A student having partly adopted the methodology used by Steven D. Levitt attempts to estimate the impact of prison population (PP), on violent crime rate (UCK) across 20 contiguous states in the U.S with the highest crime rates. He uses the number of ongoing trials (Trials) as an instrument to remove simultaneity between prison population and violent crime rate. Verdicts in ongoing trials affect the prison population but are unlikely to be related to the violent crime rate, except through thei effect on prison population. PP measures the per capita prisoners held in state prisons as on December 31, 2015. UCR is measured in violent and property crimes indexes; i.e., per capita rate of violent and property crimes reported to the police, as compiled in the FBI's Uniform Crime Reports. Trials is measured by the number of ongoing trials where the jury had not reached a verdict as on December 31, 2015. The student estimates the following second stage regression equation: UCR=0.0032-0.72PP. (0.0003) (0.42)
A student having partly adopted the methodology used by Steven D. Levitt attempts to estimate the impact of prison population (PP), on violent crime rate (UCK) across 20 contiguous states in the U.S with the highest crime rates. He uses the number of ongoing trials (Trials) as an instrument to remove simultaneity between prison population and violent crime rate. Verdicts in ongoing trials affect the prison population but are unlikely to be related to the violent crime rate, except through thei effect on prison population. PP measures the per capita prisoners held in state prisons as on December 31, 2015. UCR is measured in violent and property crimes indexes; i.e., per capita rate of violent and property crimes reported to the police, as compiled in the FBI's Uniform Crime Reports. Trials is measured by the number of ongoing trials where the jury had not reached a verdict as on December 31, 2015. The student estimates the following second stage regression equation: UCR=0.0032-0.72PP. (0.0003) (0.42)
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter7: Distance And Approximation
Section7.3: Least Squares Approximation
Problem 31EQ
Related questions
Question
4
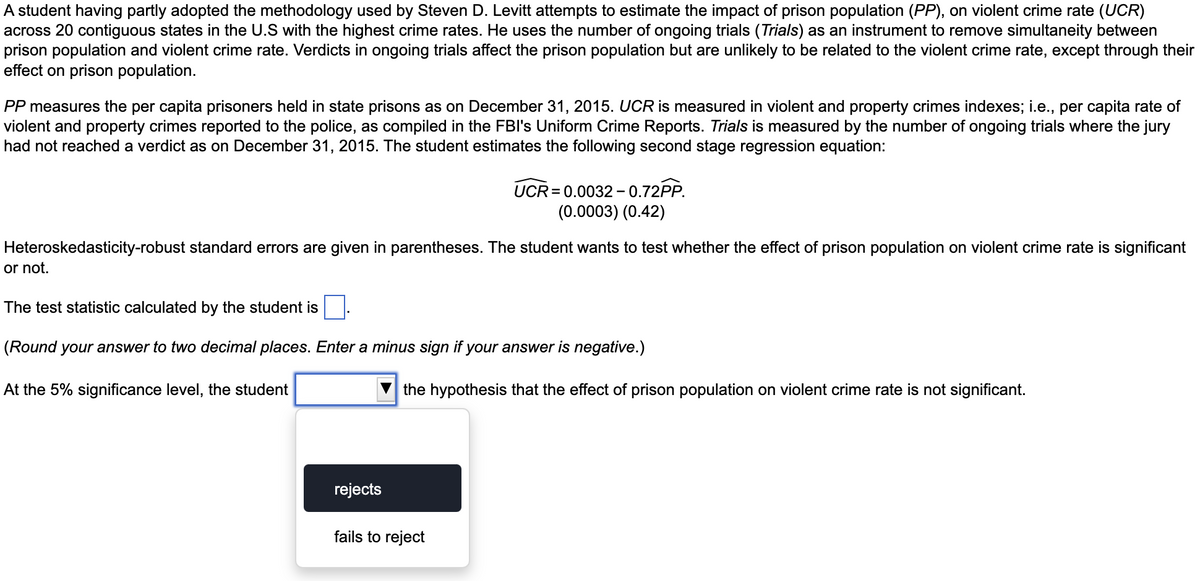
Transcribed Image Text:A student having partly adopted the methodology used by Steven D. Levitt attempts to estimate the impact of prison population (PP), on violent crime rate (UCR)
across 20 contiguous states in the U.S with the highest crime rates. He uses the number of ongoing trials (Trials) as an instrument to remove simultaneity between
prison population and violent crime rate. Verdicts in ongoing trials affect the prison population but are unlikely to be related to the violent crime rate, except through their
effect on prison population.
PP measures the per capita prisoners held in state prisons as on December 31, 2015. UCR is measured in violent and property crimes indexes; i.e., per capita rate of
violent and property crimes reported to the police, as compiled in the FBI's Uniform Crime Reports. Trials is measured by the number of ongoing trials where the jury
had not reached a verdict as on December 31, 2015. The student estimates the following second stage regression equation:
UCR=0.0032-0.72PP.
(0.0003) (0.42)
Heteroskedasticity-robust standard errors are given in parentheses. The student wants to test whether the effect of prison population on violent crime rate is significant
or not.
The test statistic calculated by the student is
(Round your answer to two decimal places. Enter a minus sign if your answer is negative.)
At the 5% significance level, the student
the hypothesis that the effect of prison population on violent crime rate is not significant.
rejects
fails to reject
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill