An empirical study is done on estimating the value of the houses in a city based on the following underlying factors: Price= Value of the house (in *1000 Dollars) otsize=Size of the property lot (in acres) Bedroom3 Unit number of bedrooms of a house Bathroom= Unit number of bathrooms in a house Driveway= A binary variable specifying if "Driveway=1" the house has a driveway, and if "Driveway=0" otherwise Garage= A binary variable specifying if "Garage=1" the house has a single-door garage, and if "Garage=0" otherwise A statistician has reviewed a database of 1000 records of houses sold in the city, and has come up with the following regression equation, to try to find a elationship among variables: Price(i)=B0 + B1[Lotsize(i)] + B2[Bedroom(i)] + B3[Bathroom(i)] + B4[Driveway(i)] + B5[Garage(i)] +u(i) A. By reviewing the result of GRETL outcomes in the attachment, perform a hypothesis test to verify the validity of all slope coefficients, collectively. Show the teps of the deployed hypothesis method. 3. Test if both Driveway & Garage need to be jointly included in the model as important variables in estimating the price of the houses in the city. Make sure ye vrite down all necessary equations & steps required. Show your calculations.
An empirical study is done on estimating the value of the houses in a city based on the following underlying factors: Price= Value of the house (in *1000 Dollars) otsize=Size of the property lot (in acres) Bedroom3 Unit number of bedrooms of a house Bathroom= Unit number of bathrooms in a house Driveway= A binary variable specifying if "Driveway=1" the house has a driveway, and if "Driveway=0" otherwise Garage= A binary variable specifying if "Garage=1" the house has a single-door garage, and if "Garage=0" otherwise A statistician has reviewed a database of 1000 records of houses sold in the city, and has come up with the following regression equation, to try to find a elationship among variables: Price(i)=B0 + B1[Lotsize(i)] + B2[Bedroom(i)] + B3[Bathroom(i)] + B4[Driveway(i)] + B5[Garage(i)] +u(i) A. By reviewing the result of GRETL outcomes in the attachment, perform a hypothesis test to verify the validity of all slope coefficients, collectively. Show the teps of the deployed hypothesis method. 3. Test if both Driveway & Garage need to be jointly included in the model as important variables in estimating the price of the houses in the city. Make sure ye vrite down all necessary equations & steps required. Show your calculations.
Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies and Tactics (MindTap Course List)
14th Edition
ISBN:9781305506381
Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Chapter4: Estimating Demand
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1E
Related questions
Question
3)
![An empirical study is done on estimating the value of the houses in a city based on the following underlying factors:
Price= Value of the house (in *1000 Dollars)
Lotsize=Size of the property lot (in acres)
Bedroom= Unit number of bedrooms of a house
Bathroom= Unit number of bathrooms in a house
Driveway= A binary variable specifying if "Driveway=1" the house has a driveway, and if "Driveway=0" otherwise
Garage= A binary variable specifying if "Garage=1" the house has a single-door garage, and if "Garage=0" otherwise
A statistician has reviewed a database of 1000 records of houses sold in the city, and has come up with the following regression equation, to try to find a
relationship among variables:
Price(i)=B0 + B1[Lotsize(i)] + B2[Bedroom(i)] + B3[Bathroom(i)] + B4[Driveway(i)] + B5[Garage(i)] +u(i)
A. By reviewing the result of GRETL outcomes in the attachment, perform a hypothesis test to verify the validity of all slope coefficients, collectively. Show the
steps of the deployed hypothesis method.
B. Test if both Driveway & Garage need to be jointly included in the model as important variables in estimating the price of the houses in the city. Make sure you
write down all necessary equations & steps required. Show your calculations.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fe779c950-a70e-4610-a191-11ec3afdb7c4%2Ff643841c-98e3-408c-87db-e97f8b39ddbe%2Fdm1vuh_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:An empirical study is done on estimating the value of the houses in a city based on the following underlying factors:
Price= Value of the house (in *1000 Dollars)
Lotsize=Size of the property lot (in acres)
Bedroom= Unit number of bedrooms of a house
Bathroom= Unit number of bathrooms in a house
Driveway= A binary variable specifying if "Driveway=1" the house has a driveway, and if "Driveway=0" otherwise
Garage= A binary variable specifying if "Garage=1" the house has a single-door garage, and if "Garage=0" otherwise
A statistician has reviewed a database of 1000 records of houses sold in the city, and has come up with the following regression equation, to try to find a
relationship among variables:
Price(i)=B0 + B1[Lotsize(i)] + B2[Bedroom(i)] + B3[Bathroom(i)] + B4[Driveway(i)] + B5[Garage(i)] +u(i)
A. By reviewing the result of GRETL outcomes in the attachment, perform a hypothesis test to verify the validity of all slope coefficients, collectively. Show the
steps of the deployed hypothesis method.
B. Test if both Driveway & Garage need to be jointly included in the model as important variables in estimating the price of the houses in the city. Make sure you
write down all necessary equations & steps required. Show your calculations.
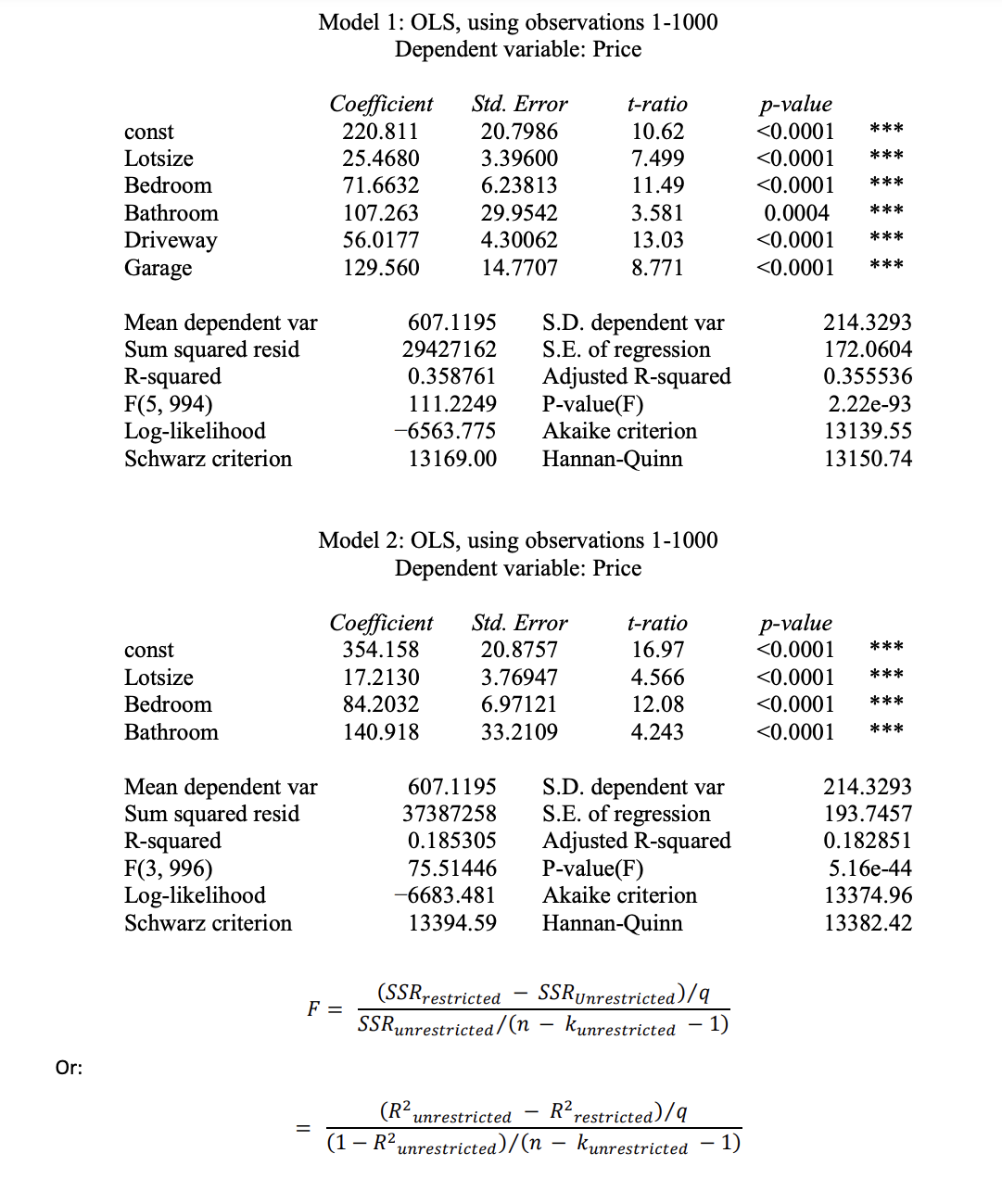
Transcribed Image Text:Model 1: OLS, using observations 1-1000
Dependent variable: Price
Coefficient
220.811
р-value
<0.0001
Std. Error
t-ratio
const
20.7986
10.62
***
Lotsize
25.4680
3.39600
7.499
<0.0001
***
Bedroom
71.6632
6.23813
11.49
<0.0001
***
Bathroom
107.263
29.9542
3.581
0.0004
***
Driveway
Garage
56.0177
4.30062
13.03
<0.0001
***
129.560
14.7707
8.771
<0.0001
***
Mean dependent var
Sum squared resid
R-squared
F(5, 994)
Log-likelihood
Schwarz criterion
S.D. dependent var
S.E. of regression
Adjusted R-squared
P-value(F)
Akaike criterion
214.3293
172.0604
607.1195
29427162
0.358761
0.355536
111.2249
2.22e-93
-6563.775
13139.55
13169.00
Hannan-Quinn
13150.74
Model 2: OLS, using observations 1-1000
Dependent variable: Price
Coefficient
354.158
р-value
<0.0001
Std. Error
t-ratio
const
20.8757
16.97
***
Lotsize
17.2130
3.76947
4.566
<0.0001
***
Bedroom
84.2032
6.97121
12.08
<0.0001
***
Bathroom
140.918
33.2109
4.243
<0.0001
***
Mean dependent var
Sum squared resid
R-squared
F(3, 996)
Log-likelihood
Schwarz criterion
S.D. dependent var
S.E. of regression
Adjusted R-squared
P-value(F)
Akaike criterion
607.1195
214.3293
37387258
193.7457
0.185305
0.182851
75.51446
5.16e-44
-6683.481
13374.96
13394.59
Hannan-Quinn
13382.42
SSRUnrestricted)/q
(SSRrestricted
SSRunrestricted/(n
F =
kunrestricted
1)
Or:
(R²,
R² restricted)/9
unrestricted
(1 – R².
unrestricted)/(n – kunrestricted
- 1)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



