An engine has a bore of 78mm, a stroke of 82mm, and a con- necting rod length of 168mm. The crank is turning at 7200rpm. At top dead centre, the flat top of the piston is level with the upper deck of the block. At the instant when the crank is at 90° after top dead centre, using the approximate formula for the piston displacement as shown in part (b) of this question, cal- culate; i the depth of the flat top of the piston below the upper deck of the engine block ii the velocity of the piston in the direction of the cylinder axis ii the acceleration of the piston in the direction of the cylinder axis
An engine has a bore of 78mm, a stroke of 82mm, and a con- necting rod length of 168mm. The crank is turning at 7200rpm. At top dead centre, the flat top of the piston is level with the upper deck of the block. At the instant when the crank is at 90° after top dead centre, using the approximate formula for the piston displacement as shown in part (b) of this question, cal- culate; i the depth of the flat top of the piston below the upper deck of the engine block ii the velocity of the piston in the direction of the cylinder axis ii the acceleration of the piston in the direction of the cylinder axis
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Chapter1: Tension, Compression, And Shear
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.8.7P: A special-purpose eye boll with a shank diameter d - 0.50 in. passes through, a hole in a steel...
Related questions
Question
please send handwritten solution for part c
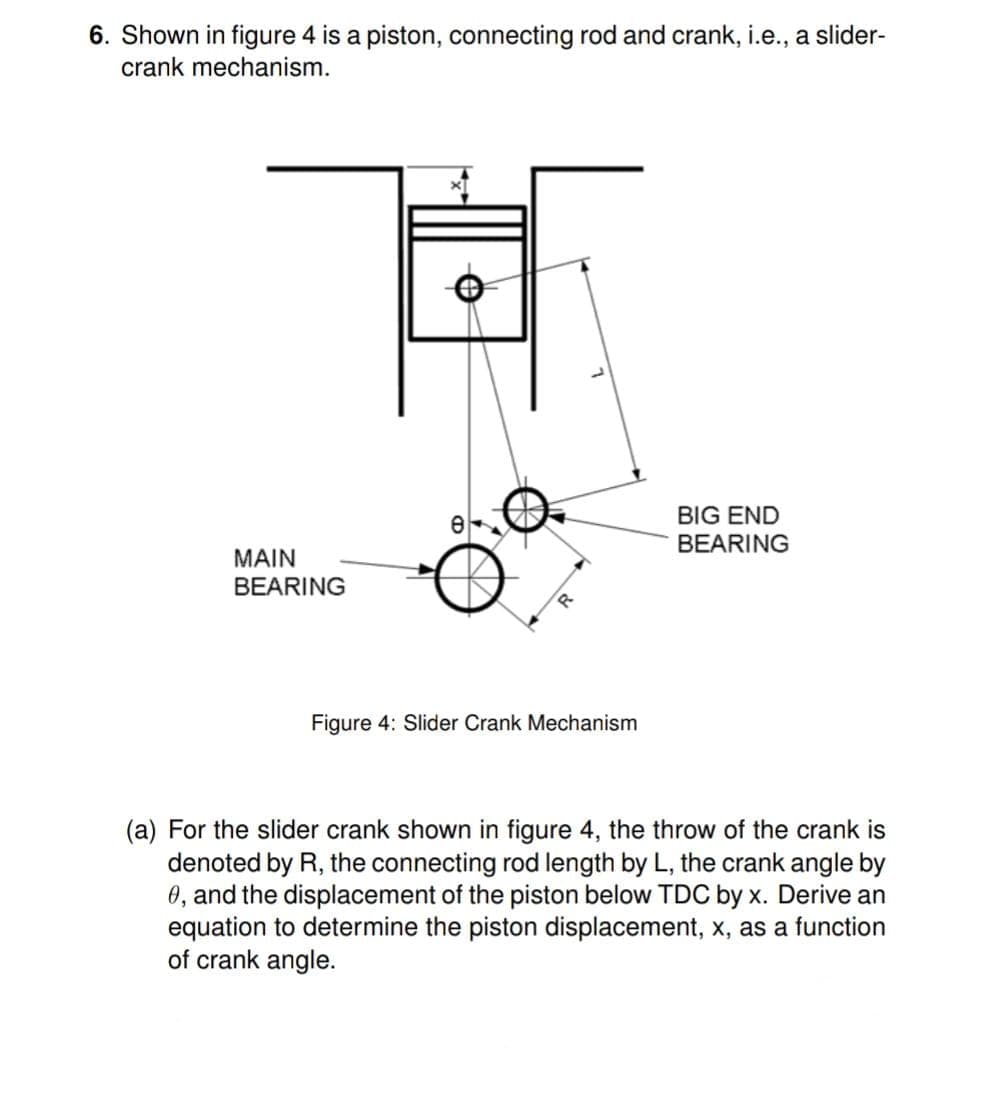
Transcribed Image Text:6. Shown in figure 4 is a piston, connecting rod and crank, i.e., a slider-
crank mechanism.
BIG END
BEARING
MAIN
BEARING
Figure 4: Slider Crank Mechanism
(a) For the slider crank shown in figure 4, the throw of the crank is
denoted by R, the connecting rod length by L, the crank angle by
0, and the displacement of the piston below TDC by x. Derive an
equation to determine the piston displacement, x, as a function
of crank angle.
![Question 6 continued
(b) Using the binomial expansion;
(1+ p)" = 1+ np+
n(n - 1)p n(n – 1)p
+...
2!
and the double angle formula;
2sin (0) = 1 – cos(20)
Show that the piston displacement may be represented by the
approximate formula below;
R2
I R(1 – cos(0)) +
[1 – cos(26)]
4L
(c) An engine has a bore of 78mm, a stroke of 82mm, and a con-
necting rod length of 168mm. The crank is turning at 7200rpm.
At top dead centre, the flat top of the piston is level with the
upper deck of the block. At the instant when the crank is at
90° after top dead centre, using the approximate formula for the
piston displacement as shown in part (b) of this question, cal-
culate;
i the depth of the flat top of the piston below the upper deck
of the engine block
ii the velocity of the piston in the direction of the cylinder axis
ii the acceleration of the piston in the direction of the cylinder
axis
Question 6 continued
(d) Summarise the crankshaft layouts and therefore the also de-
scribe the out of balance forces and moments for the following
engine types;
i single cylinder four stroke engine
ii four cylinder inline four stroke engine
iii three cylinder inline four stroke engine](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fd5df6af1-0b99-4174-9b43-5e51b8eadbdc%2F8dc46c9e-6752-447b-b77a-0e2be67a1fd3%2F88z7u36_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:Question 6 continued
(b) Using the binomial expansion;
(1+ p)" = 1+ np+
n(n - 1)p n(n – 1)p
+...
2!
and the double angle formula;
2sin (0) = 1 – cos(20)
Show that the piston displacement may be represented by the
approximate formula below;
R2
I R(1 – cos(0)) +
[1 – cos(26)]
4L
(c) An engine has a bore of 78mm, a stroke of 82mm, and a con-
necting rod length of 168mm. The crank is turning at 7200rpm.
At top dead centre, the flat top of the piston is level with the
upper deck of the block. At the instant when the crank is at
90° after top dead centre, using the approximate formula for the
piston displacement as shown in part (b) of this question, cal-
culate;
i the depth of the flat top of the piston below the upper deck
of the engine block
ii the velocity of the piston in the direction of the cylinder axis
ii the acceleration of the piston in the direction of the cylinder
axis
Question 6 continued
(d) Summarise the crankshaft layouts and therefore the also de-
scribe the out of balance forces and moments for the following
engine types;
i single cylinder four stroke engine
ii four cylinder inline four stroke engine
iii three cylinder inline four stroke engine
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning