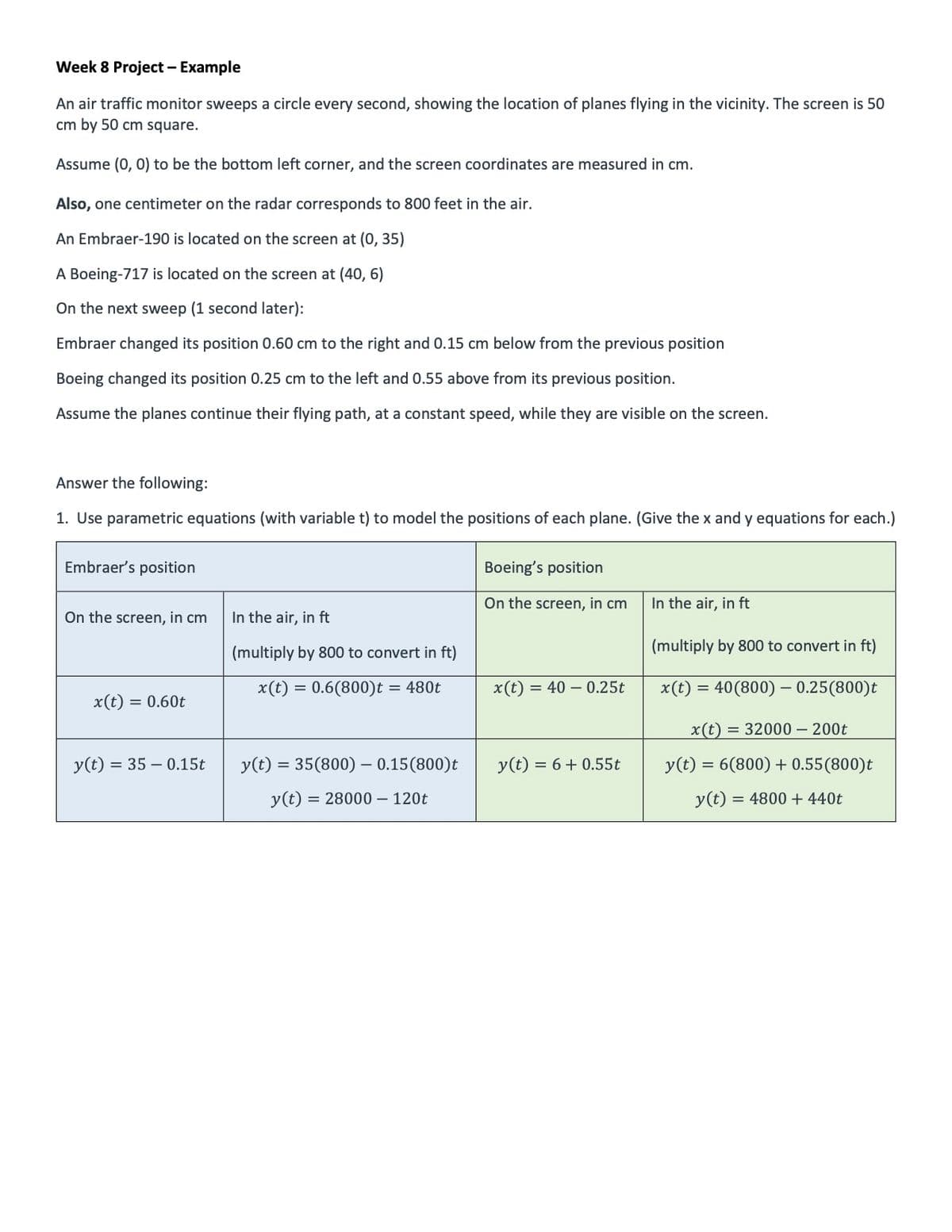
An air traffic monitor sweeps a circle every second, showing the location of planes flying in the vicinity. The screen is 50 cm by 50 cm square. An Embraer 190 is located along the left edge of the screen 25 cm from the bottom corner. A Boeing 717 is located 35 cm to the right and 4 cm above the lower left corner. On the next rotation (1 second later),the Embraer is now located at position 0.55 cm to the right and 0.25 cm below its previous position and the Boeing is 0.35 cm to the left and 0.45 above its previous position. Assume the planes continue to fly in the same direction at a constant speed while they are visible on the screen. Note: one centimeter on the radar corresponds to 800 feet in the air. Answer the following: 1. Use parametric equations (with variable t) to model the positions of each plane.(Give the x and y equations for each.) 2. Sketch the flight paths of the two planes. 3. Give the speed (in feet/sec) and headings for each of the two planes. 4. Assuming the planes fly at the same altitude, will they collide? Justify your answer.
An air traffic monitor sweeps a
An Embraer 190 is located along the left edge of the screen 25 cm from the bottom corner. A Boeing 717 is located 35 cm to the right and 4 cm above the lower left corner. On the next rotation (1 second later),the Embraer is now located at position 0.55 cm to the right and 0.25 cm below its previous position and the Boeing is 0.35 cm to the left and 0.45 above its previous position. Assume the planes continue to fly in the same direction at a constant speed while they are visible on the screen.
Note: one centimeter on the radar corresponds to 800 feet in the air.
Answer the following:
1. Use parametric equations (with variable t) to model the positions of each plane.(Give the x and y equations for each.)
2. Sketch the flight paths of the two planes.
3. Give the speed (in feet/sec) and headings for each of the two planes.
4. Assuming the planes fly at the same altitude, will they collide? Justify your answer.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 2 images









