An industrial firm can purchase a special machine for $70,000. A down payment of $5,000 is required, and the unpaid balance can be paid off in five equal year-end installments at 9% interest. As an alternative, the machine can be purchased for $66,000 in cash. If the firm's MARR is 10%, use the annual equivalent method to determine which alternative should be accepted. 6 Click the icon to view the interest factors for discrete compounding when i= 9% per year. 7 Click the icon to view the interest factors for discrete compounding when MARR = 10% per year. The annual equivalent worth of the first option is S (Round to the nearest dollar.) The annual equivalent worth of the second option is S -(Round to the nearest dollar.) Select the correct choice from the drop-down menu below. (1). - is a better choice.
An industrial firm can purchase a special machine for $70,000. A down payment of $5,000 is required, and the unpaid balance can be paid off in five equal year-end installments at 9% interest. As an alternative, the machine can be purchased for $66,000 in cash. If the firm's MARR is 10%, use the annual equivalent method to determine which alternative should be accepted. 6 Click the icon to view the interest factors for discrete compounding when i= 9% per year. 7 Click the icon to view the interest factors for discrete compounding when MARR = 10% per year. The annual equivalent worth of the first option is S (Round to the nearest dollar.) The annual equivalent worth of the second option is S -(Round to the nearest dollar.) Select the correct choice from the drop-down menu below. (1). - is a better choice.
Fundamentals Of Financial Management, Concise Edition (mindtap Course List)
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337902571
Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. Houston
Publisher:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. Houston
Chapter12: Cash Flow Estimation And Risk Analysis
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10P: Dauten is offered a replacement machine which has a cost of 8,000, an estimated useful life of 6...
Related questions
Question
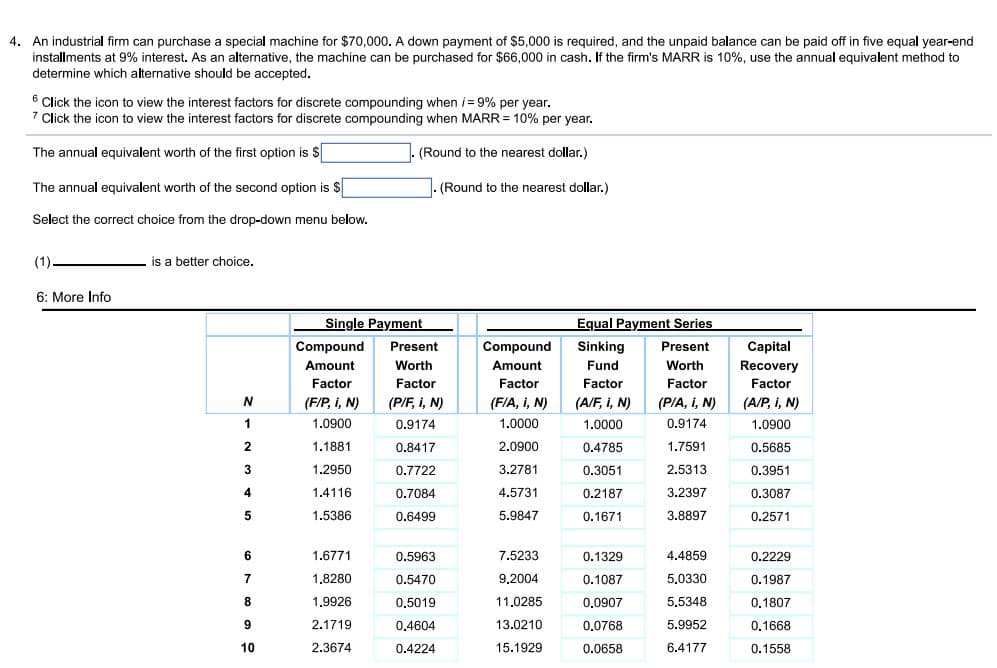
Transcribed Image Text:4. An industrial firm can purchase a special machine for $70,000. A down payment of $5,000 is required, and the unpaid balance can be paid off in five equal year-end
installments at 9% interest. As an alternative, the machine can be purchased for $66,000 in cash. If the firm's MARR is 10%, use the annual equivalent method to
determine which alternative should be accepted.
6
6 Click the icon to view the interest factors for discrete compounding when i= 9% per year.
7 Click the icon to view the interest factors for discrete compounding when MARR = 10% per year.
The annual equivalent worth of the first option is $
(Round to the nearest dollar.)
The annual equivalent worth of the second option is $
(Round to the nearest dollar.)
Select the correct choice from the drop-down menu below.
(1).
is a better choice.
6: More Info
Single Payment
Equal Payment Series
Compound
Present
Compound
Sinking
Present
Capital
Amount
Worth
Amount
Fund
Worth
Recovery
Factor
Factor
Factor
Factor
Factor
Factor
(F/P, i, N)
(P/F, i, N)
(F/A, i, N)
(A/F, i, N)
(PIA, I, N)
(A/P, i, N)
1
1.0900
0.9174
1.0000
1.0000
0.9174
1.0900
1.1881
0.8417
2.0900
0.4785
1.7591
0.5685
3
1.2950
0.7722
3.2781
0.3051
2.5313
0.3951
4
1.4116
0.7084
4.5731
0.2187
3.2397
0.3087
1.5386
0.6499
5.9847
0.1671
3.8897
0.2571
1.6771
0.5963
7.5233
0.1329
4.4859
0.2229
7
1.8280
0.5470
9,2004
0.1087
5.0330
0.1987
8
1.9926
0,5019
11,0285
0,0907
5.5348
0,1807
2.1719
0.4604
13.0210
0,0768
5.9952
0.1668
10
2.3674
0.4224
15.1929
0.0658
6.4177
0.1558
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Fundamentals Of Financial Management, Concise Edi…
Finance
ISBN:
9781337902571
Author:
Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. Houston
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Finance
ISBN:
9781337514835
Author:
MOYER
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals Of Financial Management, Concise Edi…
Finance
ISBN:
9781337902571
Author:
Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. Houston
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Finance
ISBN:
9781337514835
Author:
MOYER
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305970663
Author:
Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course…
Finance
ISBN:
9781337395083
Author:
Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Publisher:
Cengage Learning