Action potential +40 Failed nitlations ss Threshold Resting state -70 Stimulus 1 Refractory period 3. Time (ms) The refractory period or the hyperpolarization phase of an action potential in a neuron, is due to which of the following ? the prolonged opening of Na+ channels the closure of Na+ channels the closure of K+ channels the prolonged opening of K+ channels Repolarization Voltage (mV)
Action potential +40 Failed nitlations ss Threshold Resting state -70 Stimulus 1 Refractory period 3. Time (ms) The refractory period or the hyperpolarization phase of an action potential in a neuron, is due to which of the following ? the prolonged opening of Na+ channels the closure of Na+ channels the closure of K+ channels the prolonged opening of K+ channels Repolarization Voltage (mV)
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Chapter39: Information Flow And The Neuron
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8TYK: Which of the following statements best describes saltatory conduction? a. It inhibits direct...
Related questions
Question
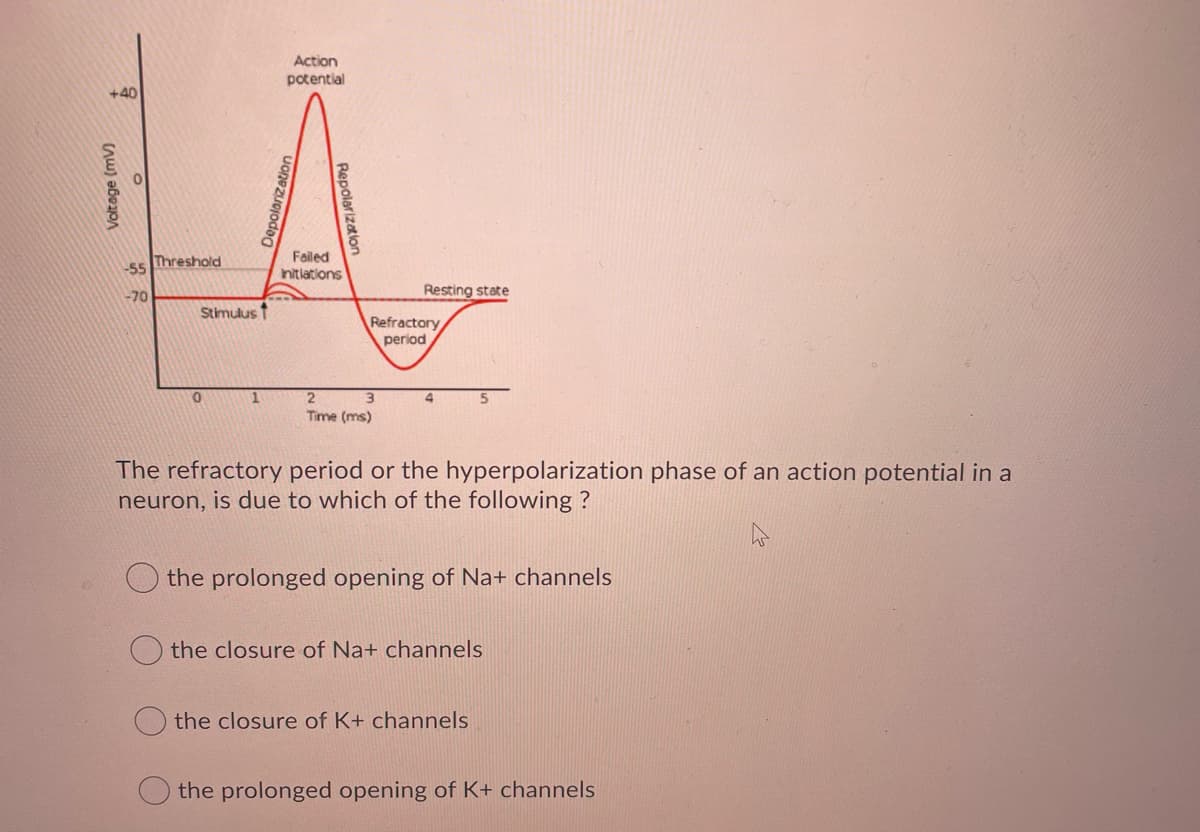
Transcribed Image Text:Action
potential
+40
Threshold
-55
Failed
Initiations
-70
Resting state
Stimulus
Refractory
period
1.
3.
Time (ms)
The refractory period or the hyperpolarization phase of an action potential in a
neuron, is due to which of the following ?
the prolonged opening of Na+ channels
the closure of Na+ channels
the closure of K+ channels
the prolonged opening of K+ channels
Repolarization
Uonezuojoda0
Voltage (mV)
Expert Solution
Explanation
Hyperpolarization is when the membrane potential is more negative than the membrane spot.
An action potential begins when depolarization increases the membrane potential enough to cross the threshold value of -55mV. This is followed by the opening of the Na+ gated channels which allows for the steep rise in potential upto +44mV. After a short time the sodium channels self inactivate with the potassium voltage gated channels opening to cause the rushing out of the potassium down it's electrochemical gradient. They remain open a little longer than is necessary which causes the undershoot to occur. Eventually, they close and the membrane potential returns back to normal.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305389892
Author:
Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap …
Biology
ISBN:
9781285866932
Author:
Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305389892
Author:
Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap …
Biology
ISBN:
9781285866932
Author:
Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781938168130
Author:
Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax