A. State the null hypothesis H0 and the alternative hypothesis H1 B. Find the value of the test statistic. (Round to three or more decimal places.) C. Find the two critical values at the 0.10 level of significance. (Round to three or more decimal places.)
A. State the null hypothesis H0 and the alternative hypothesis H1 B. Find the value of the test statistic. (Round to three or more decimal places.) C. Find the two critical values at the 0.10 level of significance. (Round to three or more decimal places.)
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter2: Systems Of Linear Equations
Section2.4: Applications
Problem 28EQ
Related questions
Question
A. State the null hypothesis H0 and the alternative hypothesis H1
B. Find the value of the test statistic. (Round to three or more decimal places.)
C. Find the two critical values at the 0.10 level of significance. (Round to three or more decimal places.)
.
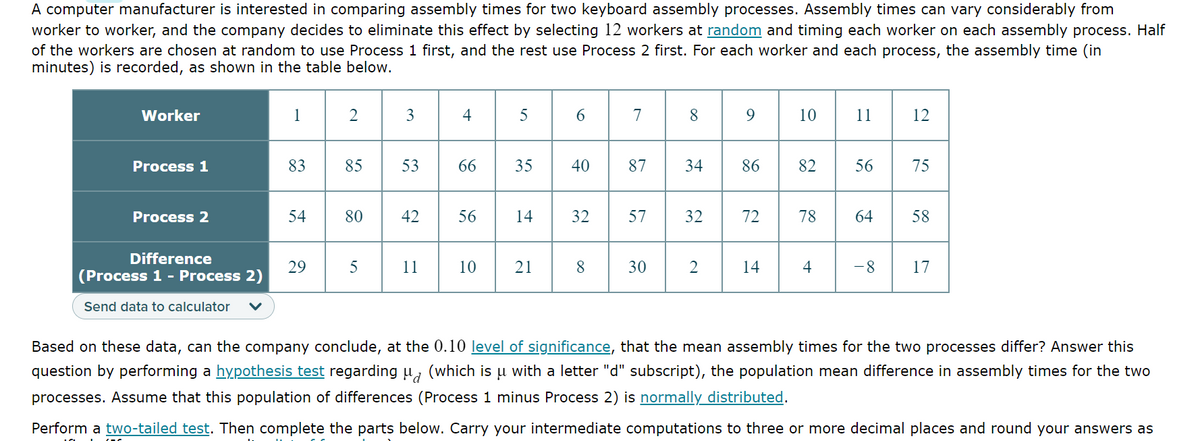
Transcribed Image Text:A computer manufacturer is interested in comparing assembly times for two keyboard assembly processes. Assembly times can vary considerably from
worker to worker, and the company decides to eliminate this effect by selecting 12 workers at random and timing each worker on each assembly process. Half
of the workers are chosen at random to use Process 1 first, and the rest use Process 2 first. For each worker and each process, the assembly time (in
minutes) is recorded, as shown in the table below.
Worker
Process 1
Process 2
Difference
(Process 1 - Process 2)
Send data to calculator V
1
83
54
29
2
85
80
5
3
53
42
11
4
66
56
10
er
5
35
14
21
6
40
7
8
87
32 57
30
8
34
32
2
9
86
10
14
82
72 78
4
11
56
64
12
75
58
-8 17
Based on these data, can the company conclude, at the 0.10 level of significance, that the mean assembly times for the two processes differ? Answer this
question by performing a hypothesis test regarding µ (which is u with a letter "d" subscript), the population mean difference in assembly times for the two
processes. Assume that this population of differences (Process 1 minus Process 2) is normally distributed.
Perform a two-tailed test. Then complete the parts below. Carry your intermediate computations to three or more decimal places and round your answers as
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage