8. Suppose that aggregate demand and supply for a hypothetical economy are as shown: P TITIX Amount of real Price Amount rea AS GDP supplie billions GDP level demanded, (price index) billions 100 300 450 200 250 400 AD' 300 200 300 AD 400 150 200 500 100 100 Real 100 200 300 400 GDP Use these sets of data to graph the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves. What is the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium level of real output in this hypothetical economy? Equilibrium price level = Is the equilibrium real output also necessarily the full-capacity real output? ( Yes, No The full-capacity level of GDP is more lil cut ' at $_ а. Equilibrium real output = $_ billion billion. b. Why will a price level of 150 not be an equilibrium price level in this economy? Why not 250? At a price level of 150, real GDP supplied is a maximum of $ the real GDP demanded of $ price level up. At a price level of 250, real GDP supplied is $400 billion, which is more than the real GDP demanded of $200 billion. The (shortage, surplus) of real output will drive down the price level. Equilibrium occurs at the price level at which AS and AD intersect. billion, (more, less ) than billion. The (shortage, surplus) of real output will drive the c. Suppose that buyers desire to purchase $200 billion of extra real domestic output at each price level. Sketch in the new aggregate demand curve as AD1. (It is drawn on the graph above with a dashed line.) What factors (determinants or shifters) might cause this change in aggregate demand? (Increases, Decreases) in consumer, investment, government, or net export spending might shift the AD curve rightward from AD to AD'. New equilibrium price level New equilibrium GDP = $ billion. %3D
8. Suppose that aggregate demand and supply for a hypothetical economy are as shown: P TITIX Amount of real Price Amount rea AS GDP supplie billions GDP level demanded, (price index) billions 100 300 450 200 250 400 AD' 300 200 300 AD 400 150 200 500 100 100 Real 100 200 300 400 GDP Use these sets of data to graph the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves. What is the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium level of real output in this hypothetical economy? Equilibrium price level = Is the equilibrium real output also necessarily the full-capacity real output? ( Yes, No The full-capacity level of GDP is more lil cut ' at $_ а. Equilibrium real output = $_ billion billion. b. Why will a price level of 150 not be an equilibrium price level in this economy? Why not 250? At a price level of 150, real GDP supplied is a maximum of $ the real GDP demanded of $ price level up. At a price level of 250, real GDP supplied is $400 billion, which is more than the real GDP demanded of $200 billion. The (shortage, surplus) of real output will drive down the price level. Equilibrium occurs at the price level at which AS and AD intersect. billion, (more, less ) than billion. The (shortage, surplus) of real output will drive the c. Suppose that buyers desire to purchase $200 billion of extra real domestic output at each price level. Sketch in the new aggregate demand curve as AD1. (It is drawn on the graph above with a dashed line.) What factors (determinants or shifters) might cause this change in aggregate demand? (Increases, Decreases) in consumer, investment, government, or net export spending might shift the AD curve rightward from AD to AD'. New equilibrium price level New equilibrium GDP = $ billion. %3D
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:N. Gregory Mankiw
Chapter33: Aggregate Demand And Aggregate Supply
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3PA
Related questions
Question
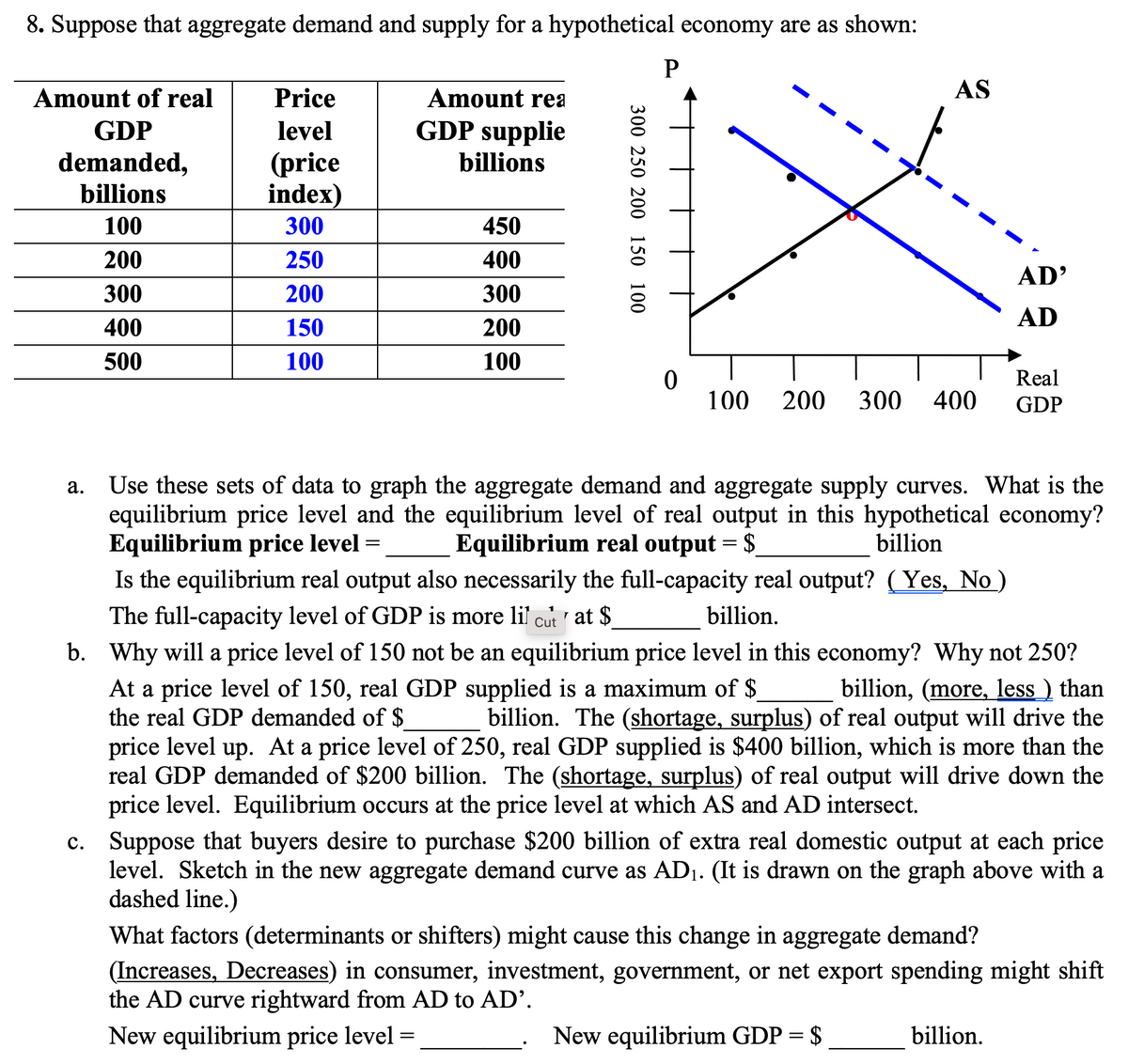
Transcribed Image Text:8. Suppose that aggregate demand and supply for a hypothetical economy are as shown:
P
Amount of real
Price
Amount rea
AS
GDP
level
GDP supplie
demanded,
billions
(price
index)
billions
100
300
450
200
250
400
AD'
300
200
300
AD
400
150
200
500
100
100
Real
100
200
300
400
GDP
Use these sets of data to graph the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves. What is the
equilibrium price level and the equilibrium level of real output in this hypothetical economy?
Equilibrium price level =
Is the equilibrium real output also necessarily the full-capacity real output? (Yes, No )
The full-capacity level of GDP is more lil cut at $
а.
Equilibrium real output = $
billion
billion.
b. Why will a price level of 150 not be an equilibrium price level in this economy? Why not 250?
billion, (more, less ) than
billion. The (shortage, surplus) of real output will drive the
At a price level of 150, real GDP supplied is a maximum of $
the real GDP demanded of $
price level up. At a price level of 250, real GDP supplied is $400 billion, which is more than the
real GDP demanded of $200 billion. The (shortage, surplus) of real output will drive down the
price level. Equilibrium occurs at the price level at which AS and AD intersect.
c. Suppose that buyers desire to purchase $200 billion of extra real domestic output at each price
level. Sketch in the new aggregate demand curve as AD1. (It is drawn on the graph above with a
dashed line.)
What factors (determinants or shifters) might cause this change in aggregate demand?
(Increases, Decreases) in consumer, investment, government, or net export spending might shift
the AD curve rightward from AD to AD'.
New equilibrium price level =
New equilibrium GDP = $
billion.
300 250 200 150 100
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours…
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091985
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971509
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning