A solid tungsten block of mass m is pressed against a spring of force constant k. As a result, the spring is compressed a distance x. The spring then expands and pushes the block to the right. The block, therefore, slides up the incline and eventually stops. If we repeat this activity but this time compress the spring a distance of 2x- k m Smooth Smooth
A solid tungsten block of mass m is pressed against a spring of force constant k. As a result, the spring is compressed a distance x. The spring then expands and pushes the block to the right. The block, therefore, slides up the incline and eventually stops. If we repeat this activity but this time compress the spring a distance of 2x- k m Smooth Smooth
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Katz, Debora M.
Chapter11: Collisions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 22PQ: In a laboratory experiment, 1 a block of mass M is placed on a frictionless table at the end of a...
Related questions
Question
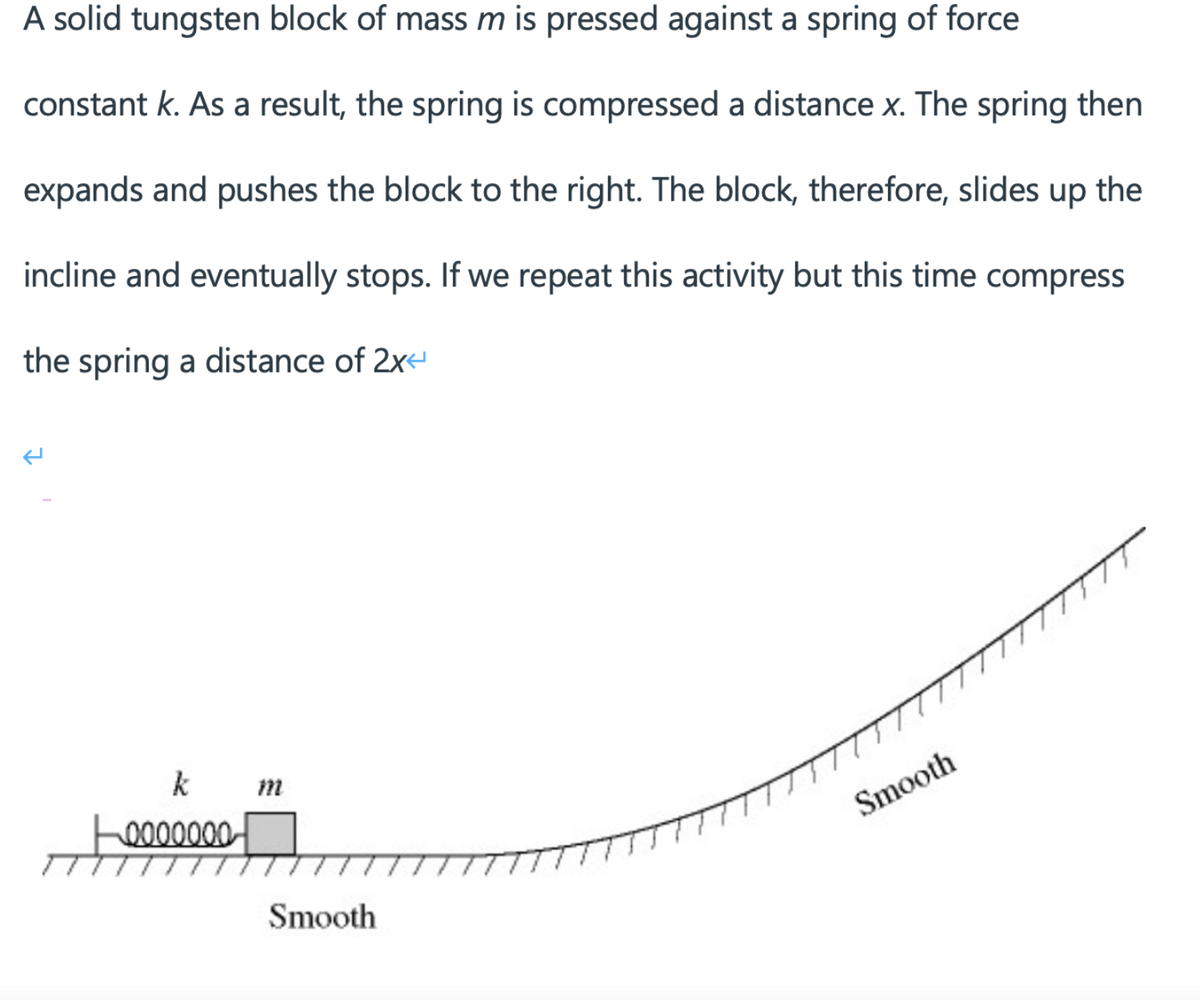
Transcribed Image Text:A solid tungsten block of mass m is pressed against a spring of force
constant k. As a result, the spring is compressed a distance x. The spring then
expands and pushes the block to the right. The block, therefore, slides up the
incline and eventually stops. If we repeat this activity but this time compress
the spring a distance of 2x
k
m
0000000-
Smooth
Smooth

Transcribed Image Text:A. just as it moves free of the spring, the box will be traveling four times as
fast as before.4
B. just as it moves free of the spring, the box will have twice as much kinetic
energy as before.
C. just before it is released, the box has twice as much elastic potential energy
as before.
D. the box will go up the incline twice as high as before.
E. just as it moves free of the spring, the box willI be traveling twice as fast as
before.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning