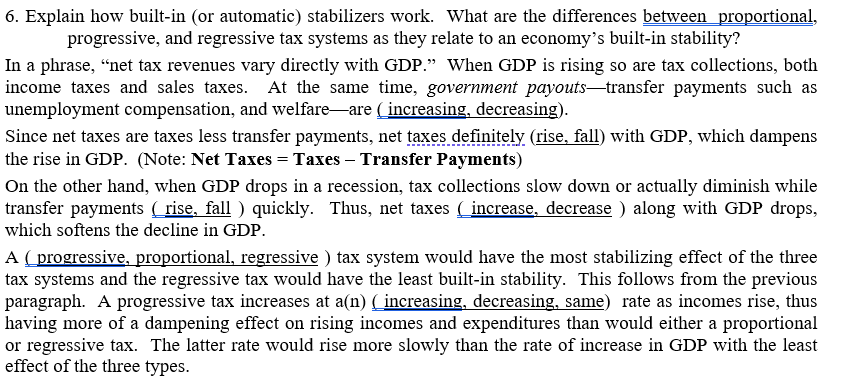
6. Explain how built-in (or automatic) stabilizers work. What are the differences between proportional, progressive, and regressive tax systems as they relate to an economy’s built-in stability? In a phrase, “net tax revenues vary directly with GDP." When GDP is rising so are tax collections, both income taxes and sales taxes. At the same time, government payouts–transfer payments such as unemployment compensation, and welfare-are ( increasing, decreasing). Since net taxes are taxes less transfer payments, net taxes definitely (rise, fall) with GDP, which dampens the rise in GDP. (Note: Net Taxes = Taxes – Transfer Payments) On the other hand, when GDP drops in a recession, tax collections slow down or actually diminish while transfer payments ( rise, fall ) quickly. Thus, net taxes (_increase, decrease ) along with GDP drops, which softens the decline in GDP. A ( progressive, proportional, regressive ) tax system would have the most stabilizing effect of the three tax systems and the regressive tax would have the least built-in stability. This follows from the previous paragraph. A progressive tax increases at a(n) ( increasing, decreasing, same) rate as incomes rise, thus having more of a dampening effect on rising incomes and expenditures than would either a proportional or regressive tax. The latter rate would rise more slowly than the rate of increase in GDP with the least effect of the three types.
6. Explain how built-in (or automatic) stabilizers work. What are the differences between proportional, progressive, and regressive tax systems as they relate to an economy’s built-in stability? In a phrase, “net tax revenues vary directly with GDP." When GDP is rising so are tax collections, both income taxes and sales taxes. At the same time, government payouts–transfer payments such as unemployment compensation, and welfare-are ( increasing, decreasing). Since net taxes are taxes less transfer payments, net taxes definitely (rise, fall) with GDP, which dampens the rise in GDP. (Note: Net Taxes = Taxes – Transfer Payments) On the other hand, when GDP drops in a recession, tax collections slow down or actually diminish while transfer payments ( rise, fall ) quickly. Thus, net taxes (_increase, decrease ) along with GDP drops, which softens the decline in GDP. A ( progressive, proportional, regressive ) tax system would have the most stabilizing effect of the three tax systems and the regressive tax would have the least built-in stability. This follows from the previous paragraph. A progressive tax increases at a(n) ( increasing, decreasing, same) rate as incomes rise, thus having more of a dampening effect on rising incomes and expenditures than would either a proportional or regressive tax. The latter rate would rise more slowly than the rate of increase in GDP with the least effect of the three types.
Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781337091985
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:N. Gregory Mankiw
Chapter18: Six Debates Over Macroeconomic Policy
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6PA
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:6. Explain how built-in (or automatic) stabilizers work. What are the differences between proportional,
progressive, and regressive tax systems as they relate to an economy's built-in stability?
In a phrase, “net tax revenues vary directly with GDP." When GDP is rising so are tax collections, both
income taxes and sales taxes. At the same time, government payouts-transfer payments such as
unemployment compensation, and welfare-are ( increasing, decreasing).
Since net taxes are taxes less transfer payments, net taxes definitely (rise, fall) with GDP, which dampens
the rise in GDP. (Note: Net Taxes = Taxes – Transfer Payments)
On the other hand, when GDP drops in a recession, tax collections slow down or actually diminish while
transfer payments ( rise, fall ) quickly. Thus, net taxes ( increase, decrease ) along with GDP drops,
which softens the decline in GDP.
A ( progressive, proportional, regressive ) tax system would have the most stabilizing effect of the three
tax systems and the regressive tax would have the least built-in stability. This follows from the previous
paragraph. A progressive tax increases at a(n) ( increasing, decreasing, same) rate as incomes rise, thus
having more of a dampening effect on rising incomes and expenditures than would either a proportional
or regressive tax. The latter rate would rise more slowly than the rate of increase in GDP with the least
effect of the three types.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours…
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091985
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165912
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971509
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours…
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091985
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165912
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971509
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
