A case-control study of patients on antihypertensive drugs related an increased risk of myocardial infarction (MI) for patients using calcium channel blockers. In this study, cases were antihypertensive drug patients who had suffered a first fatal or nonfatal MI through 1993, and controls were antihypertensive drug patients, matched by demographic factors, who had not suffered a MI. Among the comparisons reported were patients receiving calcium channel (CC) blockers (with and without diuretics) and patients receiving B-blockers (with and without diuretics). Results of numbers of patient by drug/MI status combination are given in the following table. Antihypertensive O HO: p1=p2 vs. Ha: p1 < p2 O HO: p1>p2 vs. Ha: p1=p2 Drug Does it appear that an increased risk of myocardial infarction (MI) is related to using calcium channel (CC) blockers? The case-control nature of this study requires we compare the proportion of CC blocker users among those had MI attack (p1) vs. the proportion of CC blocker users among those had no MI (p2). What is your hypothesis for this test? ⒸHO: p1=p2 vs. Ha: p1=p2 CC blocker B-blocker O HO: p1=p2 vs. Ha: p1>p2 Occurrence of Yes (cases) 80 85 Myocardial Infarction No (controls) 230 395
A case-control study of patients on antihypertensive drugs related an increased risk of myocardial infarction (MI) for patients using calcium channel blockers. In this study, cases were antihypertensive drug patients who had suffered a first fatal or nonfatal MI through 1993, and controls were antihypertensive drug patients, matched by demographic factors, who had not suffered a MI. Among the comparisons reported were patients receiving calcium channel (CC) blockers (with and without diuretics) and patients receiving B-blockers (with and without diuretics). Results of numbers of patient by drug/MI status combination are given in the following table. Antihypertensive O HO: p1=p2 vs. Ha: p1 < p2 O HO: p1>p2 vs. Ha: p1=p2 Drug Does it appear that an increased risk of myocardial infarction (MI) is related to using calcium channel (CC) blockers? The case-control nature of this study requires we compare the proportion of CC blocker users among those had MI attack (p1) vs. the proportion of CC blocker users among those had no MI (p2). What is your hypothesis for this test? ⒸHO: p1=p2 vs. Ha: p1=p2 CC blocker B-blocker O HO: p1=p2 vs. Ha: p1>p2 Occurrence of Yes (cases) 80 85 Myocardial Infarction No (controls) 230 395
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:True or False? We have strong evidence against Ho: P1 = P2 and support the claim that an increased risk of myocardial infarction (MI) is related to using calcium channel (CC) blockers.
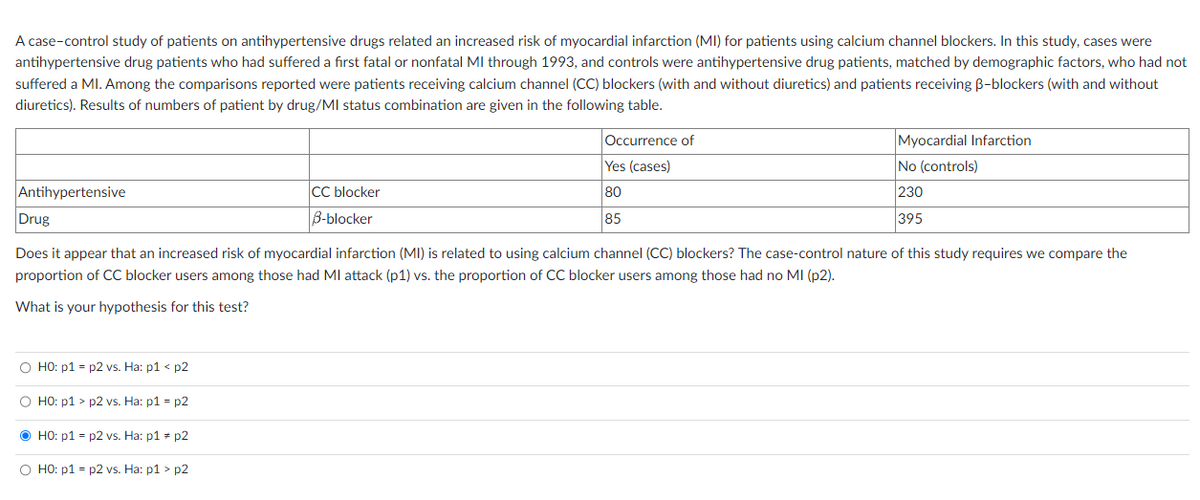
Transcribed Image Text:A case-control study of patients on antihypertensive drugs related an increased risk of myocardial infarction (MI) for patients using calcium channel blockers. In this study, cases were
antihypertensive drug patients who had suffered a first fatal or nonfatal Ml through 1993, and controls were antihypertensive drug patients, matched by demographic factors, who had not
suffered a MI. Among the comparisons reported were patients receiving calcium channel (CC) blockers (with and without diuretics) and patients receiving B-blockers (with and without
diuretics). Results of numbers of patient by drug/MI status combination are given in the following table.
Antihypertensive
O HO: p1=p2 vs. Ha: p1 < p2
O HO: p1> p2 vs. Ha: p1=p2
ⒸHO: p1=p2 vs. Ha: p1 = p2
CC blocker
B-blocker
O HO: p1=p2 vs. Ha: p1 > p2
Occurrence of
Yes (cases)
80
85
Drug
Does it appear that an increased risk of myocardial infarction (MI) is related to using calcium channel (CC) blockers? The case-control nature of this study requires we compare the
proportion of CC blocker users among those had MI attack (p1) vs. the proportion of CC blocker users among those had no MI (p2).
What is your hypothesis for this test?
Myocardial Infarction
No (controls)
230
395
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman