(a) The diagram below on the right-hand side illustrates the polar Asp(a94)... Asn (102) interaction that stabilizes the R (oxy) conformation of human hemoglobin (HbA). This sidechain inter- action underlies the allosteric, structural transition of hemoglobin and helps to maintain its tetramer structure. In the table below the properties of several mutants of hemoglobin involving the a94 position are compared at pH ~ 7.4.
(a) The diagram below on the right-hand side illustrates the polar Asp(a94)... Asn (102) interaction that stabilizes the R (oxy) conformation of human hemoglobin (HbA). This sidechain inter- action underlies the allosteric, structural transition of hemoglobin and helps to maintain its tetramer structure. In the table below the properties of several mutants of hemoglobin involving the a94 position are compared at pH ~ 7.4.
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
15th Edition
ISBN:9781337408332
Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Chapter9: From Dna To Protein
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5SQ: The main function of a DNA molecule is to ________ . a. store heritable information b. carry a...
Related questions
Question
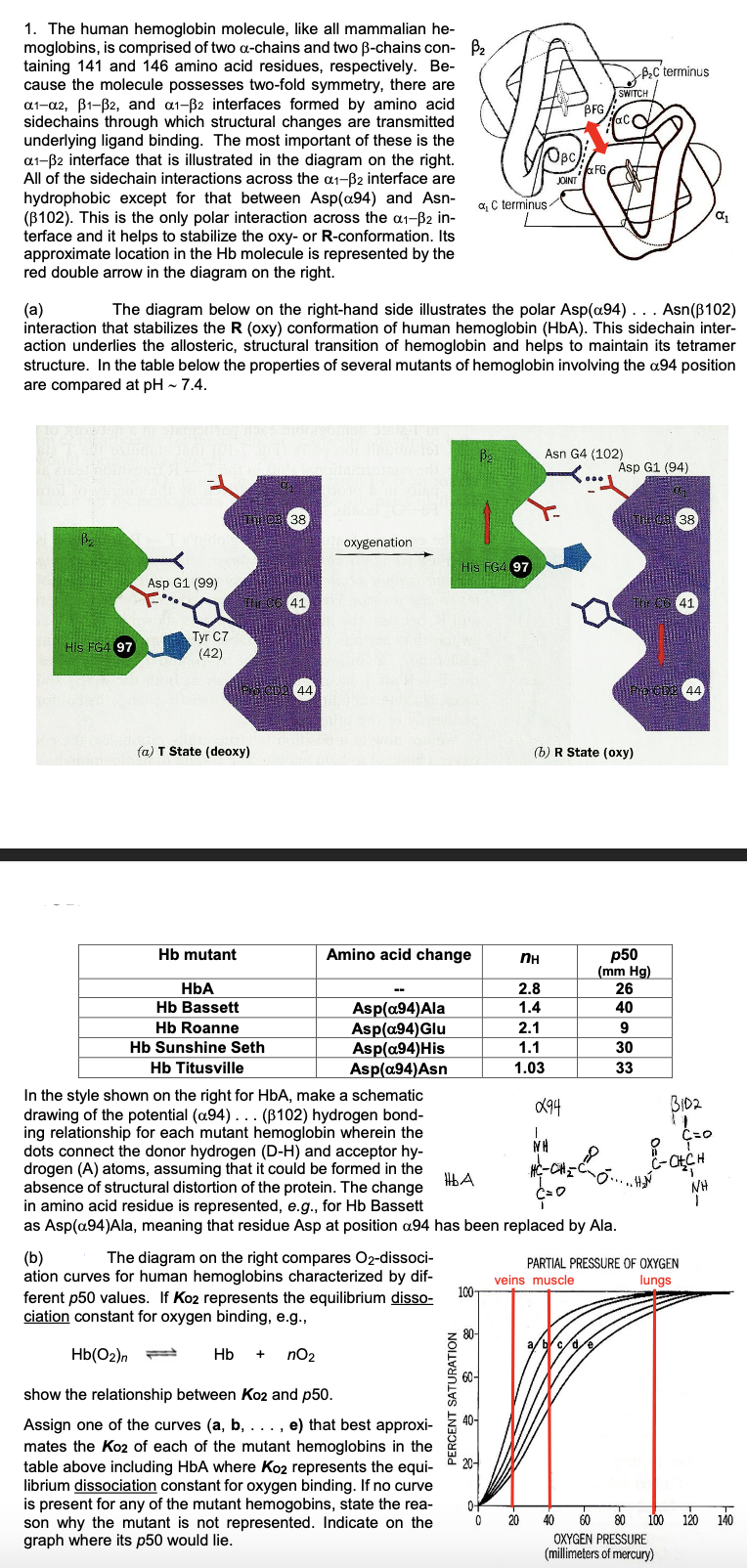
Transcribed Image Text:1. The human hemoglobin molecule, like all mammalian he-
moglobins, is comprised of two a-chains and two ß-chains con- ₂
taining 141 and 146 amino acid residues, respectively. Be-
cause the molecule possesses two-fold symmetry, there are
a1-a2, B1-B2, and a1-B2 interfaces formed by amino acid
sidechains through which structural changes are transmitted
underlying ligand binding. The most important of these is the
a1-B2 interface that is illustrated in the diagram on the right.
All of the sidechain interactions across the a1-B2 interface are
hydrophobic except for that between Asp(a94) and Asn-
(B102). This is the only polar interaction across the α1-³2 in-
terface and it helps to stabilize the oxy- or R-conformation. Its
approximate location in the Hb molecule is represented by the
red double arrow in the diagram on the right.
His FG4 97
Asp G1 (99)
Tyr C7
(42)
Hb mutant
(a) T State (deoxy)
95
The C6 41
(a)
The diagram below on the right-hand side illustrates the polar Asp(a94). . . Asn (102)
interaction that stabilizes the R (oxy) conformation of human hemoglobin (HbA). This sidechain inter-
action underlies the allosteric, structural transition of hemoglobin and helps to maintain its tetramer
structure. In the table below the properties of several mutants of hemoglobin involving the a94 position
are compared at pH ~ 7.4.
38
POTCDA 44
HbA
Hb Bassett
Hb Roanne
Hb Sunshine Seth
oxygenation
Amino acid change
Asp(a94)Ala
Asp(a94) Glu
Asp(a94) His
Asp(a94)Asn
(b)
The diagram on the right compares O2-dissoci-
ation curves for human hemoglobins characterized by dif-
ferent p50 values. If Ko2 represents the equilibrium disso-
ciation constant for oxygen binding, e.g.,
Hb(02)n
Hb + nO₂
show the relationship between Ko2 and p50.
Assign one of the curves (a, b, . . . , e) that best approxi-
mates the Ko2 of each of the mutant hemoglobins in the
table above including HbA where Ko2 represents the equi-
librium dissociation constant for oxygen binding. If no curve
is present for any of the mutant hemogobins, state the rea-
son why the mutant is not represented. Indicate on the
graph where its p50 would lie.
a C terminus
His FG4 97
HbA
PERCENT SATURATION
B₂
OBC
100-
JOINT
nн
2.8
1.4
2.1
1.1
1.03
0-
0 20
BFG
FG
Asn G4 (102)
Hb Titusville
In the style shown on the right for HbA, make a schematic
drawing of the potential (a94)... (B102) hydrogen bond-
ing relationship for each mutant hemoglobin wherein the
dots connect the donor hydrogen (D-H) and acceptor hy-
drogen (A) atoms, assuming that it could be formed in the
absence of structural distortion of the protein. The change
in amino acid residue is represented, e.g., for Hb Bassett
as Asp(a94)Ala, meaning that residue Asp at position a94 has been replaced by Ala.
094
WH
HỆ CHÍ
SWITCH
(b) R State (oxy)
a/b/c/d/e
Asp G1 (94)
01
B₂C terminus
The CG 41
p50
(mm Hg)
26
40
9
30
33
38
CDP 44
BID2
PARTIAL PRESSURE OF OXYGEN
veins muscle
lungs
C=O
8
C-CH₂CH
NH
α₁
40 60 80 100 120 140
OXYGEN PRESSURE
(millimeters of mercury)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap…
Biology
ISBN:
9781337408332
Author:
Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap…
Biology
ISBN:
9781337408332
Author:
Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax