a) Ketoacid Z below can be synthesized from ethyl acetoacetate W via an acetoacetic ester synthesis. The B-ketoester W can be initially synthesized by Claisen condensation reaction of ester V. NaOEt NaOEt Base Ester V OEt CH,Br OEt | HO CH, Ketoacid Z i) Identify the structure of ester V. ii) Transformation of W to X and X to Y are alkylation reactions. Draw the structures of the intermediates X and Y. Determine a suitable base for the conversion of X to Y. iii) With regards to the formation of the ketoacid Z from Y, show the steps involved in the reaction by giving the appropriate intermediates, reagents and reaction conditions. iv) Explain why only one of the carbonyl groups in Y is lost as carbon dioxide gas.
a) Ketoacid Z below can be synthesized from ethyl acetoacetate W via an acetoacetic ester synthesis. The B-ketoester W can be initially synthesized by Claisen condensation reaction of ester V. NaOEt NaOEt Base Ester V OEt CH,Br OEt | HO CH, Ketoacid Z i) Identify the structure of ester V. ii) Transformation of W to X and X to Y are alkylation reactions. Draw the structures of the intermediates X and Y. Determine a suitable base for the conversion of X to Y. iii) With regards to the formation of the ketoacid Z from Y, show the steps involved in the reaction by giving the appropriate intermediates, reagents and reaction conditions. iv) Explain why only one of the carbonyl groups in Y is lost as carbon dioxide gas.
Chapter23: Carbonyl Condensation Reactions
Section23.SE: Something Extra
Problem 73AP
Related questions
Question
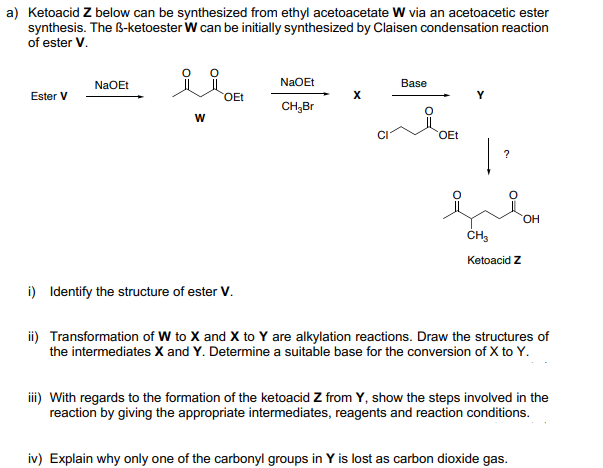
Transcribed Image Text:a) Ketoacid Z below can be synthesized from ethyl acetoacetate W via an acetoacetic ester
synthesis. The B-ketoester W can be initially synthesized by Claisen condensation reaction
of ester V.
NaOEt
NaOEt
Base
Ester V
OEt
CH,Br
OEt
|
HO
CH,
Ketoacid Z
i) Identify the structure of ester V.
ii) Transformation of W to X and X to Y are alkylation reactions. Draw the structures of
the intermediates X and Y. Determine a suitable base for the conversion of X to Y.
iii) With regards to the formation of the ketoacid Z from Y, show the steps involved in the
reaction by giving the appropriate intermediates, reagents and reaction conditions.
iv) Explain why only one of the carbonyl groups in Y is lost as carbon dioxide gas.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning