The next three questions go together. Duchenne's muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a disease caused by a recessive allele at a gene on the X chromosome. Polydactyly is caused by a dominant allele at an autosomal gene. If a phenotypically normal woman who's father had DMD has a child with man who is heterozygous for the allele causing polydactyly but is otherwise normal, what is the probability that the child will have elther DMD or polydactyly, but not both? Part I: What is the cross? A ppxx x PpxDxD B- PPXPXX Ppx©y C- ppx"x x PpXdy D- ppxPx* x PpxDY Question 11 Part II: What is the probability the child will have polydactyly but not DMD? Enter your answer to two decimal places les. 0.88).
The next three questions go together. Duchenne's muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a disease caused by a recessive allele at a gene on the X chromosome. Polydactyly is caused by a dominant allele at an autosomal gene. If a phenotypically normal woman who's father had DMD has a child with man who is heterozygous for the allele causing polydactyly but is otherwise normal, what is the probability that the child will have elther DMD or polydactyly, but not both? Part I: What is the cross? A ppxx x PpxDxD B- PPXPXX Ppx©y C- ppx"x x PpXdy D- ppxPx* x PpxDY Question 11 Part II: What is the probability the child will have polydactyly but not DMD? Enter your answer to two decimal places les. 0.88).
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Michael Cummings
Chapter4: Pedigree Analysis In Human Genetics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 21QP: Analysis of X-Linked Dominant and Recessive Traits As a genetic counselor investigating a genetic...
Related questions
Question
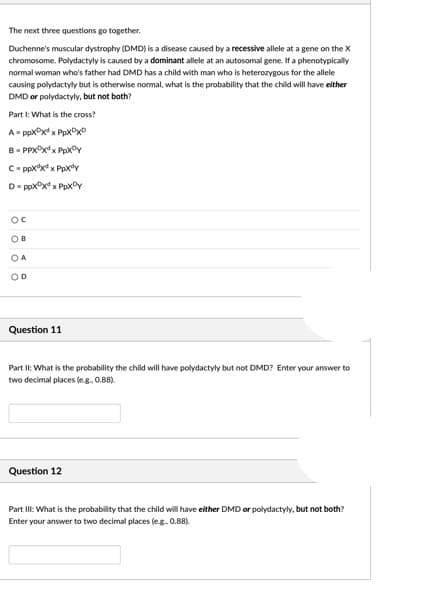
Transcribed Image Text:The next three questions go together.
Duchenne's muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a disease caused by a recessive allele at a gene on the X
chromosome. Polydactyly is caused by a dominant allele at an autosomal gene. If a phenotypically
normal woman who's father had DMD has a child with man who is heterozygous for the allele
causing polydactyly but is otherwise normal, what is the probability that the child will have elther
DMD or polydactyly, but not both?
Part I: What is the cross?
A ppxx x PpxDxD
B- PPXPXX Ppx©y
C- ppx"x x Ppxdy
D- ppxx x PpxOy
OC
OB
O A
OD
Question 11
Part II: What is the probability the child will have polydactyly but not DMD? Enter your answer to
two decimal places leg. 0.88).
Question 12
Part II: What is the probability that the child will have either DMD or polydactyly, but not both?
Enter your answer to two decimal places (eg. 0.88).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning