A realtor wants to compare the mean sales-to-appraisal ratios of residential properties sold in four neighborhoods (A, B, C, and D). Four properties are randomly selected from each neighborhood and the ratios recorded for each, as shown below. A: 1.2, 1.1, 0.9, 0.4 B: 2.5, 2.1, 1.9, 1.6 C: 1.0, 1.5, 1.1, 1.3 D: 0.8, 1.3, 1.1, 0.7 Interpret the results of the analysis summarized in the following table: Source df SS MS F PR >F Neighborhoods Error 3.1819 1.0606 10.76 0.001 12 Total 4.3644 Referring to Table 10-17, what should be the decision for the Levene's test for homogeneity of variances at a 5% level of significance? Seleccione una: O A. Reject the null hypothesis because the p-value is smaller than the level of significance. OB. Reject the null hypothesis because the p-value is larger than the level of significance. Oc. Do not reject the null hypothesis because the p-value is larger than the level of significance. OD. Do not reject the null hypothesis because the p-value is smaller than the level of significance.
A realtor wants to compare the mean sales-to-appraisal ratios of residential properties sold in four neighborhoods (A, B, C, and D). Four properties are randomly selected from each neighborhood and the ratios recorded for each, as shown below. A: 1.2, 1.1, 0.9, 0.4 B: 2.5, 2.1, 1.9, 1.6 C: 1.0, 1.5, 1.1, 1.3 D: 0.8, 1.3, 1.1, 0.7 Interpret the results of the analysis summarized in the following table: Source df SS MS F PR >F Neighborhoods Error 3.1819 1.0606 10.76 0.001 12 Total 4.3644 Referring to Table 10-17, what should be the decision for the Levene's test for homogeneity of variances at a 5% level of significance? Seleccione una: O A. Reject the null hypothesis because the p-value is smaller than the level of significance. OB. Reject the null hypothesis because the p-value is larger than the level of significance. Oc. Do not reject the null hypothesis because the p-value is larger than the level of significance. OD. Do not reject the null hypothesis because the p-value is smaller than the level of significance.
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.3: Measures Of Spread
Problem 21PFA
Related questions
Question
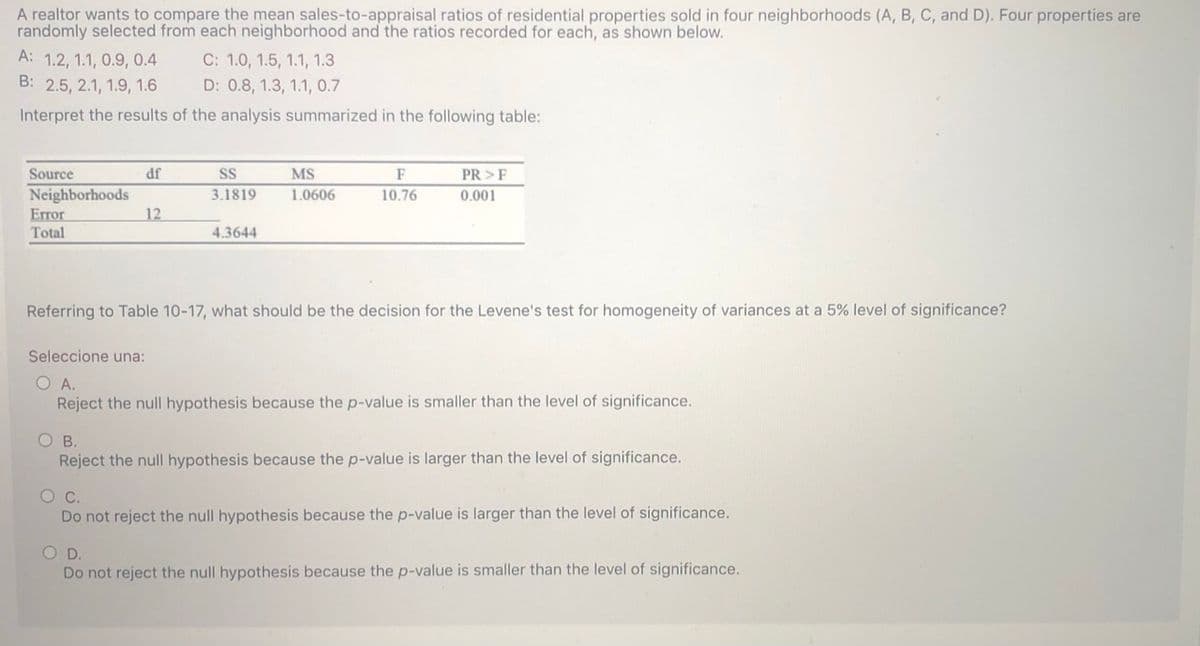
Transcribed Image Text:A realtor wants to compare the mean sales-to-appraisal ratios of residential properties sold in four neighborhoods (A, B, C, and D). Four properties are
randomly selected from each neighborhood and the ratios recorded for each, as shown below.
A: 1.2, 1.1, 0.9, 0.4
B: 2.5, 2.1, 1.9, 1.6
C: 1.0, 1.5, 1.1, 1.3
D: 0.8, 1.3, 1.1, 0.7
Interpret the results of the analysis summarized in the following table:
Source
df
SS
MS
F
PR >F
Neighborhoods
Error
Total
3.1819
1.0606
10.76
0.001
12
4.3644
Referring to Table 10-17, what should be the decision for the Levene's test for homogeneity of variances at a 5% level of significance?
Seleccione una:
O A.
Reject the null hypothesis because the p-value is smaller than the level of significance.
OB.
Reject the null hypothesis because the p-value is larger than the level of significance.
Oc.
Do not reject the null hypothesis because the p-value is larger than the level of significance.
OD.
Do not reject the null hypothesis because the p-value is smaller than the level of significance.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill