* 88. Go Two blocks are sliding to the right across a horizontal surface, as the drawing shows. In Case A the mass of each block is 3.0 kg. In Case B the mass of block 1 (the block behind) is 6.0 kg, and the mass of block 2 is 3.0 kg. No frictional force acts on block 1 in either Case A or Case B. However, a kinetic frictional force of 5.8 N does act on block 2 in both cases and opposes the motion. For both Case A and Case B determine (a) the magnitude of the forces with which the blocks push against each other and (b) the magnitude of the acceleration of the blocks.
* 88. Go Two blocks are sliding to the right across a horizontal surface, as the drawing shows. In Case A the mass of each block is 3.0 kg. In Case B the mass of block 1 (the block behind) is 6.0 kg, and the mass of block 2 is 3.0 kg. No frictional force acts on block 1 in either Case A or Case B. However, a kinetic frictional force of 5.8 N does act on block 2 in both cases and opposes the motion. For both Case A and Case B determine (a) the magnitude of the forces with which the blocks push against each other and (b) the magnitude of the acceleration of the blocks.
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Katz, Debora M.
Chapter5: Newton's Laws Of Motion
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 47PQ: A block with mass m1 hangs from a rope that is extended over an ideal pulley and attached to a...
Related questions
Question
100%
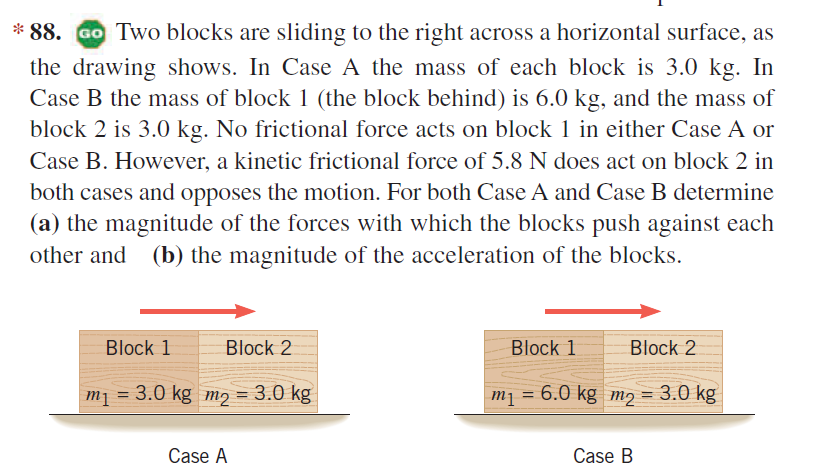
Transcribed Image Text:* 88. GO Two blocks are sliding to the right across a horizontal surface, as
the drawing shows. In Case A the mass of each block is 3.0 kg. In
Case B the mass of block 1 (the block behind) is 6.0 kg, and the mass of
block 2 is 3.0 kg. No frictional force acts on block 1 in either Case A or
Case B. However, a kinetic frictional force of 5.8 N does act on block 2 in
both cases and opposes the motion. For both Case A and Case B determine
(a) the magnitude of the forces with which the blocks push against each
other and (b) the magnitude of the acceleration of the blocks.
Block 1
Block 2
Block 1
Block 2
m1 = 3.0 kg m2 = 3.0 kg
m1 = 6.0 kg m2 = 3.0 kg
%D
Case A
Case B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning