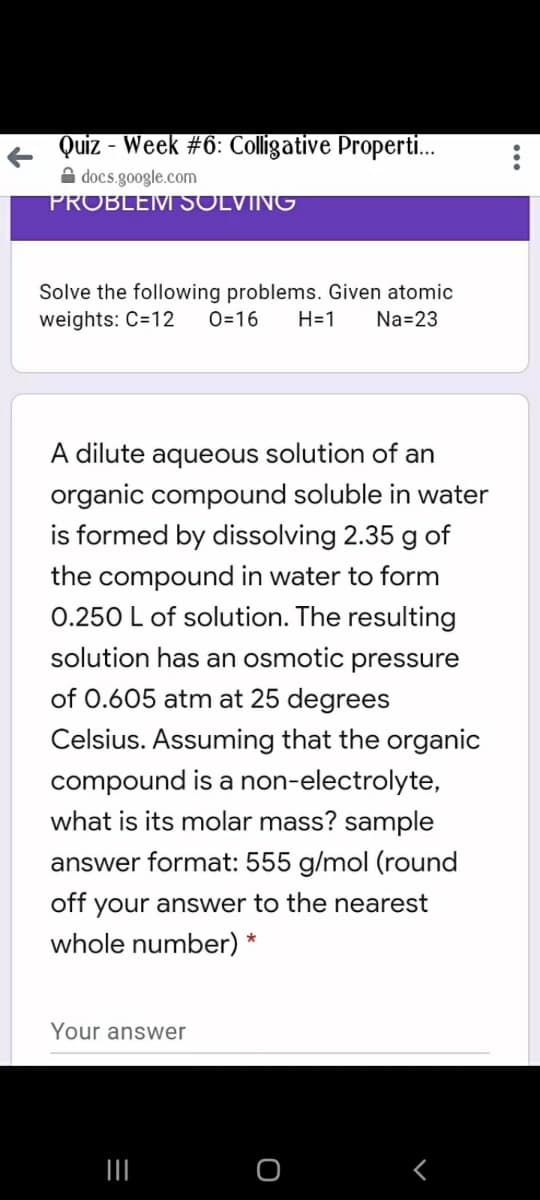
A dilute aqueous solution of an organic compound soluble in water is formed by dissolving 2.35 g of the compound in water to form 0.250 L of solution. The resulting solution has an osmotic pressure of 0.605 atm at 25 degrees Celsius. Assuming that the organic compound is a non-electrolyte, what is its molar mass? sample answer format: 555 g/mol (round off your answer to the nearest whole number) * Your answer
A dilute aqueous solution of an organic compound soluble in water is formed by dissolving 2.35 g of the compound in water to form 0.250 L of solution. The resulting solution has an osmotic pressure of 0.605 atm at 25 degrees Celsius. Assuming that the organic compound is a non-electrolyte, what is its molar mass? sample answer format: 555 g/mol (round off your answer to the nearest whole number) * Your answer
Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Chapter10: Solutions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 51QAP: A biochemist isolates a new protein and determines its molar mass by osmotic pressure measurements....
Related questions
Concept explainers
Question
100%
Help please asap thank you
Transcribed Image Text:Quiz - Week #6: Colligative Properti.
A docs.google.com
PROBLEMI SOLVING
Solve the following problems. Given atomic
weights: C=12
0=16
H=1
Na=23
A dilute aqueous solution of an
organic compound soluble in water
is formed by dissolving 2.35 g of
the compound in water to form
0.250 L of solution. The resulting
solution has an osmotic pressure
of 0.605 atm at 25 degrees
Celsius. Assuming that the organic
compound is a non-electrolyte,
what is its molar mass? sample
answer format: 555 g/mol (round
off your answer to the nearest
whole number) *
Your answer
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning