A round steel alloy bar with a diameter of 19mm and a gauge length of 76mm was subjected to tension, with the results shown in Table. Using a computer spreadsheet program, plot the stress–strain relationship. From the graph, determine the Young’s modulus of the steel alloy and the deformation corresponding to a 37kN load.
A round steel alloy bar with a diameter of 19mm and a gauge length of 76mm was subjected to tension, with the results shown in Table.
Using a computer spreadsheet program, plot the stress–strain relationship. From the graph, determine the Young’s modulus of the steel alloy and the deformation corresponding to a 37kN load.
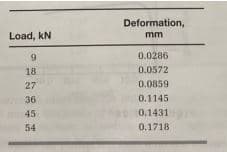
Given data:
Diameter of round steel alloy bar = D = 19 mm
Gauge length = L = 76 mm
Area of steel bar is calculated as:
Now, stress in the bar for a load of 9 kN is calculated as:'
Stress for loads are calculated as follows:
Now, the strain is calculated as:
As per the values of deformation given in the table, the strain corresponding to different deformations is calculated as:
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images









