a. Calculate the SST. SST= (Round to three decimal places as needed.). b. Partition the total sum of squares into the SSR and SSE. SSR= SSE = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) c. Calculate the sample coefficient of determination. R²=0 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) d. Test the significance of the population coefficient of determination using a = 0.05. Choogo th wor holow
a. Calculate the SST. SST= (Round to three decimal places as needed.). b. Partition the total sum of squares into the SSR and SSE. SSR= SSE = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) c. Calculate the sample coefficient of determination. R²=0 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) d. Test the significance of the population coefficient of determination using a = 0.05. Choogo th wor holow
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337111348
Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Chapter3: Straight Lines And Linear Functions
Section3.CR: Chapter Review Exercises
Problem 15CR: Life Expectancy The following table shows the average life expectancy, in years, of a child born in...
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:K
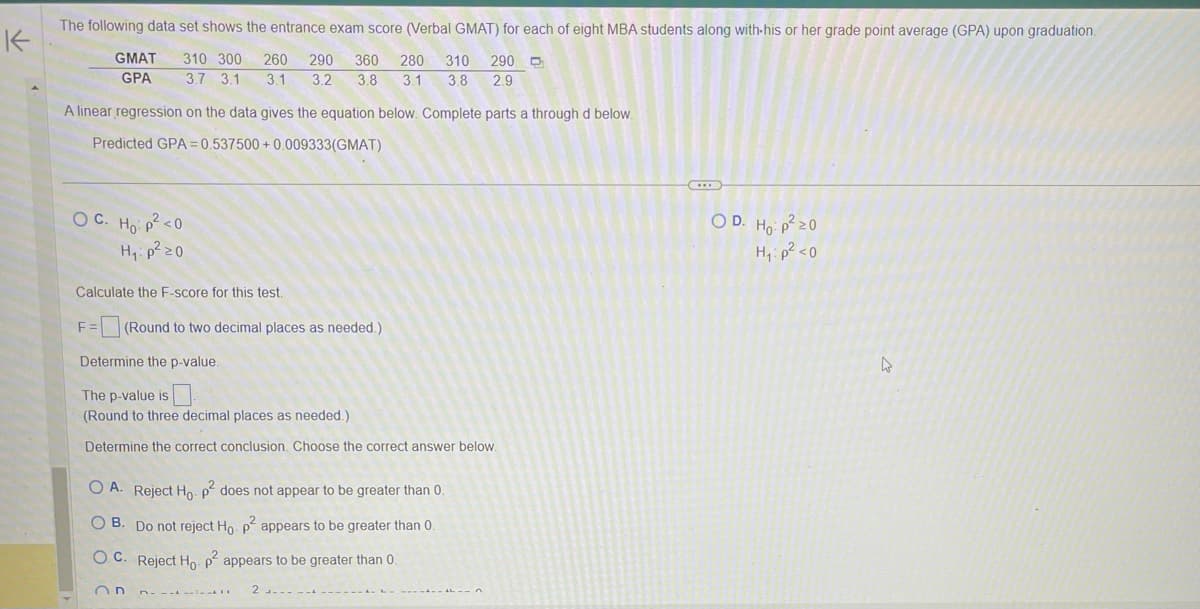
The following data set shows the entrance exam score (Verbal GMAT) for each of eight MBA students along with his or her grade point average (GPA) upon graduation.
310 300 260 290 360 280 310 290
3.8 3.1 3.8 2.9
3.7 3.1 3.1 3.2
GMAT
GPA
A linear regression on the data gives the equation below. Complete parts a through d below.
Predicted GPA=0.537500+0.009333(GMAT)
OC. Ho: p² <0
H₁: p²20
Calculate the F-score for this test.
F=(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
Determine the p-value.
The p-value is
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
Determine the correct conclusion. Choose the correct answer below.
OA. Reject Ho. p² does not appear to be greater than 0.
O B. Do not reject Ho. p² appears to be greater than 0.
OC. Reject Ho. p² appears to be greater than 0.
On
2-------
OD. Ho: p²20
H₁: p² <0
4
Transcribed Image Text:K
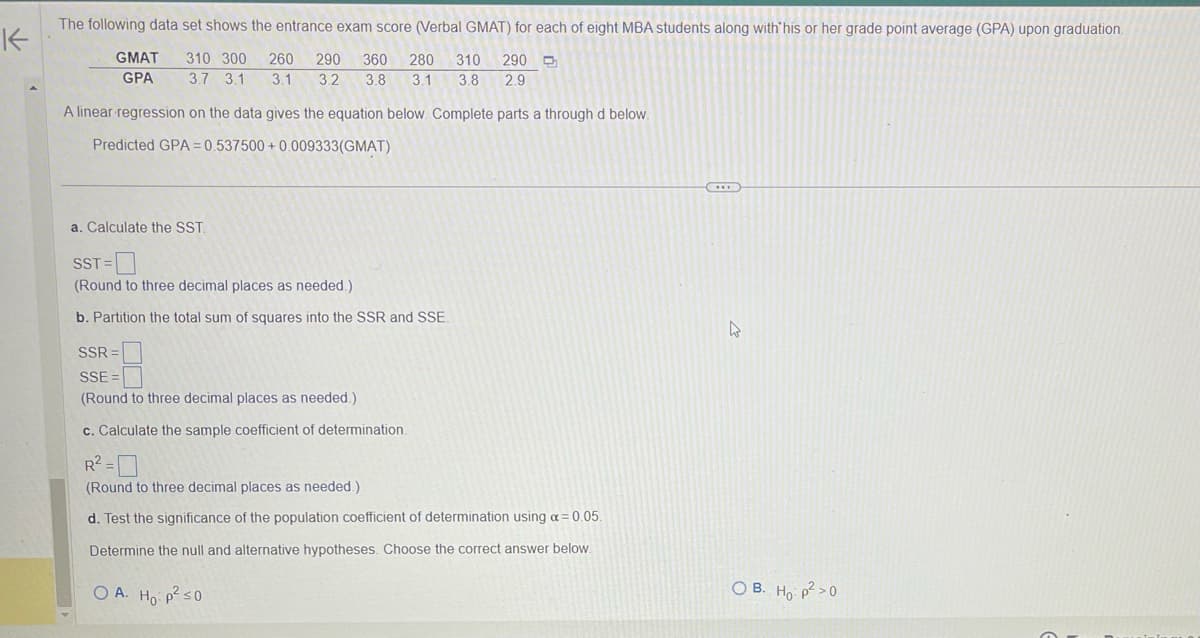
The following data set shows the entrance exam score (Verbal GMAT) for each of eight MBA students along with his or her grade point average (GPA) upon graduation.
GMAT 310 300 260 290 360 280 310 290
GPA 3.7 3.1 3.1 3.2 3.8 3.1 3.8 2.9
A linear regression on the data gives the equation below. Complete parts a through d below.
Predicted GPA=0.537500+ 0.009333(GMAT)
a. Calculate the SST.
SST=
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
b. Partition the total sum of squares into the SSR and SSE.
SSR=
SSE
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
c. Calculate the sample coefficient of determination.
R²=0
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
d. Test the significance of the population coefficient of determination using a = 0.05.
Determine the null and alternative hypotheses. Choose the correct answer below.
OA. Ho: p² ≤0
CH
4
OB. Ho: p²>0
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
