A certain nonvolatile hydrocarbon that weighed 1.00 g was dissolved in 50.00 g of benzene. The resulting solution was boiled at 0.285 °C higher than the boiling point of pure benzene which boils at 80.1°C. Find the molar mass of the hydrocarbon. (Hint: See Table 1 for given constant.)
A certain nonvolatile hydrocarbon that weighed 1.00 g was dissolved in 50.00 g of benzene. The resulting solution was boiled at 0.285 °C higher than the boiling point of pure benzene which boils at 80.1°C. Find the molar mass of the hydrocarbon. (Hint: See Table 1 for given constant.)
Principles of Modern Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Chapter14: Chemical Equilibrium
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 93AP
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Problem Solving:
1. A solution is made of 2.00 g of sucrose, C12H22011, in water, H20. The molar
mass (MM) of sucrose is 342 g/mol. Calculate the (a) boiling point and (h)
freezing point of the solution. (Hint: See Table 1 for given constants.)
2. A certain nonvolatile hydrocarbon that weighed 1.00 g was dissolved in
50.00 g of benzene. The resulting solution was boiled at 0.285 °C higher
than the boiling point of pure benzene which boils at 80.1°C. Find the molar
mass of the hydrocarbon. (Hint: See Table 1 for given constant.)
14
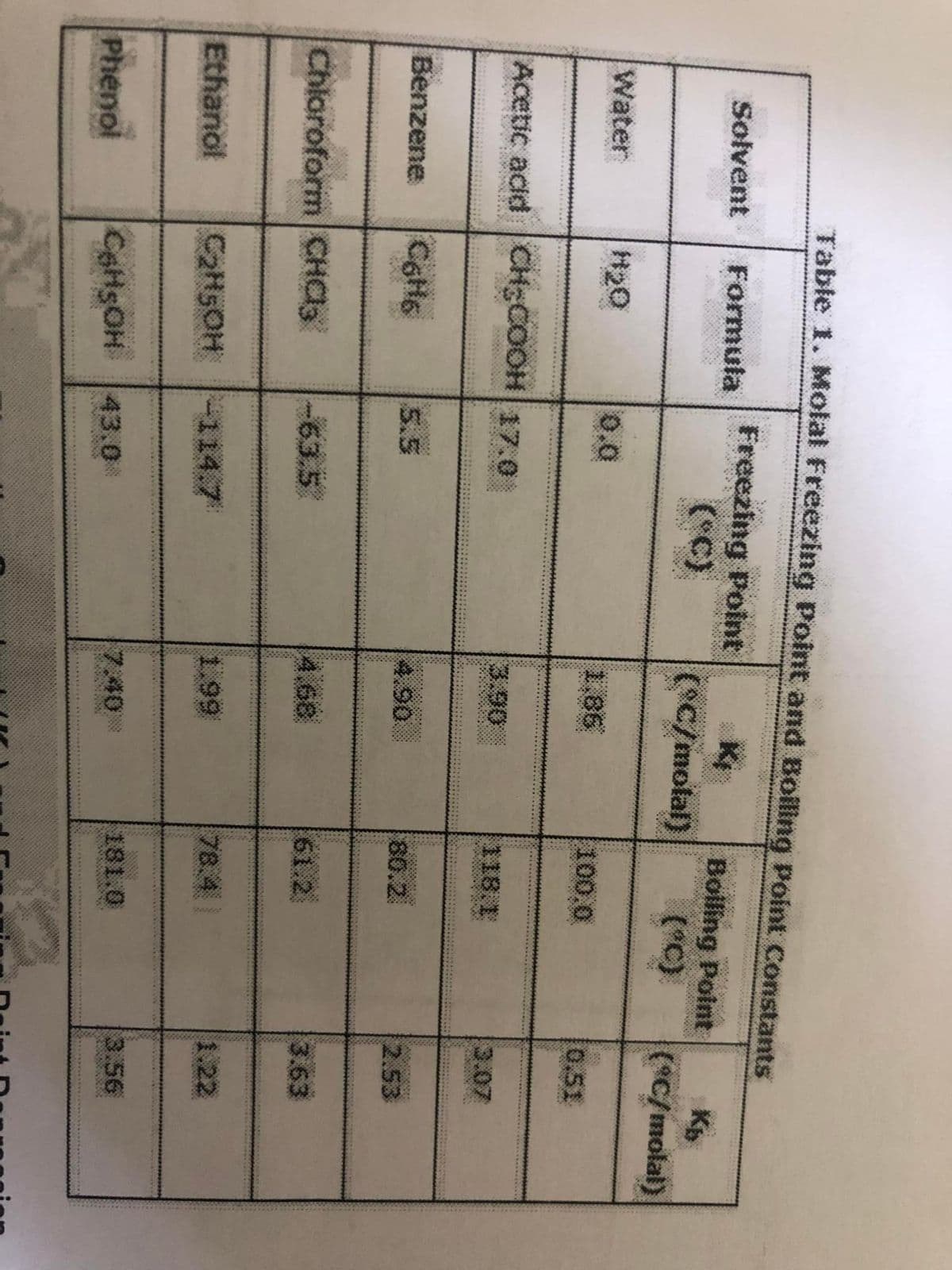
Transcribed Image Text:Table 1. Molal Freezing Point and Boiling Point Constants
Freezing Point
(C)
Solvent
Formula
Bolling Point
(*C)
(C/molal)
(c/molal)
Water
H20
0.0
1.86
100.0
0.51
Acetic acid CH:COOH 17.0
3.90
118.1
3.07
Benzene
5.5
4.90
80.2.
2.53
Chloroform CHC3
-63.5
4.68
61.2
3.63
Ethanol
C2H5OH
114.7
1.99
78.
78.4
1.22
7.40
181.0
3.56
Phenol
CeHsOH
43.0
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC L
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305446021
Author:
Lampman
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC L
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305446021
Author:
Lampman
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT