An educational psychologist is studying two methods of tutoring young children: Method A and Method B. She wants to test whether there is any difference in puzzle solving skills between children tutored by one method versus children tutored by the other. Independent samples of 11 children who were tutored using Method A and 10 children who were tutored using Method B were chosen at random. The Method A children took a mean of 43 minutes to solve a certain puzzle with a standard deviation of 8 minutes. The Method B children took a mean of 42 minutes to solve the same puzzle with a standard deviation of 7 minutes. Assume that the two populations of completion times are normally distributed and that the population varlances are equal. Construct a 90% confidence interval for the difference u,-H, between the mean puzzle-solving times for Method A children (u) and for Method B children (1,). Then find the lower limit and upper limit of the 90% confidence interval. Carry your intermediate computations to at least three decimal places. Round your responses to at least two decimal places. (If necessary, consult a list of formulas.) Lower limit: M Upper limit:
An educational psychologist is studying two methods of tutoring young children: Method A and Method B. She wants to test whether there is any difference in puzzle solving skills between children tutored by one method versus children tutored by the other. Independent samples of 11 children who were tutored using Method A and 10 children who were tutored using Method B were chosen at random. The Method A children took a mean of 43 minutes to solve a certain puzzle with a standard deviation of 8 minutes. The Method B children took a mean of 42 minutes to solve the same puzzle with a standard deviation of 7 minutes. Assume that the two populations of completion times are normally distributed and that the population varlances are equal. Construct a 90% confidence interval for the difference u,-H, between the mean puzzle-solving times for Method A children (u) and for Method B children (1,). Then find the lower limit and upper limit of the 90% confidence interval. Carry your intermediate computations to at least three decimal places. Round your responses to at least two decimal places. (If necessary, consult a list of formulas.) Lower limit: M Upper limit:
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
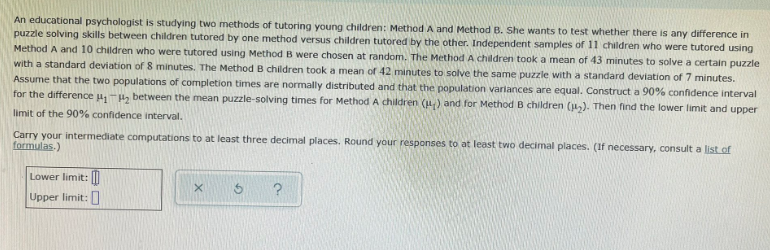
Transcribed Image Text:An educational psychologist is studying two methods of tutoring young children: Method A and Method B. She wants to test whether there is any difference in
puzzle solving skills between children tutored by one method versus children tutored by the other. Independent samples of 11 children who were tutored using
Method A and 10 children who were tutored using Method B were chosen at random. The Method A children took a mean of 43 minutes to solve a certain puzzle
with a standard deviation of 8 minutes. The Method B children took a mean of 42 minutes to solve the same puzzle with a standard deviation of 7 minutes.
Assume that the two populations of completion times are normally distributed and that the population varlances are equal. Construct a 90% confidence interval
for the difference u,-H, between the mean puzzle-solving times for Method A children (u) and for Method B children (1,). Then find the lower limit and upper
limit of the 90% confidence interval.
Carry your intermediate computations to at least three decimal places. Round your responses to at least two decimal places. (If necessary, consult a list of
formulas.)
Lower limit: M
Upper limit:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman