(a) Write equations for the internal forces at J (axial (F), shear (V), and bending (M)) in terms of only P and a. (b) Graph your equations as functions of P, using a = 45°, from 0
(a) Write equations for the internal forces at J (axial (F), shear (V), and bending (M)) in terms of only P and a. (b) Graph your equations as functions of P, using a = 45°, from 0
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning with these NEW titles from Engineering!)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Chapter5: Analysis Of Convection Heat Transfer
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5.8P
Related questions
Question
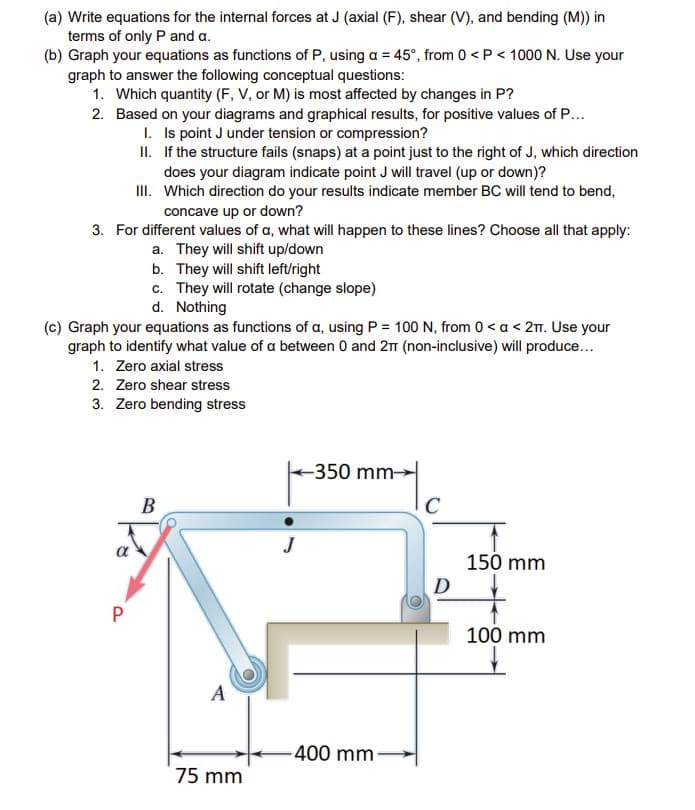
Transcribed Image Text:(a) Write equations for the internal forces at J (axial (F), shear (V), and bending (M)) in
terms of only P and a.
(b) Graph your equations as functions of P, using a = 45°, from 0 < P < 1000 N. Use your
graph to answer the following conceptual questions:
1. Which quantity (F, V, or M) is most affected by changes in P?
2. Based on your diagrams and graphical results, for positive values of P...
I.
Is point J under tension or compression?
II.
If the structure fails (snaps) at a point just to the right of J, which direction
does your diagram indicate point J will travel (up or down)?
III.
Which direction do your results indicate member BC will tend to bend,
concave up or down?
3. For different values of a, what will happen to these lines? Choose all that apply:
a. They will shift up/down
b. They will shift left/right
c. They will rotate (change slope)
d. Nothing
(c) Graph your equations as functions of a, using P = 100 N, from 0 < a < 2π. Use your
graph to identify what value of a between 0 and 2π (non-inclusive) will produce...
1. Zero axial stress
2. Zero shear stress
3. Zero bending stress
α
P
B
A
75 mm
J
-350 mm-
400 mm-
C
D
150 mm.
100 mm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 11 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning