A light spring with a spring constant k = 370 N/m is attached to a vertical wall at one end and a block with a mass m = 0.582 kg at the other end. The block rests on a horizontal frictionless surface and is initially at the equilibrium length of the spring. The block is then displaced from the equilibrium position of the spring in such a manner as to stretch the spring by an amount A = 0.110 m and then released. As the block oscillates about the equilibrium position, determine the amount of work done on the block by the spring for the following segments of travel. (a) the block traveling from the equilibrium position (x = 0) to the position x = A (Enter your answer to at least two decimal places.) Wo-A (b) the block traveling from the position x = A to the equilibrium position (x = 0) (Enter your answer to at least two decimal places.) WA -o- (c) the round trip from the equilibrium position (x = 0) to the position x = A and then back to the equilibrium position Wo -A-0 Additional Materials O eBook Tutorial
A light spring with a spring constant k = 370 N/m is attached to a vertical wall at one end and a block with a mass m = 0.582 kg at the other end. The block rests on a horizontal frictionless surface and is initially at the equilibrium length of the spring. The block is then displaced from the equilibrium position of the spring in such a manner as to stretch the spring by an amount A = 0.110 m and then released. As the block oscillates about the equilibrium position, determine the amount of work done on the block by the spring for the following segments of travel. (a) the block traveling from the equilibrium position (x = 0) to the position x = A (Enter your answer to at least two decimal places.) Wo-A (b) the block traveling from the position x = A to the equilibrium position (x = 0) (Enter your answer to at least two decimal places.) WA -o- (c) the round trip from the equilibrium position (x = 0) to the position x = A and then back to the equilibrium position Wo -A-0 Additional Materials O eBook Tutorial
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Katz, Debora M.
Chapter16: Oscillations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 77PQ: A lightweight spring with spring constant k = 225 N/m is attached to a block of mass m1 = 4.50 kg on...
Related questions
Question
100%
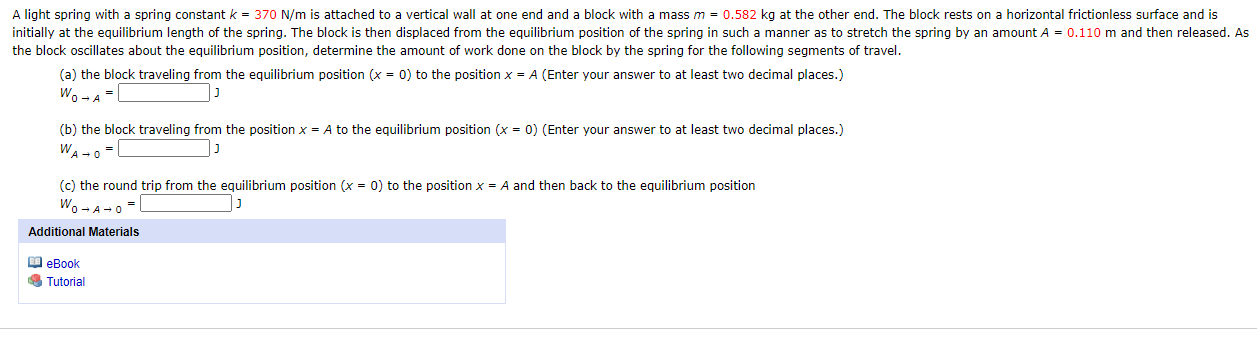
Transcribed Image Text:A light spring with a spring constant k = 370 N/m is attached to a vertical wall at one end and a block with a mass m = 0.582 kg at the other end. The block rests on a horizontal frictionless surface and is
initially at the equilibrium length of the spring. The block is then displaced from the equilibrium position of the spring in such a manner as to stretch the spring by an amount A = 0.110 m and then released. As
the block oscillates about the equilibrium position, determine the amount of work done on the block by the spring for the following segments of travel.
(a) the block traveling from the equilibrium position (x = 0) to the position x = A (Enter your answer to at least two decimal places.)
Wo-A
(b) the block traveling from the position x = A to the equilibrium position (x = 0) (Enter your answer to at least two decimal places.)
WA -o-
(c) the round trip from the equilibrium position (x = 0) to the position x = A and then back to the equilibrium position
Wo -A-0
Additional Materials
O eBook
Tutorial
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning