a. Applying the MSE measure of forecast accuracy, would you prefer a smoothing constant of a 0.1 or a = 0.2 for the gasoline sales time series? Do not round your interim computations and round your final answers to three decimal places. a = 0.1 a = 0.2 MSE Prefer: b. Are the results the same if you apply MAE as the measure of accuracy? Do not round your interim computations and round your final answers to three decimal places. a = 0.1 a = 0.2 MAE Prefer: c. What are the results if MAPE is used? Do not round your interim computations and round your final answers to two decimal places. a = 0.1 a = 0.2 MAPE Prefer: % %
a. Applying the MSE measure of forecast accuracy, would you prefer a smoothing constant of a 0.1 or a = 0.2 for the gasoline sales time series? Do not round your interim computations and round your final answers to three decimal places. a = 0.1 a = 0.2 MSE Prefer: b. Are the results the same if you apply MAE as the measure of accuracy? Do not round your interim computations and round your final answers to three decimal places. a = 0.1 a = 0.2 MAE Prefer: c. What are the results if MAPE is used? Do not round your interim computations and round your final answers to two decimal places. a = 0.1 a = 0.2 MAPE Prefer: % %
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter4: Eigenvalues And Eigenvectors
Section4.6: Applications And The Perron-frobenius Theorem
Problem 25EQ
Related questions
Question
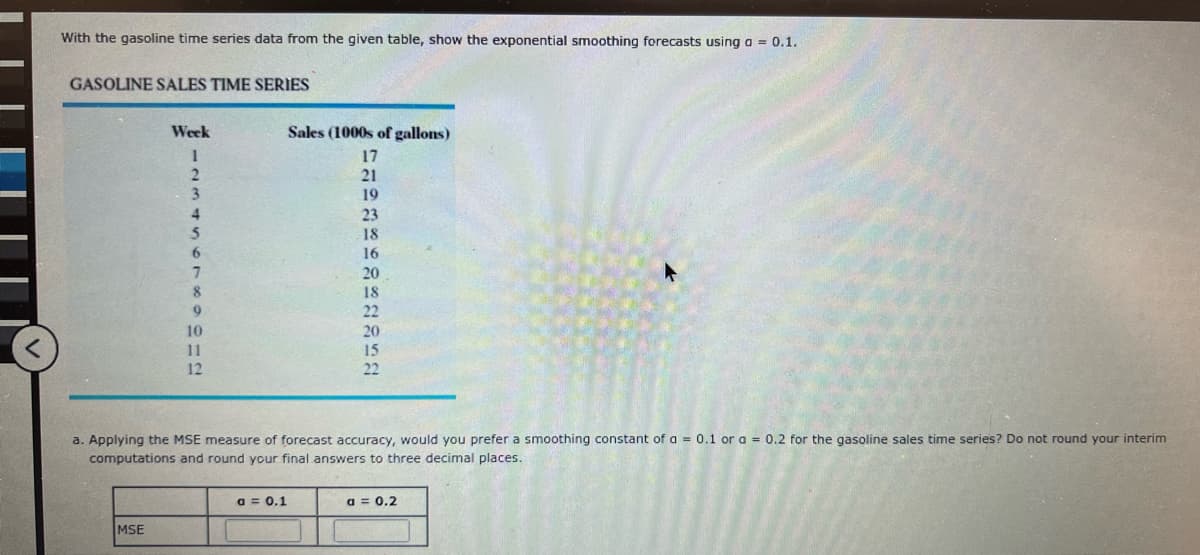
Transcribed Image Text:With the gasoline time series data from the given table, show the exponential smoothing forecasts using a = 0.1.
GASOLINE SALES TIME SERIES
Week
Sales (1000s of gallons)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
a. Applying the MSE measure of forecast accuracy, would you prefer a smoothing constant of a = 0.1 or a = 0.2 for the gasoline sales time series? Do not round your interim
computations and round your final answers to three decimal places.
a = 0.1
a = 0.2
MSE
S723BE132852
19
16
20
20
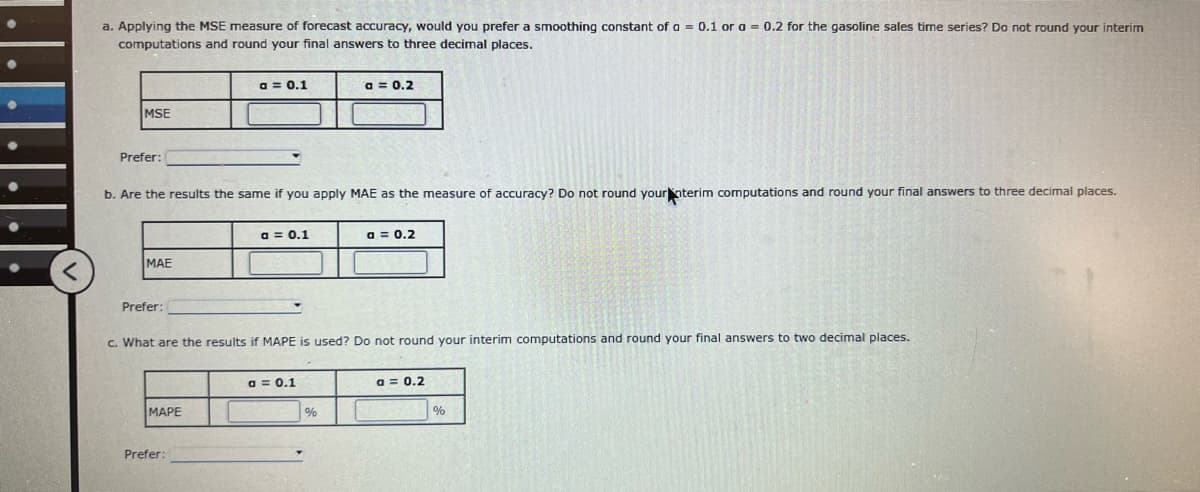
Transcribed Image Text:a. Applying the MSE measure of forecast accuracy, would you prefer a smoothing constant of a = 0.1 or a = 0.2 for the gasoline sales time series? Do not round your interim
computations and round your final answers to three decimal places.
a = 0.1
a = 0.2
MSE
Prefer:
b. Are the results the same if you apply MAE as the measure of accuracy? Do not round your interim computations and round your final answers to three decimal places.
a = 0.1
a = 0.2
MAE
Prefer:
c. What are the results if MAPE is used? Do not round your interim computations and round your final answers to two decimal places.
a = 0.1
a = 0.2
MAPE
Prefer:
%
%
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage