A. Combination B. Bouble displacement B. Decomposition c. Single displacement E. Combustion F. Acid-base 1. Na OH + KNO3 -----→ Na NO3 + K OH 2. CH4 + O2 -------→ 3. Fe + Na Br -- 4. Ca SO4 + Mg ( OH )2 ------→ Ca (OH )2 + Mg SO4 5. NH4 OH + H Br -------→ H2O + NH4 Br 6. P4 + O2 --------→ P2 Os 7. Na NOs ------→ Na NO2 + O2 8. C18 H18 + O2 -------→ CO2 + H2O 9. H2 SO4 + Na OH 10. Ni SO4 + Lis PO4 ----→ Ni3 ( PO4 )2 + Liz SO4 CO2 + 2 H20 ---→ Fe Br3 + Na -→ Na SO. + H20
A. Combination B. Bouble displacement B. Decomposition c. Single displacement E. Combustion F. Acid-base 1. Na OH + KNO3 -----→ Na NO3 + K OH 2. CH4 + O2 -------→ 3. Fe + Na Br -- 4. Ca SO4 + Mg ( OH )2 ------→ Ca (OH )2 + Mg SO4 5. NH4 OH + H Br -------→ H2O + NH4 Br 6. P4 + O2 --------→ P2 Os 7. Na NOs ------→ Na NO2 + O2 8. C18 H18 + O2 -------→ CO2 + H2O 9. H2 SO4 + Na OH 10. Ni SO4 + Lis PO4 ----→ Ni3 ( PO4 )2 + Liz SO4 CO2 + 2 H20 ---→ Fe Br3 + Na -→ Na SO. + H20
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Chapter20: Environmental Chemistry-earth's Environment, Energy, And Sustainability
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 41PS
Related questions
Question
Classify the following unbalanced chemical equations according to the six
types of
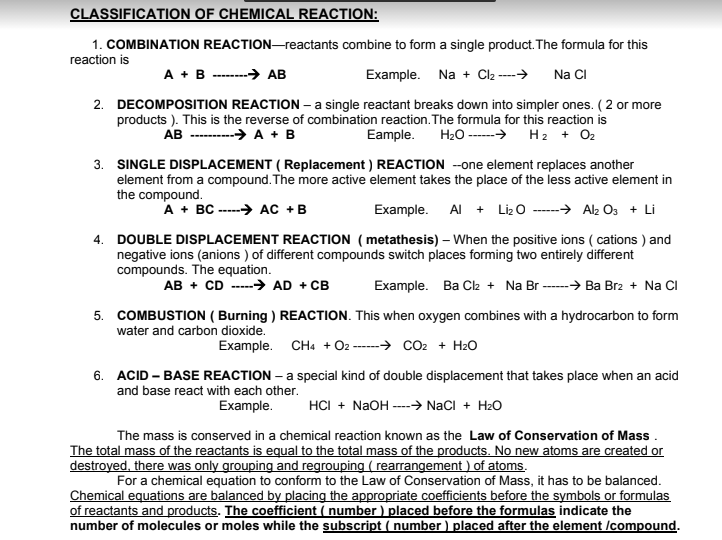
Transcribed Image Text:CLASSIFICATION OF CHEMICAL REACTION:
1. COMBINATION REACTION-reactants combine to form a single product. The formula for this
reaction is
A + B-----→ AB
Example. Na + Cl2 ----→
Na CI
2. DECOMPOSITION REACTION – a single reactant breaks down into simpler ones. ( 2 or more
products ). This is the reverse of combination reaction. The formula for this reaction is
Eample.
AB ----
→ A + B
H20 ------>
H2 + O2
3. SINGLE DISPLACEMENT ( Replacement ) REACTION --one element replaces another
element from a compound. The more active element takes the place of the less active element in
the compound.
A + BC -----→ AC +B
Example. Al + Liz O ------→ Al Os + Li
4. DOUBLE DISPLACEMENT REACTION ( metathesis) – When the positive ions ( cations ) and
negative ions (anions ) of different compounds switch places forming two entirely different
compounds. The equation.
AB + CD -----> AD + CB
Example. Ba Cl2 + Na Br ---> Ba Brz + Na CI
5. COMBUSTION ( Burning ) REACTION. This when oxygen combines with a hydrocarbon to form
water and carbon dioxide.
Example. CH4 + O2 ----→ cO2 + H2O
6. ACID – BASE REACTION – a special kind of double displacement that takes place when an acid
and base react with each other.
Example.
HCI + NaOH ----→ NaCI + H2O
The mass is conserved in a chemical reaction known as the Law of Conservation of Mass .
The total mass of the reactants is equal to the total mass of the products. No new atoms are created or
destroyed. there was only grouping and regrouping ( rearrangement ) of atoms.
For a chemical equation to conform to the Law of Conservation of Mass, it has to be balanced.
Chemical equations are balanced by placing the appropriate coefficients before the symbols or formulas
of reactants and products. The coefficient ( number) placed before the formulas indicate the
number of molecules or moles while the subscript ( number ) placed after the element /compound.
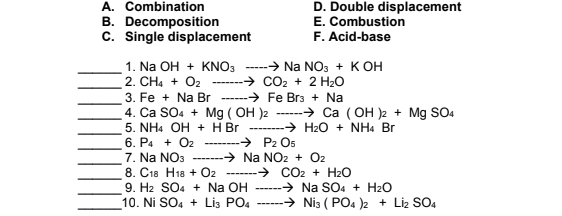
Transcribed Image Text:A. Combination
B. Decomposition
C. Single displacement
D. Double displacement
E. Combustion
F. Acid-base
1. Na OH + KNO3 ----> Na NO3 + K OH
2. CH4 + O2 -------→ CO2 + 2 H20
3. Fe + Na Br
4. Ca SO4 + Mg ( OH )2 -----→ Ca (OH )2 + Mg SO4
5. NH4 OH + H Br --------> H2O + NH4 Br
6. P4 + O2
7. Na NO3 -------→ Na NO2 + O2
8. C18 H18 + O2
9. H2 SO4 + Na OH ------
10. Ni SO4 + Lis PO4
→ Fe Brs + Na
-------- P2 Os
-→ CO2 + H2O
-------*
→ Na SO4 + H2O
-→ Ni3 ( PO4 )2 + Liz SO4
-------
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning