A food delivery service claims that it delivers orders to customers in 39.6 minutes or less, on average. However, many people report that their recent orders have taken much longer to arrive. A secret shopping firm would like to test the company's claim. The firm collected data from 243 randomly selected orders and found that the average delivery time was 39.86 minutes with a standard deviation of 5.66 minutes. Using a significance level of 0.5%, test the hypothesis that the average delivery time from this food delivery service is greater than 39.6 minutes. Use the critical value method.
A food delivery service claims that it delivers orders to customers in 39.6 minutes or less, on average. However, many people report that their recent orders have taken much longer to arrive. A secret shopping firm would like to test the company's claim. The firm collected data from 243 randomly selected orders and found that the average delivery time was 39.86 minutes with a standard deviation of 5.66 minutes. Using a significance level of 0.5%, test the hypothesis that the average delivery time from this food delivery service is greater than 39.6 minutes. Use the critical value method.
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:The standard hormat
Determine the critical value(s) for this hypothesis test. Round the solution(s) to four decimal places. If
more than one critical value exists, enter the solutions using a comma-separated list.
Determine the test statistic. Round the solution to four decimal places.
Determine the appropriate conclusion for this hypothesis test.
O The sample data provide sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis that the average food
delivery time from this company is 39.6 minutes or less and thus we conclude that average food
delivery time is likely greater than 39.6 minutes.
O The sample data provide sufficient evidence to reject the alternative hypothesis that the average
food delivery time is greater than 39.6 minutes and thus we conclude that the average food delivery
time from this company is 39.6 minutes or less, as advertised.
O The sample data do not provide sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis that the average
food delivery time from this company is 39.6 minutes or less and thus we conclude that average food
delivery time is likely 39.6 minutes or less, as advertised.
O The sample data do not provide sufficient evidence to reject the alternative hypothesis that the
average food delivery time is greater than 39.6 minutes and thus we conclude that the average food
delivery time from this company is likely greater than 39.6 minutes.
76°F
Mostly clear
R
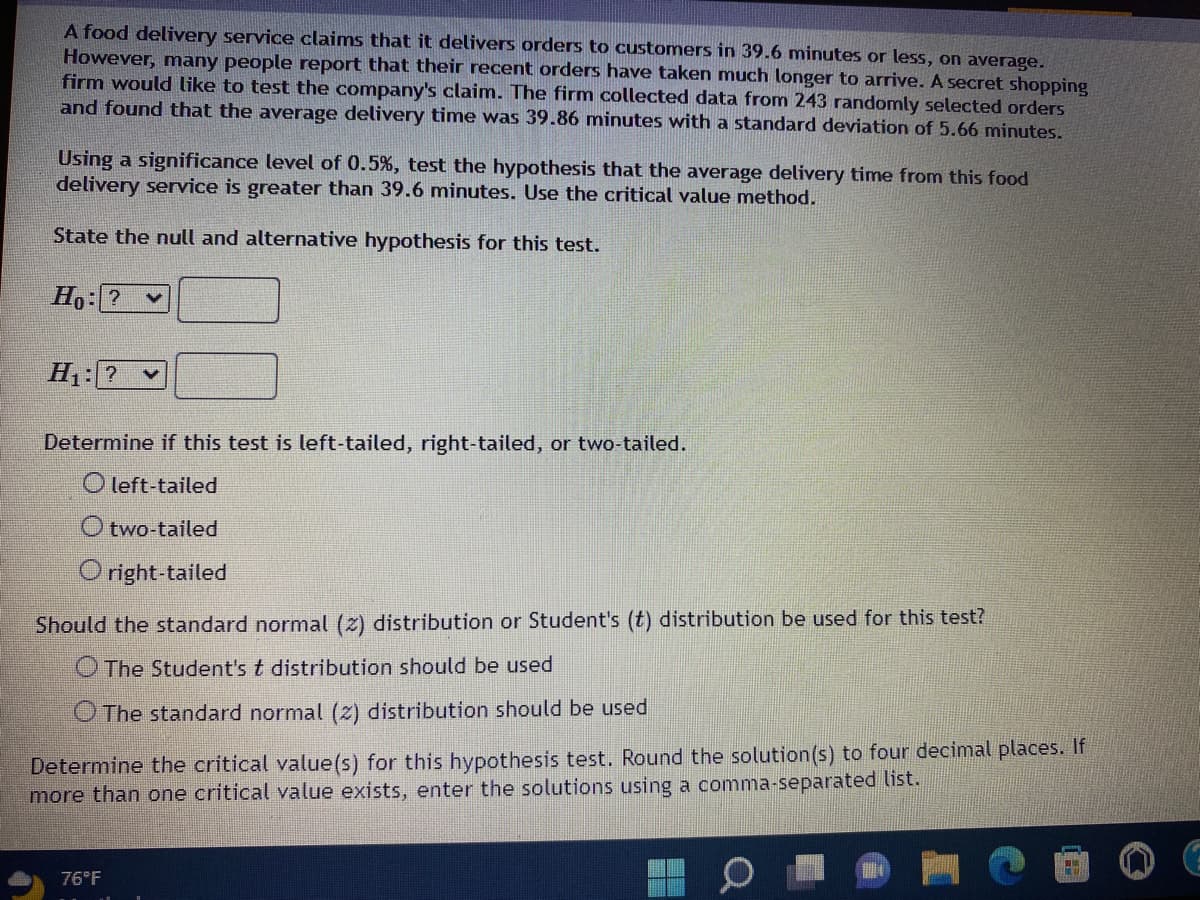
Transcribed Image Text:A food delivery service claims that it delivers orders to customers in 39.6 minutes or less, on average.
However, many people report that their recent orders have taken much longer to arrive. A secret shopping
firm would like to test the company's claim. The firm collected data from 243 randomly selected orders
and found that the average delivery time was 39.86 minutes with a standard deviation of 5.66 minutes.
Using a significance level of 0.5%, test the hypothesis that the average delivery time from this food
delivery service is greater than 39.6 minutes. Use the critical value method.
State the null and alternative hypothesis for this test.
Ho: ? V
H₁:?
Determine if this test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed.
O left-tailed
two-tailed
Oright-tailed
Should the standard normal (2) distribution or Student's (t) distribution be used for this test?
The Student's t distribution should be used
O The standard normal (2) distribution should be used
Determine the critical value(s) for this hypothesis test. Round the solution (s) to four decimal places. If
more than one critical value exists, enter the solutions using a comma-separated list.
76°F
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman