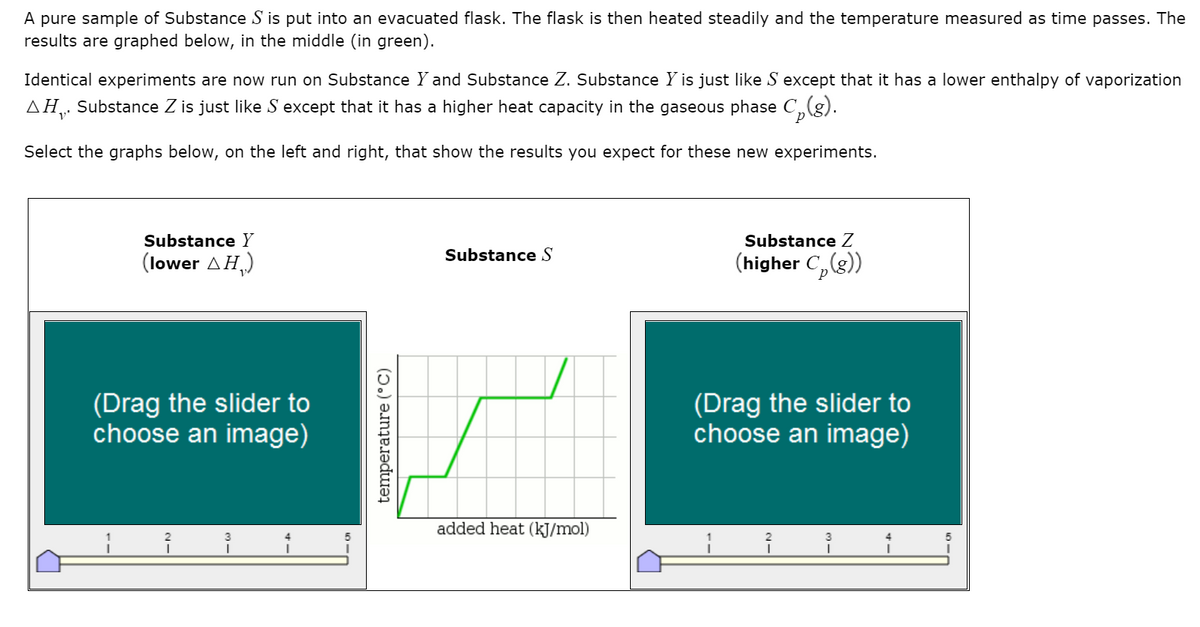
A pure sample of Substance S is put into an evacuated flask. The flask is then heated steadily and the temperature measured as time passes. The results are graphed below, in the middle (in green). Identical experiments are now run on Substance Y and Substance Z. Substance Y is just like S except that it has a lower enthalpy of vaporization AH. Substance Z is just like S except that it has a higher heat capacity in the gaseous phase C„(g). Select the graphs below, on the left and right, that show the results you expect for these new experiments.
States of Matter
The substance that constitutes everything in the universe is known as matter. Matter comprises atoms which in turn are composed of electrons, protons, and neutrons. Different atoms combine together to give rise to molecules that act as a foundation for all kinds of substances. There are five states of matter based on their energies of attraction, namely solid, liquid, gases, plasma, and BEC (Bose-Einstein condensates).
Chemical Reactions and Equations
When a chemical species is transformed into another chemical species it is said to have undergone a chemical reaction. It consists of breaking existing bonds and forming new bonds by changing the position of electrons. These reactions are best explained using a chemical equation.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images









