8. You are studying the biochemical pathway of purrine production. (Purrines are a type of nucleotide used in feline DNA, a little different than the purines in the DNA of lower species like humans.) You have several mutants that cannot make purrine, and you do complementation tests to see how many different genes you've identified. Here are your data: mutant 1 2 3 7 8 9. 1 2 4 6. 7 8 + a) What is the deal with mutant #1 and why must you ignore it when figuring out complementation groups? b) For the rest of the problem, ignore mutant #1. List your complementation groups. Hint: every single one of your mutants (except #1 of course) must be in a group. c) How many genes did you, therefore, identify?
8. You are studying the biochemical pathway of purrine production. (Purrines are a type of nucleotide used in feline DNA, a little different than the purines in the DNA of lower species like humans.) You have several mutants that cannot make purrine, and you do complementation tests to see how many different genes you've identified. Here are your data: mutant 1 2 3 7 8 9. 1 2 4 6. 7 8 + a) What is the deal with mutant #1 and why must you ignore it when figuring out complementation groups? b) For the rest of the problem, ignore mutant #1. List your complementation groups. Hint: every single one of your mutants (except #1 of course) must be in a group. c) How many genes did you, therefore, identify?
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Chapter19: Genomes And Proteomes
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1TYK
Related questions
Question
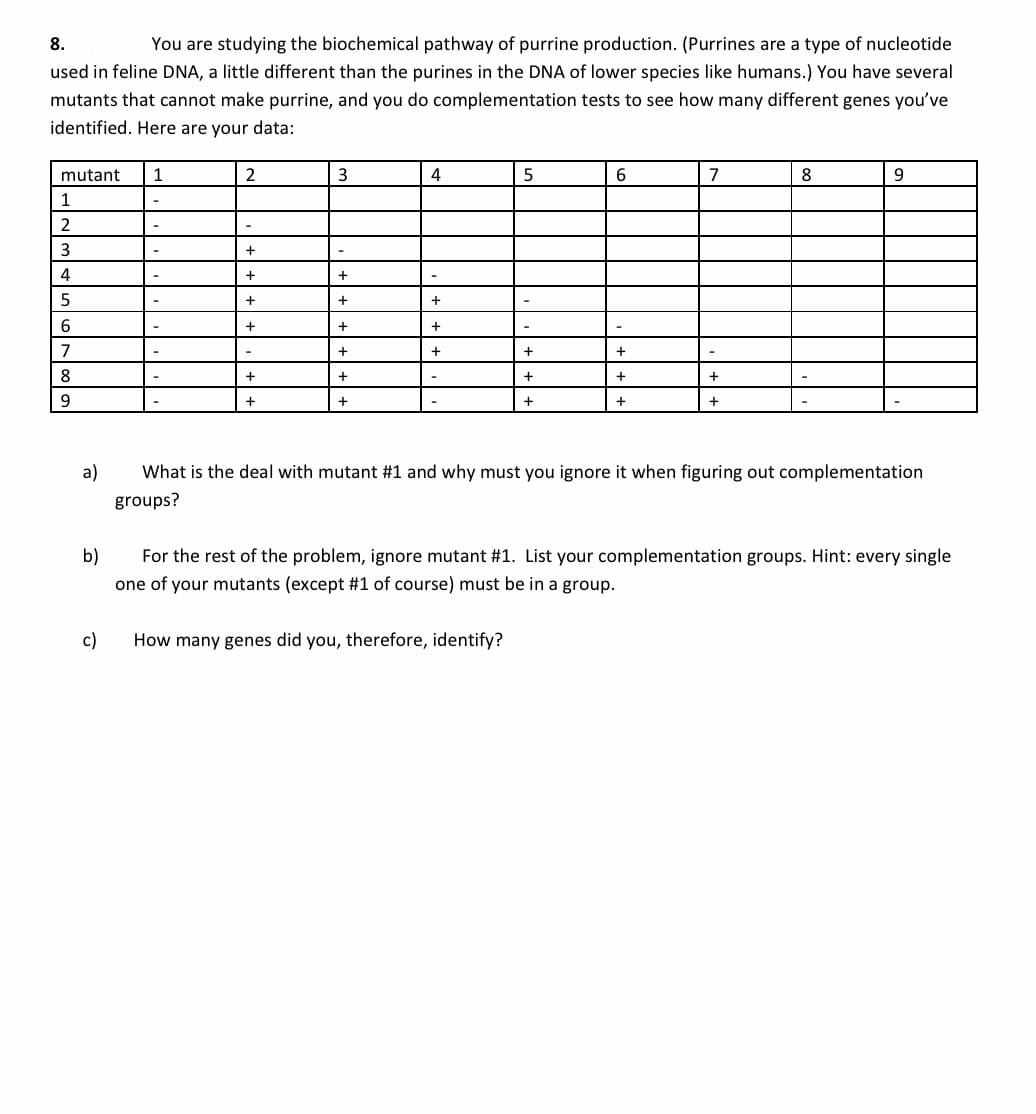
Transcribed Image Text:8.
You are studying the biochemical pathway of purrine production. (Purrines are a type of nucleotide
used in feline DNA, a little different than the purines in the DNA of lower species like humans.) You have several
mutants that cannot make purrine, and you do complementation tests to see how many different genes you've
identified. Here are your data:
mutant
1
4
6
8
1
3
4
5
+
6
+
+
+
8.
+
+
9
+
a)
What is the deal with mutant #1 and why must you ignore it when figuring out complementation
groups?
b)
For the rest of the problem, ignore mutant #1. List your complementation groups. Hint: every single
one of your mutants (except #1 of course) must be in a group.
c)
How many genes did you, therefore, identify?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305389892
Author:
Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305389892
Author:
Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax