An example of X-linked inheritance First cross Second cross X Y Red female White male White female Red male Male gametes Male gametes Female gametes Female gametes Red temale Red male Red female White male Male gametes Male gametes 0 w Red female Red male Red female Red male Female gametes Female gametes | Red temale i Whte male i White female i White male FIGURE 2-17 Reciprocal crosses between red-eyed (red) and white-eyed (white) Drosophila give different results. The alleles are X linked, and the inheritance of the X chromosome explains the phenotypic ratios observed, which are different from those of autosomal genes. (In Drosophila and many other experimental systems, a superscript plus sign is used to designate the normal, or wild-type, allele. Here, wt encodes red eyes and w encodes white eyes.)
An example of X-linked inheritance First cross Second cross X Y Red female White male White female Red male Male gametes Male gametes Female gametes Female gametes Red temale Red male Red female White male Male gametes Male gametes 0 w Red female Red male Red female Red male Female gametes Female gametes | Red temale i Whte male i White female i White male FIGURE 2-17 Reciprocal crosses between red-eyed (red) and white-eyed (white) Drosophila give different results. The alleles are X linked, and the inheritance of the X chromosome explains the phenotypic ratios observed, which are different from those of autosomal genes. (In Drosophila and many other experimental systems, a superscript plus sign is used to designate the normal, or wild-type, allele. Here, wt encodes red eyes and w encodes white eyes.)
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Michael Cummings
Chapter4: Pedigree Analysis In Human Genetics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 17QP: Analysis of X-Linked Dominant and Recessive Traits A young boy is color-blind. His one brother and...
Related questions
Question
. In Figure 2-17, how does the 3:1 ratio in the bottom-lefthand grid differ from the 3:1 ratios obtained by Mendel?
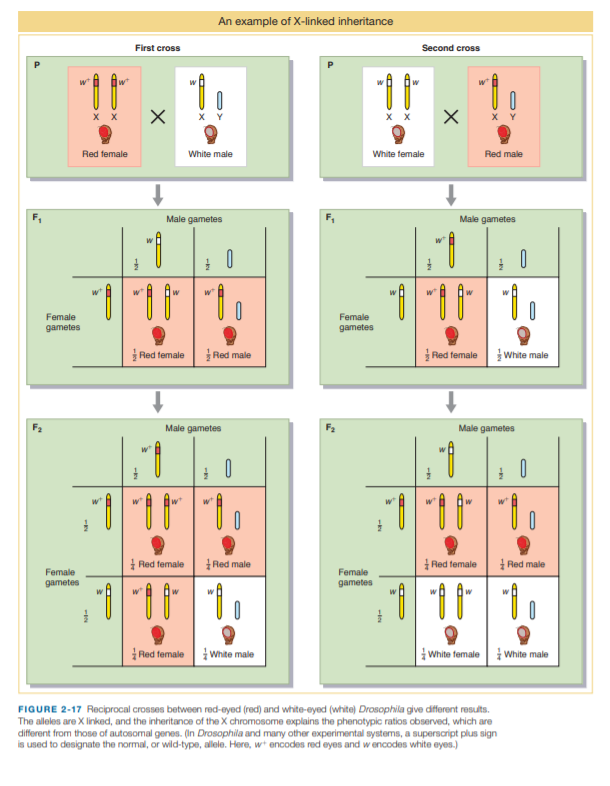
Transcribed Image Text:An example of X-linked inheritance
First cross
Second cross
X Y
Red female
White male
White female
Red male
Male gametes
Male gametes
Female
gametes
Female
gametes
Red temale
Red male
Red female
White male
Male gametes
Male gametes
0
w
Red female
Red male
Red female
Red male
Female
gametes
Female
gametes
| Red temale i Whte male
i White female i White male
FIGURE 2-17 Reciprocal crosses between red-eyed (red) and white-eyed (white) Drosophila give different results.
The alleles are X linked, and the inheritance of the X chromosome explains the phenotypic ratios observed, which are
different from those of autosomal genes. (In Drosophila and many other experimental systems, a superscript plus sign
is used to designate the normal, or wild-type, allele. Here, wt encodes red eyes and w encodes white eyes.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305117396
Author:
Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305117396
Author:
Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781337392938
Author:
Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:
Cengage Learning