A set of final examination grades in an introductory statistics course is normally distributed, with a mean of 77 and a standard deviation of 9. Complete parts (a) through (d). (Round to four decimal places as needed.) c. The probability is 15% that a student taking the test scores higher than what grade? The probability is 15% that a student taking the test scores higher than 86. (Round to the nearest integer as needed.) d. If the professor grades on a curve (for example, the professor could give A's to the top 10% of the class, regardless of the score), is a student better off with a grade of 95 on the exam with a mean of 77 and a standard deviation of 9 or a grade of 70 on a different exam, where the mean is 66 and the standard deviation is 4? Show your answer statistically and explain. A student is better off with a grade of 95 on the exam with a mean of 77 and a standard deviation of 9 because the Z value for the grade of 95 is 2.00 and the Z value for the grade of 70 on the different exam is 1.00. (Round to two decimal places as needed.)
A set of final examination grades in an introductory statistics course is normally distributed, with a mean of 77 and a standard deviation of 9. Complete parts (a) through (d). (Round to four decimal places as needed.) c. The probability is 15% that a student taking the test scores higher than what grade? The probability is 15% that a student taking the test scores higher than 86. (Round to the nearest integer as needed.) d. If the professor grades on a curve (for example, the professor could give A's to the top 10% of the class, regardless of the score), is a student better off with a grade of 95 on the exam with a mean of 77 and a standard deviation of 9 or a grade of 70 on a different exam, where the mean is 66 and the standard deviation is 4? Show your answer statistically and explain. A student is better off with a grade of 95 on the exam with a mean of 77 and a standard deviation of 9 because the Z value for the grade of 95 is 2.00 and the Z value for the grade of 70 on the different exam is 1.00. (Round to two decimal places as needed.)
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.4: Distributions Of Data
Problem 19PFA
Related questions
Question
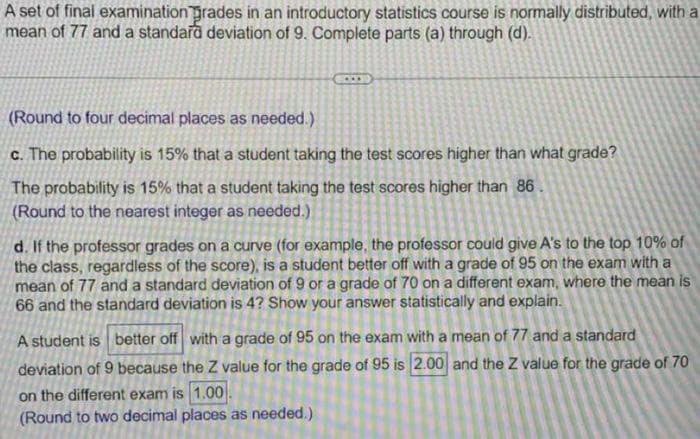
Transcribed Image Text:A set of final examination grades in an introductory statistics course is normally distributed, with a
mean of 77 and a standard deviation of 9. Complete parts (a) through (d).
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
c. The probability is 15% that a student taking the test scores higher than what grade?
The probability is 15% that a student taking the test scores higher than 86.
(Round to the nearest integer as needed.)
d. If the professor grades on a curve (for example, the professor could give A's to the top 10% of
the class, regardless of the score), is a student better off with a grade of 95 on the exam with a
mean of 77 and a standard deviation of 9 or a grade of 70 on a different exam, where the mean is
66 and the standard deviation is 4? Show your answer statistically and explain.
A student is better off with a grade of 95 on the exam with a mean of 77 and a standard
deviation of 9 because the Z value for the grade of 95 is 2.00 and the Z value for the grade of 70
on the different exam is 1.00.
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill