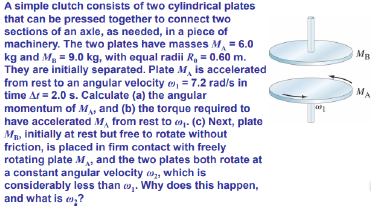
A simple clutch consists of two cylindrical plates that can be pressed together to connect two sections of an axle, as needed, in a piece of machinery. The two plates have masses M, = 6.0 kg and M. = 9.0 kg, with equal radii R, = 0.60 m. They are initially separated. Plate M, is accelerated from rest to an angular velocity e», = 7.2 rad/s in time Ar = 2.0 s. Calculate (a) the angular momentum of M, and (b) the torque required to have accelerated M, from rest to 9- (c) Next, plate Mg, initially at rest but free to rotate without friction, is placed in firm contact with freely rotating plate M, and the two plates both rotate at a constant angular velocity o, which is considerably less than o. Why does this happen, and what is e,?
Rigid Body
A rigid body is an object which does not change its shape or undergo any significant deformation due to an external force or movement. Mathematically speaking, the distance between any two points inside the body doesn't change in any situation.
Rigid Body Dynamics
Rigid bodies are defined as inelastic shapes with negligible deformation, giving them an unchanging center of mass. It is also generally assumed that the mass of a rigid body is uniformly distributed. This property of rigid bodies comes in handy when we deal with concepts like momentum, angular momentum, force and torque. The study of these properties – viz., force, torque, momentum, and angular momentum – of a rigid body, is collectively known as rigid body dynamics (RBD).
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images








