a) A 50 mm diameter carbon steel tube (ρ = 7833 kg/m3; Cp = 465 J/kg.K, k = 54 W/mK) at an initial uniform temperature of 18°C is heated in an oven with air circulation that is at a temperature of 250°C and has a convection heat transfer coefficient of 45 W/m2.K. How long must the tube be in the oven for the surface temperature to reach 100°C? b) The figure below illustrates the temperature distribution inside a flat solid at two instants for two different situations (A and B). I
a) A 50 mm diameter carbon steel tube (ρ = 7833 kg/m3; Cp = 465 J/kg.K, k = 54 W/mK) at an initial uniform temperature of 18°C is heated in an oven with air circulation that is at a temperature of 250°C and has a convection heat transfer coefficient of 45 W/m2.K. How long must the tube be in the oven for the surface temperature to reach 100°C? b) The figure below illustrates the temperature distribution inside a flat solid at two instants for two different situations (A and B). I
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305578296
Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Chapter31: Gas Heat
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5RQ: The specific gravity of natural gas is A. 0.08. B. 1.00. C. 0.42. D. 0.60.
Related questions
Question
a) A 50 mm diameter carbon steel tube (ρ = 7833 kg/m3; Cp = 465 J/kg.K, k = 54 W/mK) at an initial uniform temperature of 18°C is heated in an oven with air circulation that is at a temperature of 250°C and has a convection heat transfer coefficient of 45 W/m2.K. How long must the tube be in the oven for the surface temperature to reach 100°C?
b) The figure below illustrates the temperature distribution inside a flat solid at two instants for two different situations (A and B). In both situations is there heat transfer? What causes them to behave differently?
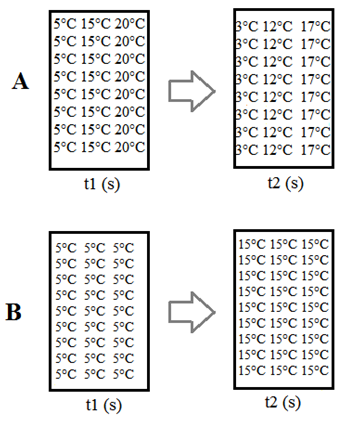
Transcribed Image Text:5°C 15°C 20°C
5°C 15°C 20°C
5°C 15°C 20°C
5°C 15°C 20°C|
А
5°C 15°C 20°C|
5°C 15°C 20°C
5°C 15°C 20°C
5°C 15°C 20°C
3°С 12°С 17°C
3°С 12°С 17°C
3°С 12°С 17°C
3°C 12°С 17°C
В°С 12°С 17°C
В°С 12°С 17°C
3°С 12°С 17°C
В°С 12°С 17°C
t1 (s)
t2 (s)
5°C 5°C 5°C
5°C 5°C 5°С
5°C 5°C 5°C
5°C 5°C 5°C
5°C 5°C 5°C
5°C 5°C 5°C
5°C 5°C 5°С
5°C 5°C 5°C
5°C 5°C 5°C
15°C 15°C 15°C
15°C 15°C 15°C
15°C 15°C 15°C
15°C 15°C 15°С
15°C 15°C 15°C
15°C 15°C 15°C
15°C 15°C 15°C
15°C 15°C 15°C
15°C 15°C 15°c
В
t1 (s)
t2 (s)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305578296
Author:
John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305578296
Author:
John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning