A country that produces paper is a price taker in the world paper market. The world price is pw: Suppose that the industry is not polluting. onor The domestic supply curve, S, is upward sloping, but the home country can ntj import as much as it wants at the world price, pw: In the free-trade equilibrium, e1, the equilibrium quantity is Q1 and the equilibrium price is the world price, pw- With a ban on imports, the equilibrium is e,, quantity falls to Q2, and price rises to p2- mes How do we know that winners from trade can compensate losers and still have Pw enough left over to benefit themselves? The winners from trade can compensate the losers and still have enough left over to benefit themselves because, with free trade, O A. consumer surplus increases by more than producer surplus decreases. Q2 Q1 Q, Tons per year O B. consumer surplus increases by more than deadweight loss increases. O C. producer surplus increases by more than consumer surplus decreases. O D. producer surplus increases by more than deadweight loss increases. O E. consumer surplus and producer surplus both increase. P. $ per ton
A country that produces paper is a price taker in the world paper market. The world price is pw: Suppose that the industry is not polluting. onor The domestic supply curve, S, is upward sloping, but the home country can ntj import as much as it wants at the world price, pw: In the free-trade equilibrium, e1, the equilibrium quantity is Q1 and the equilibrium price is the world price, pw- With a ban on imports, the equilibrium is e,, quantity falls to Q2, and price rises to p2- mes How do we know that winners from trade can compensate losers and still have Pw enough left over to benefit themselves? The winners from trade can compensate the losers and still have enough left over to benefit themselves because, with free trade, O A. consumer surplus increases by more than producer surplus decreases. Q2 Q1 Q, Tons per year O B. consumer surplus increases by more than deadweight loss increases. O C. producer surplus increases by more than consumer surplus decreases. O D. producer surplus increases by more than deadweight loss increases. O E. consumer surplus and producer surplus both increase. P. $ per ton
Chapter28: International Trade
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9P
Related questions
Question
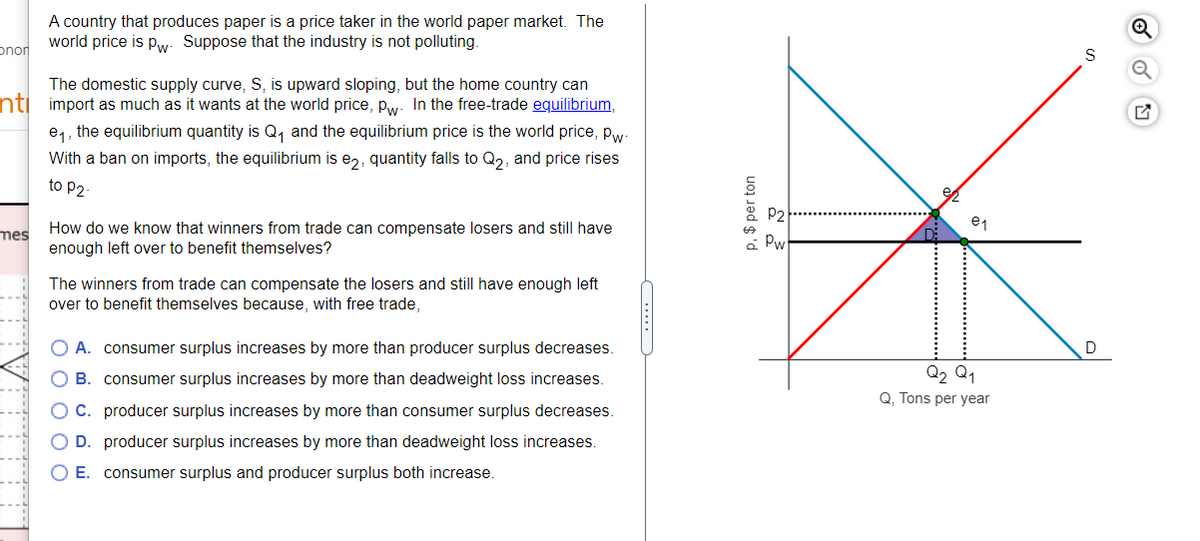
Transcribed Image Text:A country that produces paper is a price taker in the world paper market. The
world price is pw: Suppose that the industry is not polluting.
onor
The domestic supply curve, S, is upward sloping, but the home country can
nti import as much as it wants at the world price, pw. In the free-trade equilibrium,
e1, the equilibrium quantity is Q, and the equilibrium price is the world price, pw-
With a ban on imports, the equilibrium is e2, quantity falls to Q2, and price rises
to P2
P2
How do we know that winners from trade can compensate losers and still have
enough left over to benefit themselves?
mes
The winners from trade can compensate the losers and still have enough left
over to benefit themselves because, with free trade,
O A. consumer surplus increases by more than producer surplus decreases.
Q2 Q1
Q, Tons per year
O B. consumer surplus increases by more than deadweight loss increases.
O C. producer surplus increases by more than consumer surplus decreases.
O D. producer surplus increases by more than deadweight loss increases.
O E. consumer surplus and producer surplus both increase.
.....
p, $ per ton
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc



Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:
9781544336329
Author:
Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:
SAGE Publications, Inc



Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165912
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning