According to a 2018 article in Esquire magazine, approximately 70% of males over age 70 will develop cancerous cells in their prostate. Prostate cancer is second only to skin cancer as the most common form of cancer for males in t United States. One of the most common tests for the detection of prostate cancer is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test. However, this test known to have a high false-positive rate (tests that come back positive for cancer whe cancer is present). Suppose there is a 0.02 probability that a male patient has prostate cancer before testing. The probability of a false-positive test is 0.75, and the probability of a false-negative (no indication of cancer when cancer actually present) is 0.20. Let C event male patient has prostate cancer += positive PSA test for prostate cancer -= negative PSA test for prostate cancer a. What is the probability that the male patient has prostate cancer if the PSA test comes back positive (to 4 decimals)? b. What is the probability that the male patient has prostate cancer if the PSA test comes back negative (to 4 decimals)? c. For older men, the prior probability of having cancer increases. Suppose that the prior probability of the male patient is 0.3 rather than 0.02. What is the probability that the male patient has prostate cancer if the PSA test comes positive (to 4 decimals)? What is the probability that the male patient has prostate cancer if the PSA test comes back negative (to 4 decimals)? d. What can you infer about the PSA test from the results of parts (a), (b), and (c)? The difference between P(CI+) and P(C-) in parts (a) and (b) is-Select your answer than the difference between P(C+) and P(C-) in part (c).
According to a 2018 article in Esquire magazine, approximately 70% of males over age 70 will develop cancerous cells in their prostate. Prostate cancer is second only to skin cancer as the most common form of cancer for males in t United States. One of the most common tests for the detection of prostate cancer is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test. However, this test known to have a high false-positive rate (tests that come back positive for cancer whe cancer is present). Suppose there is a 0.02 probability that a male patient has prostate cancer before testing. The probability of a false-positive test is 0.75, and the probability of a false-negative (no indication of cancer when cancer actually present) is 0.20. Let C event male patient has prostate cancer += positive PSA test for prostate cancer -= negative PSA test for prostate cancer a. What is the probability that the male patient has prostate cancer if the PSA test comes back positive (to 4 decimals)? b. What is the probability that the male patient has prostate cancer if the PSA test comes back negative (to 4 decimals)? c. For older men, the prior probability of having cancer increases. Suppose that the prior probability of the male patient is 0.3 rather than 0.02. What is the probability that the male patient has prostate cancer if the PSA test comes positive (to 4 decimals)? What is the probability that the male patient has prostate cancer if the PSA test comes back negative (to 4 decimals)? d. What can you infer about the PSA test from the results of parts (a), (b), and (c)? The difference between P(CI+) and P(C-) in parts (a) and (b) is-Select your answer than the difference between P(C+) and P(C-) in part (c).
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition 2012
1st Edition
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Chapter11: Data Analysis And Probability
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8CR
Related questions
Question
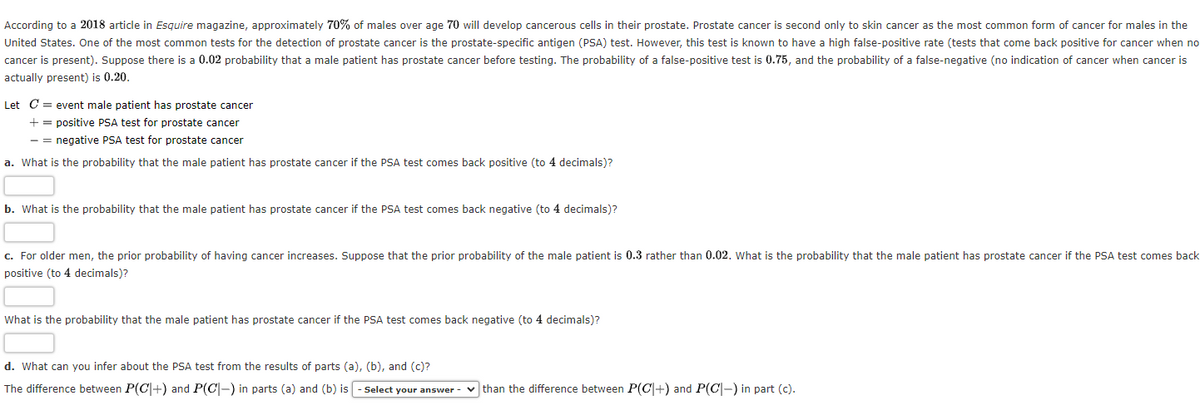
Transcribed Image Text:According to a 2018 article in Esquire magazine, approximately 70% of males over age 70 will develop cancerous cells in their prostate. Prostate cancer is second only to skin cancer as the most common form of cancer for males in the
United States. One of the most common tests for the detection of prostate cancer is the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test. However, this test is known to have a high false-positive rate (tests that come back positive for cancer when no
cancer is present). Suppose there is a 0.02 probability that a male patient has prostate cancer before testing. The probability of a false-positive test is 0.75, and the probability of a false-negative (no indication of cancer when cancer is
actually present) is 0.20.
Let C = event male patient has prostate cancer
+=
positive PSA test for prostate cancer
-= negative PSA test for prostate cancer
a. What is the probability that the male patient has prostate cancer if the PSA test comes back positive (to 4 decimals)?
b. What is the probability that the male patient has prostate cancer if the PSA test comes back negative (to 4 decimals)?
c. For older men, the prior probability of having cancer increases. Suppose that the prior probability of the male patient is 0.3 rather than 0.02. What is the probability that the male patient has prostate cancer if the PSA test comes back
positive (to 4 decimals)?
What is the probability that the male patient has prostate cancer if the PSA test comes back negative (to 4 decimals)?
d. What can you infer about the PSA test from the results of parts (a), (b), and (c)?
The difference between P(C+) and P(C-) in parts (a) and (b) is - Select your answer - ✓than the difference between P(CI+) and P(C) in part (c).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL


College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL


College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning