ACIDS AND BASES 8. The normal pH of human blood ranges from 7.35 to 7.45. Calculate the concentrations of HəO* and OH ions in human blood that has a pH of 7.45. 9. Calculate the pH of a 9.8 x 10+ M solution of NaOH. OXIDATION=REDUC TION REACTIONS 10. Balance the following equations. For each equation identify which reactant is oxidized, which is reduced, which is the oxidizing agent, and which is the reducing agent. (Assume the reaction takes place in an acidic solution) a. MnOrigg) Br → Mn²*a + Brz1) SD b. CrzO72 ag) + Fe?• → Cr³* + Fe*) LOUIS JILDS
ACIDS AND BASES 8. The normal pH of human blood ranges from 7.35 to 7.45. Calculate the concentrations of HəO* and OH ions in human blood that has a pH of 7.45. 9. Calculate the pH of a 9.8 x 10+ M solution of NaOH. OXIDATION=REDUC TION REACTIONS 10. Balance the following equations. For each equation identify which reactant is oxidized, which is reduced, which is the oxidizing agent, and which is the reducing agent. (Assume the reaction takes place in an acidic solution) a. MnOrigg) Br → Mn²*a + Brz1) SD b. CrzO72 ag) + Fe?• → Cr³* + Fe*) LOUIS JILDS
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Chapter4: Stoichiometry: Quantitative Information About Chemical Reactions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 117GQ: Gold can be dissolved from gold-bearing rock by treating the rock with sodium cyanide in the...
Related questions
Question
Answers and solutions may be handwritten or typed.
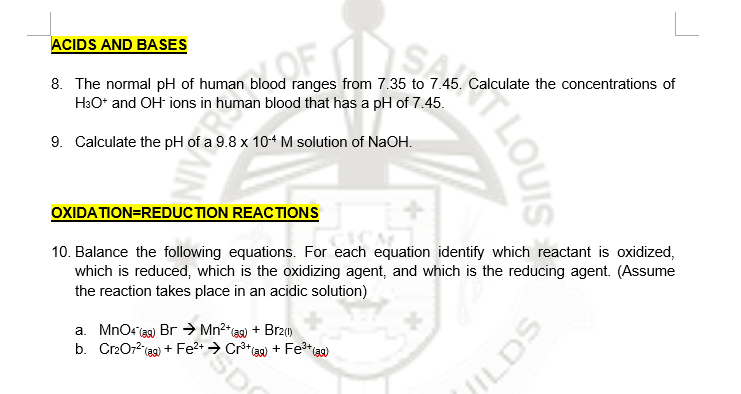
Transcribed Image Text:ACIDS AND BASES
8. The normal pH of human blood ranges from 7.35 to 7.45. Calculate the concentrations of
H3O* and OH ions in human blood that has a pH of 7.45.
9. Calculate the pH of a 9.8 x 104 M solution of NaOH.
OXIDATION=REDUCTION REACTIONS
10. Balance the following equations. For each equation identify which reactant is oxidized,
which is reduced, which is the oxidizing agent, and which is the reducing agent. (Assume
the reaction takes place in an acidic solution)
a. MnOr ag) Br → Mn²*@) + Brz()
b. Cr2072(ag)
+ Fe2+ → Cr**3a) + Fe*aa)
TLOUIS
ILDS
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
